9.5 Notes (Completed)
advertisement

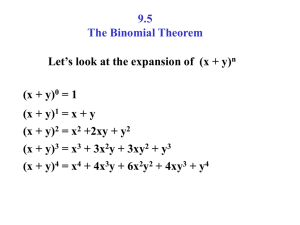
P.o.D. – Find the next 3 terms 1.) −2, −2 −2 3 , 9 ,… 2.) 5x+7, -10x-14, 20x+28, … 3.) Find the 10th term in the sequence √3, 3, 3√3, … 4.) Write a sequence that has two geometric means between 6.4 and 12.5 5.) Find the sum of the first six terms of the geometric series 2-8+32-128+… 6.) If r=-2 and 𝑎8 = −384, what is the first term of the geometric sequence? 1.) −2 −2 −2 , , 27 81 243 2.) -40x-56, 80x+112, -160x-224 3.) 243 4.) 6.4, 8, 10, 12.5 5.) -1638 6.) 3 9.5 – The Binomial Theorem Learning Target: I will be able to use the binomial theorem to calculate binomial coefficient; use Pascal’s triangle to calculate binomial coefficients. Combination – a selection of objects where the order is not important. The number of n objects taken r at a time is denoted by C(n,r) or 𝑛𝐶𝑟 𝑛! 𝐶 (𝑛, 𝑟) = [(𝑛 − 𝑟)! 𝑟!] EX: C(8,4) 8! 𝐶 (8,4) = = (8 − 4)! 4! 8! = 4! 4! 40320 = 24(24) 40320 = 70 576 *There is a combination feature on your calculator. EX: Find C(6,3) on your own. We will use this property of a combination with the Binomial Theorem. EX: Expand (𝑎 + 𝑏)2 We would most likely use FOIL. (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏) = 𝑎2 + 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑎2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 EX: Expand (𝑎 + 𝑏)3 (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏) = (𝑎2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 )(𝑎 + 𝑏) = 𝑎3 + 2𝑎2 𝑏 + 𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑎2 𝑏 + 2𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3 = 𝑎3 + 3𝑎2 𝑏 + 3𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3 We can continue this pattern for any higher exponent, but how long would it take to find (𝑥 + 𝑦)12 ? There is a quicker way to perform binomial expansion – Pascal’s Triangle. (draw Pascal’s Triangle on the board) EX: Find (𝑥 + 𝑦)5 using Pascal’s Triangle. 1𝑥 5 + 5𝑥 4 𝑦 + 10𝑥 3 𝑦 2 + 10𝑥 2 𝑦 3 + 5𝑥𝑦 4 + 1𝑦 5 Pascal’s Triangle can also be written using combinations. (show this on the whiteboard) EX: Use Pascal’s Triangle to expand (𝑥 + 2)4 The 4th row of Pascal’s Triangle is 1,4,6,4,1. 1(𝑥)4 (2)0 + 4(𝑥)3 (2)1 + 6(𝑥)2 (2)2 + 4(𝑥)1 (2)3 + 1(𝑥)0 (2)4 = 𝑥 4 + 8𝑥 3 + 24𝑥 2 + 32𝑥 + 16 Try the following on your own: a.) Expand (𝑦 − 2)4 b.) Expand (2𝑥 − 𝑦)4 a.) 𝑦 4 − 8𝑦 3 + 24𝑦 2 − 32𝑦 + 16 b.) 16𝑥 4 − 32𝑥 3 𝑦 + 24𝑥 2 𝑦 2 − 8𝑥𝑦 3 + 𝑦 4 EX: Write the binomial expansion for (3 − 𝑥 2 )4 1(3)4 (−𝑥 2 )0 + 4(3)3 (−𝑥 2 )1 + 6(3)2 (−𝑥 2 )2 + 4(3)1 (−𝑥 2 )3 + 1(3)0 (−𝑥 2 )4 = 1(81)(1) + 4(27)(−𝑥 2 ) + 6(9)𝑥 4 + 4(3)(−𝑥 6 ) + 1(1)𝑥 8 = 81 − 108𝑥 2 + 54𝑥 4 − 12𝑥 6 + 𝑥 8 For the next few questions, we will want to use the combination method for Pascal’s Triangle. EX: Find the 5th term of (𝑎 + 2𝑏)8 . Begin by determining the variable component. The 5th term must have variables 𝑎4 𝑏4 . Now find the coefficient of the 5th term. 𝐶 (8,4)(𝑎)4 (2𝑏)4 = 70𝑎4 (16𝑏 4 ) = 1120𝑎4 𝑏4 EX: Find the third term in the expansion of (2𝑎 − 3𝑏)11 𝐶 (11,2)(2𝑎)9 (−3𝑏)2 = 55(512𝑎9 )(9𝑏 2 ) = 253440𝑎9 𝑏 2 Expand each binomial on your own: a.) (𝑚 + 𝑡)6 b.) (4𝑚 + 2𝑦)4 c.)(2 − 𝑞)5 d.)(𝑥 − 𝑦)3 a.) 𝑚6 + 6𝑚5 𝑡 + 15𝑚4 𝑡 2 + 20𝑚3 𝑡 3 + 15𝑚2 𝑡 4 + 6𝑚𝑡 5 + 𝑡 6 b.) 256𝑚4 + 512𝑚3 𝑦 + 384𝑚2 𝑦 2 + 128𝑚𝑦 3 + 16𝑦 4 c.) 32 − 80𝑞 + 80𝑞2 − 40𝑞3 + 10𝑞4 − 𝑞5 d.) 𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 2 𝑦 + 3𝑥𝑦 2 − 𝑦 3 Find the indicated term of each expression on your own: a.) b.) a.) b.) Fourth term of (2𝑎 + 𝑏)5 Fifth term of (𝑦 − 5)6 40𝑎2 𝑏 3 9375𝑦 2 Let’s write a program to find each row in Pascal’s Triangle. Now let’s write a program to find a specific coefficient in Pascal’s Triangle. Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to: 1. Evaluate a combination. 2. Expand polynomials using the Binomial Theorem. 3. Expand polynomials using Pascal’s triangle. For more information, visit http://www.purplemath.com/modules/bino mial.htm HW Pg.688 3-60 3rds, 76