Review Sheet Answer Key
advertisement
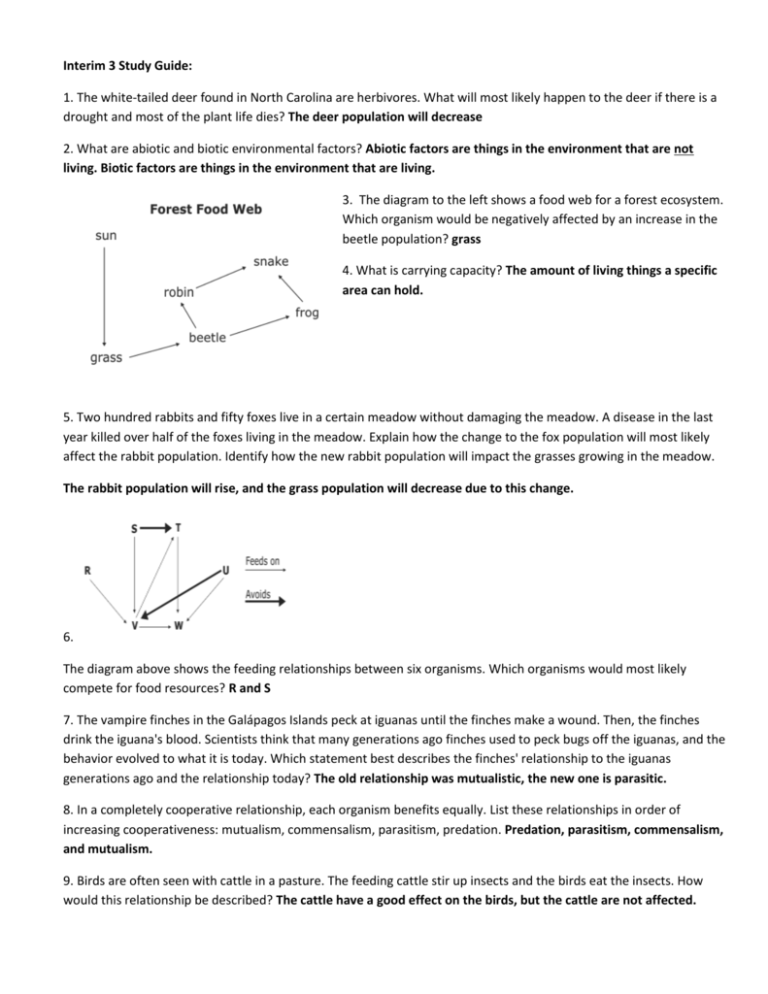
Interim 3 Study Guide: 1. The white-tailed deer found in North Carolina are herbivores. What will most likely happen to the deer if there is a drought and most of the plant life dies? The deer population will decrease 2. What are abiotic and biotic environmental factors? Abiotic factors are things in the environment that are not living. Biotic factors are things in the environment that are living. 3. The diagram to the left shows a food web for a forest ecosystem. Which organism would be negatively affected by an increase in the beetle population? grass 4. What is carrying capacity? The amount of living things a specific area can hold. 5. Two hundred rabbits and fifty foxes live in a certain meadow without damaging the meadow. A disease in the last year killed over half of the foxes living in the meadow. Explain how the change to the fox population will most likely affect the rabbit population. Identify how the new rabbit population will impact the grasses growing in the meadow. The rabbit population will rise, and the grass population will decrease due to this change. 6. The diagram above shows the feeding relationships between six organisms. Which organisms would most likely compete for food resources? R and S 7. The vampire finches in the Galápagos Islands peck at iguanas until the finches make a wound. Then, the finches drink the iguana's blood. Scientists think that many generations ago finches used to peck bugs off the iguanas, and the behavior evolved to what it is today. Which statement best describes the finches' relationship to the iguanas generations ago and the relationship today? The old relationship was mutualistic, the new one is parasitic. 8. In a completely cooperative relationship, each organism benefits equally. List these relationships in order of increasing cooperativeness: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, predation. Predation, parasitism, commensalism, and mutualism. 9. Birds are often seen with cattle in a pasture. The feeding cattle stir up insects and the birds eat the insects. How would this relationship be described? The cattle have a good effect on the birds, but the cattle are not affected. 10. What are parasitic relationships? Mutualistic? Commensalistic? Parasitic: host is harmed, parasite is happy Mutualism: both animals benefit Commensalism: one animal benefits, the other isn’t affected 11. Describes the relationship between decomposers and producers. Producers absorb nutrients from decomposed material in the soil. 12. What is the role of plants in the carbon cycle? In the water cycle? Plants take in excess carbon, and water evaporates from plants through transpiration. 13. What consume energy from dead organisms? Scavengers, fungi, and bacteria 14. What is the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the flow of energy? They convert nitrogen in the atmosphere into molecules that other organisms can use. 15. Describe how energy from the sun relates to the energy a cow gets from eating grass in a field. The grass uses energy from the sun to make food, the cow eats the grass and breaks it down to release energy for the cow. 16. What are renewable and nonrenewable energy sources? Renewable: can be used again. Examples: wind, hydroelectricity, geothermal, biomass, solar Nonrenewable: cannot be used again, once it is gone it is gone! Examples: fossil fuel, oil, coal 17. What renewable energy source is considered to be an important source of energy worldwide, but may impact plant growth? biomass 18. What methods of energy production are most likely to have a negative impact upon the environment? Coals and fossil fuels 19. Why is it important to limit the use of fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas? Fossil fuels can only be replenished after millions of years. 20. Upwelling brings what type of water to marine ecosystems near the surface? Cold, nutrient-rich waters 21. What percentage represents the amount of freshwater on Earth? 3% 22. Where does most fresh water exist? Aquifers, ice caps and glaciers 23. Rivers and streams transport nutrients, salts, sediments, and pollutants. Put these terms in the correct order for this process: ocean, watershed, estuary. Watershed->estuaries->oceans 24. Why are aquifers important? It holds uncontaminated water that we can drink 25. What is the largest ocean zone? oceanic 26. Why do plant plankton not grow in the deep ocean? There is not enough sunglight 27. Light does not reach the bottom of the ocean, yet certain species live there. Explain how species on the bottom of the ocean get energy to live. Through chemosynthesis from hydrothermal vents 28. Why are estuaries an important habitat for many marine organisms in comparison to the open ocean? There are more nutrients available in estuaries 29. A cargo ship in the open ocean spills thousands of gallons of oil off the ship. Which marine ecosystem/zone will primarily be disturbed by this spill? Photic zone 30. What are the raw materials (reactants) for photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide and water (CO2 and H2O) Good Luck! You Can Do It!