Teacher notes for ZSL London Zoo quizzes
advertisement
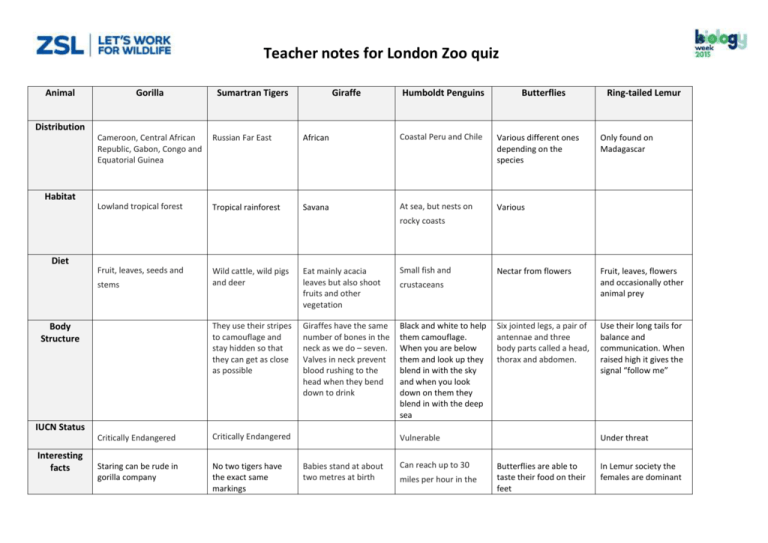
Teacher notes for London Zoo quiz Animal Gorilla Sumartran Tigers Giraffe Distribution Habitat Humboldt Penguins Butterflies Cameroon, Central African Republic, Gabon, Congo and Equatorial Guinea Russian Far East African Coastal Peru and Chile Various different ones depending on the species Lowland tropical forest Tropical rainforest Savana At sea, but nests on Various Ring-tailed Lemur Only found on Madagascar rocky coasts Diet Fruit, leaves, seeds and stems Body Structure IUCN Status Interesting facts Wild cattle, wild pigs and deer Eat mainly acacia leaves but also shoot fruits and other vegetation Small fish and They use their stripes to camouflage and stay hidden so that they can get as close as possible Giraffes have the same number of bones in the neck as we do – seven. Valves in neck prevent blood rushing to the head when they bend down to drink Black and white to help them camouflage. When you are below them and look up they blend in with the sky and when you look down on them they blend in with the deep sea Critically Endangered Critically Endangered Staring can be rude in gorilla company No two tigers have the exact same markings Nectar from flowers Fruit, leaves, flowers and occasionally other animal prey Six jointed legs, a pair of antennae and three body parts called a head, thorax and abdomen. Use their long tails for balance and communication. When raised high it gives the signal “follow me” crustaceans Vulnerable Babies stand at about two metres at birth Can reach up to 30 miles per hour in the Under threat Butterflies are able to taste their food on their feet In Lemur society the females are dominant Teacher notes for London Zoo quiz water to catch their prey National Curriculum links Key Stage 1 Using their observations and ideas to suggest answers to questions Key Stage 2 Working scientifically: Asking relevant questions and using different types of scientific enquires to answer them Living things and their habitats: Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways Physical Geography: describe and understand key aspects including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains Geographical skills and fieldwork: use maps, atlases, globes Animals: Identify producers, predators and prey Key Stage 3 Geographical skills and fieldwork: Build on their knowledge of globes, maps and atlases and apply and develop this knowledge routinely in the classroom and in the field Genetics and evolution: differences between species Motion and forces: Speed Teacher notes for London Zoo quiz