Food Web

Science: Key ideas: “observation of natural world” “evidence based”
What sorts of things does science study? What sorts of things are not studied by science?
Observation or Inference:
The leaves on my rose bush have turned yellow. The leaves are yellow because there is too little nitrogen in the soil.
Qualitative or Quantitative
There are 7 yellow finches at the bird feeder.
Define the Problem: Underline the best question.
Underline the best hypothesis.
Does fertilizer make plants grow better?
Does South Laurel brand fertilizer make tomatoes produce more fruit?
Hypothesis:
I think plants receiving the fertilizer will make more fruit.
Plants receiving South Laurel brand fertilizer will produce more fruit than plants which receive no fertilizer.
Test hypothesis with an experiment:
Select 20 identical tomato plants. Assign 10 tomatoes to Group A and 10 tomatoes to Group B. Grow the plants under identical conditions of light, moisture, and soil. Apply South Laurel Brand fertilizer to Group A according to the directions on the box. Do not add fertilizer to Group B. Count the number of tomatoes produced by each group for 6 weeks.
What type of experiment is described above?_____________________________________________
What is the manipulated or independent variable?_________________________________________
What is the dependent variable?_______________________________________________________
Which group of tomatoes is the control group?_______ Why is it necessary to have a control?
Analyze results:
Group A plants produced 2 bushels of tomatoes and Group B plants produced ¾ bushel of tomatoes.
Was the hypothesis proven, supported or refuted?_____________________
Are the researchers ready to propose a theory?Explain._________________
Should additional trial be conducted?________________________________
Draw conclusions:
Write one sentence summarizing the conclusions that can be drawn from this experiment.
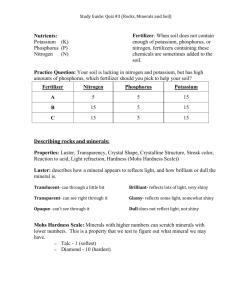
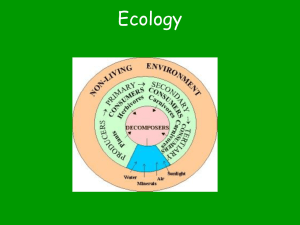
Distinguish between Biology and Ecology.
Food Web
1. For the food web, label each organism: (Some may have more than one label)
P = producer
1 = Primary Consumer
2= Secondary Consumer
3 = Tertiary Consumer
4 = Quartenary Consumer
2. Now label each animal as H = herbivore C = carnivore O = omnivore D=detritivore
3. Identify one food chain within this food web.
4. What important link is not shown in the diagram? What process could not occur without this link?
5. List the autotrophs.
List the heterotrophs.
6. What happens if you remove the frog from this web?
Food Pyramid
1.. In a ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass and # of species as you move up? Why ?
2. What is biomass?
3. In an ecosystem, can there be more carnivores than herbivores? Explain why or why not?
4. What is the 10% rule? What is its significance? Why is energy lost?
5. Label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk, grass, chicken, grasshopper. Also label and explain what happens to energy, biomass and number of organism.
8. Discuss what trophic level humans occupy on an ecological pyramid, and explain what happens to contaminants and environmental pollution (such as mercury) as you move down and up the ecological pyramid (what is this called?).
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
Carbon
1. Which organic compounds contain carbon?
2. Two major abiotic reservoirs of carbon are the ___________________ and the ___________________.
What carbon containing molecule is in these reservoirs?_________________________
3. What two biological processes play important roles in recycling carbon?
4. How is cellular respiration like combustion of fossil fuels? Where did the carbon in fossil fuels come from?
5. How are the carbon atoms in the bodies of dead organisms returned to the abiotic environment?
6. Describe the impact of human activities on the carbon cycle.
Nitrogen
1. Which organic compounds contain nitrogen?
2. What is the major reservoir for nitrogen?
3. What organisms are responsible for making nitrogen available to the producers? What organisms are
responsible for returning nitrogen to the abiotic part of the environment?
4. Describe the impact of human activities on the nitrogen cycle.
Phosphorus
1. Which organic compounds contain phosphorus?
2. How does the phosphorus cycle differ from the other cycles we have studied?
3. Describe how phosphorus moves through the food web.
Water
1. The source of energy that drives the water cycle is the ________________.
2. The water cycle is unlike the other BGCs in 2 ways:
3. The evaporation of water from plants is called _________________________.
CAN YOU????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????
TRACE THE FLOW OF MATTER AND ENERGY THROUGH AN ECOSYSTEM?
IDENTIFY THE DIFFERENCES IN THE MOVEMENT OF MATTER AND ENERGY THROUGH AN
ECOSYSTEM?
EXPLAIN HOW FOOD WEBS AND FOOD PYRAMIDS ARE MODELS FOR THE MOVEMENT OF MATTER
AND ENERGY THROUGH AN ECOSYSTEM?