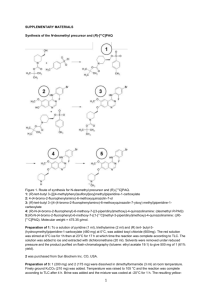
Table 1a Reaction mass input and output for the
advertisement

Using metrics and sustainability considerations to evaluate the use of bio-based and non-renewable Brønsted acidic ionic liquids to catalyse Fischer esterification reactions James H. Clark,* Thomas J. Farmer, Duncan J. Macquarrie and James Sherwood Additional data files Metrics calculations: The following tables record examples the mass input and output of the reactions discussed in the main article. These values were used to calculate the reaction metrics. Table 1a describes the use of [H-NMP][HSO4] and the use of [H-NMP][OCym] in the synthesis of benzyl acetate in terms of mass utilisation. Table 2a describes the use of [HNMP][OCym] in the synthesis of ethyl levulinate acetate in terms of mass utilisation but also incorporating the synthesis of the catalyst. Table 1a Reaction mass input and output for the synthesis of benzyl acetate Substance [H-NMP][HSO4] [H-NMP][OCym] Mass /g Contribution Mass /g Contribution Acetic acid 0.721 27.6% 0.721 1.8% Benzyl alcohol 1.30 49.7% 1.30 3.2% Diethyl ether 0 0% 7.13 17.8% Water 0 0% 30.0 74.8% 0.592 22.7% 0.940 2.3% 0.944 (52% yield) 0.697 (39% yield) Reactants Solvents Catalysts [NMP][HSO4] or [H-NMP][OCym] Desired product Benzyl acetate 1 Table 2a Reaction mass input and output for the synthesis of ethyl levulinate with N-methyl pyrrolidinonium pcymene-2-sulphonate Excluding [H-NMP][OCym] synthesis Including [H-NMP][OCym] synthesis Mass /g Contribution Mass /g Contribution Ethanol 0.553 11.3% 0.553 1.6% Levulinic acid 0.464 9.5% 0.464 1.3% 3.57 72.8% 3.57 10.2% Ammonium bromide 0.0167 0.05% Glutamic acid 0.397 1.1% Methanol 0.671 1.9% Essential oil of orange 0.928 2.6% Montmorillonite clay 0.132 0.38% Oleum 0.500 1.4% Palladium on carbon 0.0705 0.20% Water 25.1 71.6% 2.66 7.6% 0.290 (50% yield) Substance Reactants Solvents Diethyl ether Catalyst: NMP reactant Catalyst: p-CSA reactant Catalyst synthesis Dichloromethane [H-NMP][OCym] 0.313 6.4% 0.290 (50% yield) Desired product Ethyl levulinate Regulatory issues surrounding NMP: With the introduction of the REACH legislation in Europe, some traditional solvents are being subjected to restrictions on their use. Because of its reproductive toxicity, one of the solvents now classified as a substance of very high concern (SVHC) is NMP [1]. It also causes serious eye and respiratory irritation [2]. This has implications for the use of NMP directly as a solvent, but also the use of NMP as an intermediate in the synthesis of Brønsted acidic ionic liquids now comes into question. The relationship between chemical structure and toxicity is not a precise one, and is not necessarily systematic across a family of related compounds in a predictable way. For example, the liquid 1-butyl-4carboxypyrrolidinone methyl ester has been recently described as “harmless to human health” and so future generations of amide solvents, compliant with chemical legislation, may come to exist [3]. In turn, these solvents may be used to produce novel Brønsted acidic ionic liquids. References 1. http://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table, accessed 8/11/2013. 2. MSDS, 1-methylpyrrolidinone 3. Moity L, Molinier V, Benazzouz A, Barone R, Marion P, Aubry JM: In silico design of bio-based commodity chemicals: Application to itaconic acid based solvents. Green Chem 2013, advanced article. DOI: 10.1039/c3gc41442f. 3