PBIO 450/550.examI.sp94
advertisement

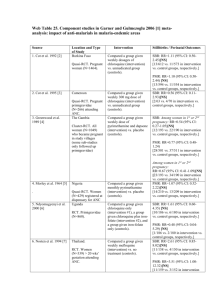
PBIO 3300/5300-Fall 2015 Practice Exam I (100 points) NAME___Practice Exam I Answers___ You have the entire class period to complete all three parts of this exam (i.e., I. General genetics knowledge, II. Multiple choice, and III. Short answer/Genetics problems). Good luck! I. General genetics knowledge-20 points (2 points/question) 1. What genomes are present in animal cells? Nuclear and mitochondrial genomes 3. What contribution did Thomas Hunt Morgan make to genetics and what organism did he use? Morgan used fruitflies to discover the basic rules of genetic recombination and linkage. 6. Define reverse genetics. Reverse genetics involves having a gene of interest, obtaining a mutant for that gene, observing a phenotype (to reveal the function of your gene of interest). 8. What type of genetic cross results in phenotypic ratios of 3:1? Of 9:3:3:1? Of 1:1:1:1? Monohybrid selfed, dihybrid selfed (independent assortment), dihybrid testcross (independent assortment), respectively b____ 2. AB/ab indicates which of the following? a. A and B are not linked genes b. AB are linked in cis c. AB are linked in trans d. linkage cannot be determined without more information e. b and c. b____ 8. If genes assort independently, a testcrossed dihybrid characteristically produces progeny phenotypes in the ratio: a. 1:1 b. 1:1:1:1 c. 1:2:1 d. 3:1 e. 9:3:3:1 d____ 9. A male mouse of genotype A/a . B/b is testcrossed multiple times. Overall, these testcrosses produce 11 mice of phenotype A B, 81 A b, 77 a B, and 14 a b. Based on these data, the genotypes of the male mouse’s parents are most likely: a. A/a;B/b and A/a;B/b b. AB/AB and ab/ab c. AB/ab and AB/ab d. Ab/Ab and aB/aB e. Ab/ab and Ab/ab III. Short answer/Genetics Problems-40 points 1. Gregor Mendel discovered that gray seed color in peas is dominant to white. In the following experiments, parents with known phenotypes but unknown genotypes produced the progeny (offspring) listed below. Using the letter W for the dominant gray allele and the letter w for the recessive white allele, give the most probable genotype for each of the parents listed below. Please place the proper letters in the spaces provided above (note: 1 letter per space). a) b) c) d) e) Parents Progeny (F1) Gray White Fill in the probable Parental genotypes gray x white gray x gray white x white gray x white gray x gray 82 118 0 74 90 _W_ _W_ _w_ _W_ _W_ _W_ 78 39 50 0 0 _w_ _w_ _w_ _W_ _W_ _W_ x x x x x x _w_ _W_ _w_ _w_ _W_ _W_ _w_ _w_ _w_ _w_ _W_ or _w_ 1 2. In mice, dwarfism is caused by an X-linked recessive allele. If a dwarf female mouse is crossed with a normal male mouse, what will be the phenotypic ratios in the F1 and the F2 for each sex? Note: to generate the F2, brothers are mated with sisters in the F1. Show your work. a) F1 phenotypic ratios1 normal (carrier) female : 1 dwarf male b) F1 work: XdXd x XDY XD Y d d D X X X Xd Y d d D X X X Xd Y c) F2 phenotypic ratios1 dwarf female : 1 normal (carrier) female : 1 dwarf male : 1 normal male d) F2 work: XdXD x XdY Xd Y d X Xd Xd Xd Y XD XD Xd XD Y 3. Draw a linkage map consistent with the following recombination frequencies: A-B 6%, A-C 18%, B-C 24%, B-D 17%, A-D 11%, C-D 7% Answer: In this case, all four genes are linked, and a consistent map is: |-------|-----------|------| OR |------|-----------|-------| C 7 D 11 A 6 B B 6 A 11 D 7 C 4. In the genetic model plant Arabidopsis, the recessive allele hyg confers seed resistance to the drug hygromycin, and her, a recessive allele of a different gene, confers seed resistance to a herbicide. A plant that was homozygous hyg/hyg . her/her was crossed with true breeding wild type (hyg+/hyg+. her+/her+), and the F1 was selfed. Seeds resulting from the F1 self were placed on petri dishes containing hygromycin and the herbicide. a) If the two genes are unlinked, what percentage of seeds is expected to grow? Show your work. b) If the two genes are linked by 28 centiMorgans, what percentage of seeds is expected to grow if the F1 plants are test crossed (instead of being selfed)? Show your work. Answer: a. If the genes are unlinked, the cross becomes: P hyg/hyg; her/her x hyg+/hyg+; her+/her+ F1 hyg+/hyg; her+/her x hyg+/hyg; her+/her F2 9/16 hyg+/-; her+/3/16 hyg+/-; her/her 3/16 hyg/hyg; her+/1/16 hyg/hyg; her/her So only 1/16 (or 6.25%) of the seeds would be expected to germinate and grow. b. If the two genes are linked by 28 centiMorgans, the F1 test cross looks like this: hyg+ her+/hyg her x hyg her/hyg her 36% hyg+ her+/hyg her (parental) *36% hyg her/hyg her (parental) 14% hyg+ her/hyg her (recombinant) 14% hyg her+/hyg her (recombinant) 2 *So only 36% are expected to germinate and grow. 3