LfP Instructional Road MAp
advertisement

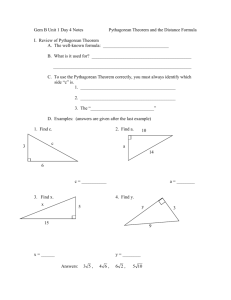
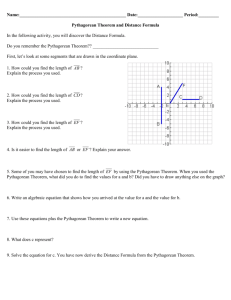
RCAS Grade 8 – Looking for Pythagoras- Instructional Roadmap November 4 – December 20: Looking for Pythagoras 25 full days assessment, intervention, and enrichment activities are included All Standards written in red are priority standards Investigation CCSS Learning Targets: CMP2/CMP3 (will need to create PLDs for each target) 4/4 1 8.G.B.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem I will utilize a coordinate grid Days Coordinate Grids and its converse. to explore distance relationships. (no standards 8.G.B.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the connection, but implicitly distance between two points in a coordinate grid. needed) [1.1/1.2] 8.G.B. 7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 4/6.5 Days 2 Square Roots 8.NS.A.2 Use rational approximations of rational numbers to compute the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions. *** Copy and add in 2.4 Cube Roots from CMP3 **** 8.EE.A2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2=p and x3=p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cube. Know that square root of 2 is irrational. 6/7 Days HS- N-QA. 3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitation on measurement when reporting quantities. 8.G.B.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 3 The Pythagorean Theorem 8.G.B.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate grid. I will be able to find the area of shapes, using properties of rectangles and right triangles. (no standards connection, but implicitly needed) [1.3] 1.) I will be able to apply my knowledge of square roots to find the side length of a given square. 2.) I will be able to approximate the value of a square root. [LT 2.3] 3.) I will be able to find the square root of a two dimensional figure or the cube root of a three dimensional figure. [2.3/2.4] 1.) I will be able to find the missing side of a right triangle using the Pythagorean Theorem. 2) I will be able to determine if a triangle is a right triangle based Assessments CFA’s: Learning targets: 1.3 Summative Assessment: None CFA’s: Learning targets: #2 Summative Assessment: Checkup after 2 CFA’s: Learning targets **** 3.4 has added good questions in part C. ***** 5/5 Days **** 4.2/4.3 is moved to Inv.5, 4.24.4 is all new ***** 5days **** New in CMP3 8.G.B. 7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 4 Using the Pythagorean Theorem: Understanding Real Numbers 8.NS.A1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. 8.NS.A.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compute the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions. 5 Using the Pythagorean Theorem: Analyzing Triangles and Circles CCSS.Math.Content.8.G.A.4 Understand that a twodimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations; given two similar two-dimensional figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the similarity between them. 8.G.B.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate grid. 8.G.B. 7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. Possible Essential Questions: How do you find the missing side of a right triangle? How can you estimate the value of an irrational #? Why does the Pythagorean Theorem work? How can we use the square root to find length or area? on the Pythagorean Theorem. 3) I will be able to explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.[3.1] Summative Assessment: Partner Quiz 1.) I will be able to approximate and order irrational numbers on a number line [4.1] 2.) I will be able to convert between rational and irrational numbers [4.2/4.3] 3.) I can identify numbers as rational or irrational [4.4] 1) I will be able to use the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems. [5.1] 2) I will be able to use the Pythagorean Theorem to analyze & determine relationships in special right triangles. [5.2/5.3] CFA’s: Learning targets 2/3 Summative Assessment: CFA’s: Learning targets 2 Summative Assessment: Unit Test Smarter Balanced ALDS 4 3 2 1 Use rational numbers to approximate irrational numbers. 8.NS.A Level 4 - Students should be able to approximate irrational numbers & use the approximations to solve problems or estimate the value of an expression. Level 3 -Students should be able to use rational approximations of irrational numbers to locate them on a number line and to make numerical comparisons; convert between fractions and repeating decimals; and compare rational numbers. Level 2 -Students should be able to identify approximate locations of familiar irrational numbers on a number line; identify numbers as rational or irrational; and convert between fractions and terminating decimals. Level 1 -Students should be able to identify square roots of numbers less than 100; identify pi as not rational; and understand that every rational number has a decimal expansion. Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.G.B Work with radicals and exponents. 8.EE.A Level 4 -Students should be able to apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system in 3D. Level 3 -Students should be able to apply the Pythagorean theorem to determine the unknown side lengths of right triangles and to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system in two dimensions. Level 2 -Students should be able to apply the Pythagorean theorem to determine whether or not a given triangle is a right triangle, given its side lengths. They should be able to find the distance between two points on a horizontal or vertical line in a two-dimensional coordinate system. Level 1 -Students should be able to identify the hypotenuse and the legs of a right triangle given the side lengths or an image of a right triangle. Level 4 -Students should be able to use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for realistic measurements, solve binomial quadratic and cubic equations, and represent the solution as a square or cube root, respectively. Level 3 -Students should be able to identify that the square root of 2 is irrational, calculate or approximate the square or cube of a rational number, solve quadratic and cubic monomial equations, and represent the solution as a square or cube root, respectively. They should be able to work with and perform operations with scientific notation and work with and apply the properties of integer exponents in order to produce or identify equivalent numerical expressions. Level 2 -Students should be able to identify and calculate the cube root of familiar perfect cubes and calculate the cube of integers. They should be able to use appropriate tools (e.g., calculator, pencil and paper) to translate large or small numbers from scientific to standard notation. They should be able to work with and apply the properties of integer exponents of degree 2 or less in order to produce or identify equivalent numerical expressions. Level 1 -Students should be able to identify and calculate square roots of familiar perfect squares and calculate the square of integers. They should be able to translate between standard form and scientific notation. (slightly modified) * Students will not be able to reach advanced in Looking for Pythagoras under clusters 8.EE.A. Day 1 - Launch of book and 1.1 Day 2 - 1.2 Suggested Ace Suggested Ace Day 6 - 2.2 finish and CFA Day 11 - 3.1 Suggested Ace Day 3 - 1.3 - CFA 1.3 Suggested ACE: 15-25 (labsheet) Day 4 - Reflection -Pass back CFA - 2.1 Day 5 - 2.2 Day 7 Day 8 - 2.3 Review Volume - CFA 2.3 2.4 Suggested ACE: pg. 24 #7-34 ? Day 9 - Reflection/ Review Day 10 -Quiz Day 12 - 3.1 Day 13 - 3.2 Day 14 3.3 Day 15 3.4 Suggested Ace Day 16 Differentiation day Day 17 Quiz Day 18 4.1 Day 19 - 4.1 Suggested Ace: Day 20 -4.2 Suggested Ace: Day 21 - 4.3 Day 22 - 4.4 Day 23 Reflection Review Day 24 - Unit Test Day 25