CHAPTER 3 NOTE FACTS Go on line to my website and find the
advertisement

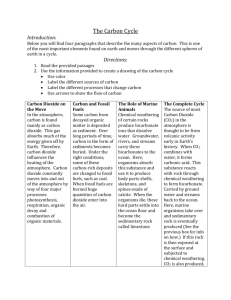
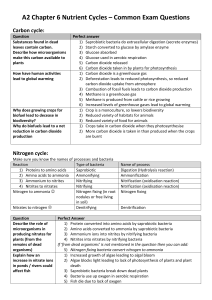
CHAPTER 3 NOTE FACTS Go on line to my website and find the chapter 3 and 4 powerpoint to find jeopardy questions. The chapter 3 notes on the powerpoint focus on: 1. Food webs 2. Food chains 3. Ecological pyramids (biomass, numbers, energy (10%) 4. Trophic levels (primary producers, primary consumers, secondary, tertiary, quarternary consumers) 5. Autotrophs-heterotrophs 6. Photosynthesis—chemosynthesis 7. Photoautotroph—chemoautotroph 8. Herbivore—carnivore—omnivore—scavengers (detritivores)—decomposers 9. Water cycle (processes) a. Evaporation—energy absorbed; water to vapor from bodies of water b. Transpiration—energy absorbed; water to vapor LOST FROM LEAVES of plants c. Condensation— warm water vapor to droplets to create clouds (energy released) d. Precipitation—gravity influenced e. Run-off—gravity influenced; water flows across surfaces f. Seepage (infiltration)—water absorption into ground to be uptaken by plant roots OR travels into groundwater to other bodies of water g. Cycle powered by SUN 10. Carbon cycle (processes) a. Photosynthesis (autotrophs uptake carbon dioxide) to create sugar and oxygen from water and carbon dioxide (BIO CYCLE) b. Cellular respiration (plants and animals release carbon dioxide) burn sugar in presence of oxygen to create energy and carbon dioxide (BIO CYCLE) c. Decomposition (plants and animals) breaks down organic molecules to return nutrients to soil (release of carbon dioxide) (BIOCHEMICAL CYCLE) d. Deposition (organic matter buried) exposed to( pressure and heat of earth to create fossil fuels (uptake of carbon dioxide) (GEO CYCLE) e. Human activity (industries/transportation) burning fossil fuels (release carbon dioxide) (CHEMICAL CYCLE) and cutting forests, mining (releasing carbon dioxide) (GEO CYCLE) f. Volcanic eruptions release carbon dioxide (GEO CYCLE) g. Sedimentation in aquatic ecosystems (uptake of carbon) h. Erosion (releases carbon) (GEO CYCLE) i. LARGEST RESERVOIR OF CARBON—Sedimentary rock j. WHERE CARBON SPENDS THE LEAST AMOUNT OF TIME—atmosphere, living things k. WHERE CARBON SPENDS THE MOST TIME—sedimentary, fossil fuels, sediments 11. Nitrogen cycle (processes) a. Nitrogen-fixation —uptake of nitrogen from atmosphere through bacteria plant roots b. Ammonification—nitrogen to ammonia (from nitrogen fixation and excretion/decomposition) c. Nitrification—ammonia to nitrates (plant food which plants use) d. Assimilation—nitrates to amino acids (proteins) and nucleotides (nucleic acids) by plants and animals e. Denitrification—nitrates to nitrogen released back into atmosphere f. Atmospheric fixation—lightning converts atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen into nitrates g. Water runoff sends nitrates into water h. Synthetic fertilizers added by humans adds nitrates to ecosystemi. Largest nitrogen reservoir--atmosphere 12. Phosphorus cycle= a. Only cycle that does not pass through atmosphere b. Largest reservoir-—sediment 13. Limiting nutrients—algal bloom