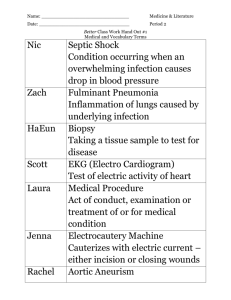
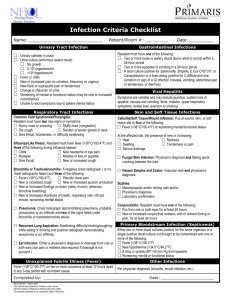
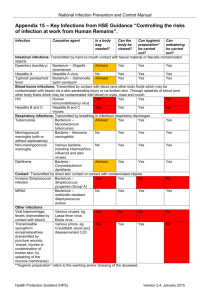
Bacterial Infectious Diseases Anthrax: multiplication of Bacillus
advertisement

Bacterial Infectious Diseases ☛ Anthrax: multiplication of Bacillus anthracis in the body. ☛ Bacterial meningitis: inflammation of the protective membranes of the central nervous system, due to Neisseria meningitidis or Streptococcus pneumoniae. ☛ Botulism: blockage of nerve function and respiratory, as well as musculoskeletal paralysis due to toxins from Clostridium botulinum. ☛ Brucellosis: entrance of Brucella spp. bacteria by direct contact or untreated/contaminated milk of animals. ☛ Campylobacteriosis: an inflammatory and at times bloody diarrhea or dysentery caused by Campylobacter jejuni. ☛ Cat scratch disease: also regarded as cat scratch fever, Teeny's Disease, or Subacute regional lymphadenitis is known to have been caused by the bacteria Bartonella henselae. Symptoms start to show between 7 to 14 days or 2 months post a cat scratch; tender regional lymphadenopathy, slight fever, headache, chills, malaise, abdominal pain, backache, convulsions or sterile suppurative papules at the site of inoculation occur. ☛ Cholera: transmission of Vibrio cholerae by ingestion of contaminated food or water causes diarrhea. ☛ Diphtheria: upper respiratory tract infection of Corynebacterium diphtheriae, and is characterized by sore throat, low-grade fever, and an adherent layer on the tonsils, nasal cavity, pharynx. ☛ Epidemic Typhus: caused by louse-borne bacteria called Rickettsia prowazekii ☛ Gonorrhea: common sexually transmitted disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. ☛ Impetigo: superficial skin infection that is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is common in the age group of 2 to 6. ☛ Kawasaki disease: also known as lymph node syndrome, an autoimmune disease of unclear etiology, and has been associated with infections as well as certain genetic and environmental factors. It affects medium-sized blood vessels, and is marked by a tendency for the blood vessels to abnormally swell up. ☛ Legionellosis: pneumonia or acute influenza-like respiratory illness caused by Legionella spp. ☛ Leprosy (Hansen's disease): granulomatous disease of the peripheral nerves and mucosa of the upper respiratory tract due to Mycobacterium leprae. ☛ Leptospirosis: biphasic disease with meningitis, liver damage and renal failure due to Leptospira spp. ☛ Listeriosis: Listeria monocytogenes infection that occurs in newborns, the elderly, and immunocompromised patients. ☛ Lyme disease: caused by bacteria from genus Borrelia, and characterized by rash and flu symptoms followed by musculoskeletal, psychiatric, neurologic, arthritic, and cardiac manifestations. ☛ Melioidosis: caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, which is found in soil and water. ☛ MRSA infection: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection characterized by rapid weight loss and muscle depletion, ☛ Nocardiosis: Nocardia asteroides or N. brasiliensis affects either the lungs or the entire body. ☛ Pertussis (Whooping cough): Bordetella pertussis infection resulting in severe hacking cough followed by palpitations. ☛ Plague: occurs when a person is bitten by a flea infected with Yersinia pestis. ☛ Pneumococcal pneumonia: Streptococcus pneumoniae infection of the lungs and respiratory system, where the alveoli are inflamed and filled with fluid. ☛ Psittacosis: arises when the bacteria Chlamydophila psittaci is contracted from parrots, pigeons, hens, ducks, sparrows, and seagulls. ☛ Q fever: due to inhalation of contaminated particles in the air or contact with the vaginal mucus, milk, feces, semen, and urine of animals infected with Coxiella burnetii. ☛ Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: severe rickettsial illness caused by ticks infected with Rickettsia rickettsii ☛ Salmonellosis: Salmonella infection that causes typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, and foodborne illness. ☛ Scarlet fever: infection may occur through bloodstream, or skin and underlying tissues. ☛ Shigellosis: dysentery due to poor hygiene leading to infection by Shigella spp. ☛ Syphilis: sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum ☛ Tetanus: prolonged contraction of skeletal muscle fibers due to infection of Clostridium tetani ☛ Trachoma: Chlamydia trachomatis infection of human eye, probably leading to blindness. ☛ Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection that generally attacks the lungs, but may affect central nervous system, circulatory system, lymphatic system, bones, joints, genitourinary system, and skin. ☛ Tularemia: characterized by an infection of Francisella tularensis bacteria leading to headache, fatigue, muscle pains, dizziness, nausea, loss of appetite, inflammation of face and eyes, and lymph nodes. ☛ Typhoid fever: due to ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Salmonella enterica enterica. ☛ Typhus: infection by bacteria of genus Rickettsia leading to severe headache, sustained high fever, severe muscle pain, rash, cough, chills, stupor, decreasing blood pressure, and delirium. ☛ Urinary tract infections: cystitis or pyelonephritis that arises due to Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus saprophyticus. [ Back to Index ] Fungal Infectious Diseases ☛ Aspergillosis: infection with fungi of the genus Aspergillus leading to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, pulmonary aspergilloma, or invasive aspergillosis. ☛ Blastomycosis: inhalation of fungus called Blastomyces dermatitidis from the natural soil habitat. ☛ Candidiasis: Candida albicans infection found in exposed and moist parts of the body, like the vagina, vulva, penis, foreskin, nostrils, ear, oral cavity, nipples, folds of skin in diaper area. ☛ Coccidioidomycosis: caused by inhalation of airborne, fungal spores called arthroconidia belonging to the fungi Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii. ☛ Cryptococcosis: caused by inhalation of soil contaminated with the encapsulated yeast Cryptococcus neoformans or C. gattii. ☛ Histoplasmosis: Histoplasma capsulatum infection that primarily affects the lungs. ☛ Tinea pedis: infection due to fungi of the genus Trichophyton that affects the epidermis of the foot. [ Back to Index ] Parasitic Infectious diseases ☛ African trypanosomiasis: caused by the protozoa called Trypanosoma brucei which is transmitted by the tsetse fly. Symptoms are fever, headaches, and joint pains. ☛ Amebiasis: due to ingestion of water, or food contaminated with cysts of amoeba or Entamoeba histolytica. ☛ Ascariasis: due to ingestion of food contaminated with fecal matter containing eggs of the parasitic roundworm called Ascaris lumbricoides. ☛ Babesiosis: caused by blood parasites belonging to the genus Babesia, and is generally transmitted by ticks. ☛ Chagas disease: Trypanosoma cruzi infection transmitted to humans by blood-sucking assassin bugs. ☛ Clonorchiasis: caused by the Chinese liver fluke termed Clonorchis sinensis. ☛ Cryptosporidiosis: caused by contaminated material, like earth, water, uncooked or crosscontaminated food in contact with the feces of a person or animal infected with parasites of the genus Cryptosporidium. ☛ Cysticercosis: caused by larvae of tapeworm called Taenia solium, generally found in pork. ☛ Diphyllobothriasis: characterized by abdominal discomfort, vomiting, weight loss, and diarrhea due to ingestion of parasites belonging to the genus Diphyllobothrium. ☛ Dracunculiasis: caused by drinking water, infected with guinea worms or Dracunculus medinensis. ☛ Echinococcosis: fatal disease due to infection by larvae of tapeworms belonging to the genus Echinococcus. ☛ Enterobiasis: infection due to pinworm or Enterobius vermicularis leading to poor appetite, restless sleep, and itching of the anus. ☛ Fascioliasis: caused by liver flukes called Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. ☛ Fasciolopsiasis: caused due to raw consumption of aquatic plants infected with intestinal fluke called Fasciolopsis buski or by consuming infected water. ☛ Filariasis: caused by roundworms belonging to the superfamily Filarioidea, which are transmitted by mosquitoes or deer fly. ☛ Free-living amebic infection: caused by Naegleria fowleri and Acanthamoeba spp. found in lakes, tap water, swimming pools, and air-conditioning units. ☛ Giardiasis: gastroenteritis that starts in the small intestine due to infection by the protozoa Giardia lamblia. ☛ Gnathostomiasis: due to migrating immature worms called Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or G. hispidum. ☛ Hymenolepiasis: caused by Hymenolepis nana or H. diminuta. ☛ Isosporiasis: Intestinal infection with Isospora belli leading to diarrhea and weight loss. It is sometimes linked with AIDS and immunocompromised states. ☛ Leishmaniasis: transmitted by certain varieties of sand fly infected with protozoa of genus Leishmania. ☛ Malaria: transmitted by female Anopheles mosquitoes infected with the blood parasites of genus Plasmodium. ☛ Metagonimiasis: infection by intestinal flatworm, mainly Metagonimus yokagawai leading to symptoms like diarrhea and colicky abdominal pain. ☛ Myiasis: caused by fly larvae feeding on the host's necrotic or living tissue. ☛ Onchocerciasis: the second leading infectious cause of blindness, with the infectious agent being Onchocerca volvulus. ☛ Pediculosis: infestation of lice, members of the order Phthiraptera, on the human body. ☛ Scabies: characterized by superficial burrows and intense itching due to skin infection with mites belonging to the genus Sarcoptes. ☛ Schistosomiasis: due to infection of the blood with Schistosoma spp. leading to weakness, liver and intestinal damage. ☛ Taeniasis: infection involving pork and beef tapeworms of the genus Taenia. ☛ Toxocariasis: caused by ingestion of dog or cat roundworms called Toxocara canis and T. cati respectively. ☛ Toxoplasmosis: due to ingestion of raw or partly cooked meat, contaminated cat feces, drinking water containing Toxoplasma gondii, transplacental infection in utero, infected organ transplant or blood transfusion. ☛ Trichinellosis: caused by eating raw or undercooked pork, and wild game products infected with the larvae of roundworm called Trichinella spiralis. ☛ Trichuriasis: infection of the large intestine by a parasite whipworm or Trichuris trichiura. ☛ Trichomoniasis: sexually transmitted disease caused by Trichomonas vaginalis that infects the genitourinary tract. ☛ Trypanosomiasis: caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosoma of the genus Trypanosoma. [ Back to Index ] Viral Infectious Diseases ☛ AIDS: specific damage to the immune system caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). ☛ Bolivian hemorrhagic fever: also known as Ordog fever, the culprit virus being Machupo virus. Fever, body ache, malaise are the primary symptoms. Nosebleeds and sore gums are also observed, however, only, when the condition is not checked on time. ☛ Chickenpox (Varicella): caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) leading to appearance of spots, mainly on the body and head. ☛ Common cold: disease of the upper respiratory system that arises due to rhinovirus, influenza viruses, picornavirus, adenoviruses, etc. It is also called acute viral nasopharyngitis. ☛ Cytomegalovirus infection: generally concerning salivary glands, though may be found anywhere in the body. ☛ Colorado tick fever: transmitted from the bite of a wood tic infected with the Colorado tick fever virus (CTFV). ☛ Dengue fever: transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquito infected with the dengue virus. ☛ Ebola hemorrhagic fever: caused by ebola viruses that lead to diarrhea, internal and external bleeding, fever, general body pain, and vomiting. ☛ Hand, foot, and mouth disease: common cause is Coxsackie A virus, which usually affects infants and children. ☛ Viral hepatitis: characterized by liver inflammation arising due to viruses belonging several families of viruses including hepadnaviridae, hepeviridae, adenoviridae, etc. ☛ Herpes simplex: caused by viruses of the family herpesviridae, and characterized by itching, swelling, emission of fluid from swelling, headache, fatigue, and overall gloomy mental state. ☛ Herpes zoster: varicella zoster virus (VZV) infection that persists and affects the nervous system with or without appearance of rash on the skin. ☛ Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections: sexually transmitted viral infections of skin and mucous membranes that arise due to HPV, and are often associated with cervical cancer. ☛ Influenza (Flu): caused by influenza viruses that belong to the family Orthomyxoviridae, and characterized by sore throat, fever, headache, muscle pains, weakness, coughing, and discomfort. ☛ Lassa fever: initially mucosa, intestine, lungs, urinary systems are affected due to the Lassa virus. The vascular system, then is affected with the condition metastasizing to every tissue in the body. ☛ Measles: is spread through respiration and is highly contagious disease caused by measles virus that belongs to Morbillivirus family of viruses. ☛ Marburg hemorrhagic fever: caused by Marburg virus which is transmitted though bodily fluids, like saliva, vomit, blood, and excrement. ☛ Infectious mononucleosis: common in adolescents and young adults, characterized by fever, muscle soreness, sore throat, and fatigue owing to an infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). ☛ Mumps: characterized by painful swelling of the salivary glands and fever due to the mumps virus belonging to genus Rubulavirus. Testicular swelling and rash may also occur. ☛ Poliomyelitis: spread from one person to other due to transmission of poliovirus via the fecaloral route, e.g., poor hand washing. ☛ Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: occurs exclusively in people with severe immune deficiency, due to infection by a polyomavirus called the JC virus (JCV). ☛ Rabies: transmission of rabies virus through bites, aerosol, mucous membranes, transplant surgery, etc. leads to acute encephalitis and flu-like symptoms. ☛ Rubella: also called as German measles, it is caused by rubella virus that enters the body via nose or throat. ☛ Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): characterized by fever, lethargy, myalgia, cough, sore throat, and gastrointestinal symptoms arising due to SARS coronavirus. ☛ Smallpox (Variola): caused by Variola major and Variola minor, this viral disease has been eradicated globally by 1980. It is characterized by skin scars and occasionally blindness due to corneal ulcerations and infertility in male survivors. ☛ Viral encephalitis: an acute inflammation of the brain resulting due infection with viruses, namely arboviruses, herpes simplex virus, rabies virus, Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), etc. ☛ Viral gastroenteritis: a rotavirus infection that grips children, especially of the developing countries. Vomiting, chill, diarrhea, and stomach cramps are some of the prominent indicants. ☛ Viral meningitis: inflammation of the protective membranes covering the nervous system due to an infection with herpes simplex virus, enteroviruses, cytomegalovirus, HIV, mumps virus, etc. ☛ Viral pneumonia: an illness of the lungs and respiratory system caused by influenza virus A and B, adenoviruses, herpes simplex virus, VZV, etc. ☛ West Nile disease: caused by the West Nile virus (WNV), and transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. ☛ Yellow fever: viral hemorrhagic illness arising due to yellow fever virus, and is common in many African and South American nations.