Exploring the Oceans notes 2011 student part 1
Exploring the Oceans 2011
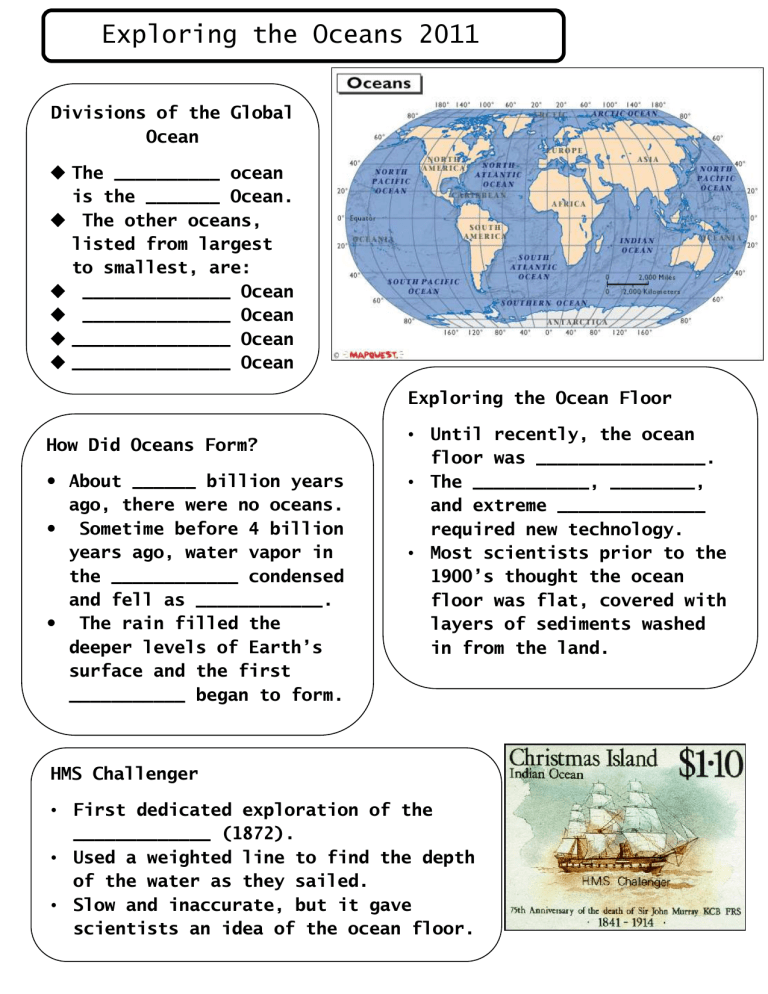
Divisions of the Global
Ocean
The __________ ocean is the _______ Ocean.
The other oceans, listed from largest to smallest, are:
______________ Ocean
______________ Ocean
_______________ Ocean
_______________ Ocean
How Did Oceans Form?
About ______ billion years ago, there were no oceans.
Sometime before 4 billion years ago, water vapor in the ____________ condensed and fell as ____________.
The rain filled the deeper levels of Earth’s surface and the first
___________ began to form.
HMS Challenger
• First dedicated exploration of the
_____________ (1872).
• Used a weighted line to find the depth of the water as they sailed.
• Slow and inaccurate, but it gave scientists an idea of the ocean floor.
•
Exploring the Ocean Floor
• Until recently, the ocean floor was ________________.
• The ___________, ________, and extreme ______________ required new technology.
• Most scientists prior to the
1900’s thought the ocean floor was flat, covered with layers of sediments washed in from the land.
•
Theory of Plate Tectonics
Totally revolutionized our understanding of the Earth, past and present.
Theory ranks with the theories on evolution, relativity, the
Big Bang, and Newton’s Laws.
Sonar
Sound Navigation and
Ranging.
Invented in WWI to hunt submarines.
____________ is bounced off the ocean floor to find the depth.
The _________ the bottom is, the ______ the echo returns.
Reveling the Ocean Floor
Regions of the Ocean Floor:
The two regions of the ocean floor are the _____________
___________ and the _______-
___________ ____________.
Underwater Real Estate:
The continental margin and the deep-ocean basin are subdivided into different areas and have different features.
Studying the Ocean Floor
Seeing by Sonar:
Scientists use sonar to determine the ocean’s __________.
Oceanography via
Satellite:
Scientists use images from the satellite
Seasat to study ocean currents.
Studying the Ocean with Geosat:
Scientists use the
Geosat satellite to measure slight changes in the height of the ocean’s surface.
Submersibles
Specially designed
______________ used by scientists to explore more than 1-km below the surface.
Thick metal hulls protect the scientists from being crushed by the immense _________.
Continental Shelf
_______ _________, shallow part of ocean floor that extends outward from the continent.
Varies from a few kilometers to over 1300-km from shore.
Provides nutrient rich home to large numbers of fish.
Continental Slope
_________ slanting portion after the shelf.
Bottom marks the edge of the continental _______.
Continental Rise
________ ______ at base of continental slope formed by accumulation of sediments that wash down.
Turbidity Current
Abyssal Plain
___________ parts of the deep
_________ ___________.
Covered with fine grained muddy ______________ (silt).
Cover ___________ areas of the ocean floor.
Rapid moving currents that carry large amounts of sediments.
Similar to ______________ on land.
Often cut canyons in the continental slope.
Mid-ocean ridge
____________ boundary underwater, where new crust is being formed from __________ deep in the ___________.
Form underwater ____________ ranges that seldom break the _____________.
Can be 1000’s of km wide, and over 80,000-km long.
Passes through all the Earth’s ___________.
Seamounts
Underwater ___________.
If they reach the surface they form islands.
Volcanic Island Arcs
These once underwater
_____________ grow so large they break the surface of the ocean.
Associated with O-O convergent boundaries.
Deep Sea Trenches
______________ part of the ocean.
Many ______________ deeper than the surrounding __________
____________.
Very long (1000’s of km), but fairly narrow
(100-km across).
Place where old crust is being subducted back into the mantle.
Sign of ______________ boundary.








