UNIT 8 OVERVIEW
advertisement

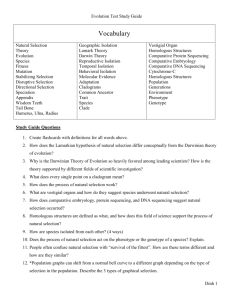
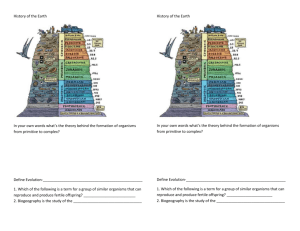
UNIT 8 EVOLUTION OVERVIEW Biology Textbook: Chapters 14 - 16 Essential Terms: Definitions- Know what the term means and be able to use this information to apply the term to various circumstances. A. B. C. D. E. Evolution Theory Fossil Artificial selection Struggle for existence F. Fitness G. H. I. J. Adaptation Survival of the fittest Natural selection Homologous structure K. Analogous Structure L. Vestigial organ M. Common descent N. Descent with modification O. Genetic Drift P. Gene Flow Q. Embryology R. Species What I Need to Know/Be able to do: 1. Know the Theory of Evolution = species have changed gradually over time 2. Be familiar with the history of Earth, “primordial soup”, and eras of that time period. Know earliest life forms they believe were similar to bacteria and then know how life gradually changed overtime into how we know Earth today: (From Heterotrophs Autotrophs more complex organisms). 3. Know the 4 types & definitions of Indirect Evidence for the Theory of Evolution: Fossil Record, Comparative Anatomy, Comparative Embryology, & Comparative Biochemistry. Know how to read and compare these types of evidence and their examples. 4. Know the 1 type and definition of the Direct Evidence for the Theory of Evolution: Current Observations 5. Know what Fossils are and how to read what layers of sediment are oldest vs youngest = Relative Dating = Law of Superposition 6. Know the Definitions, examples of each, and how to compare the following anatomical structures: 1. Homologous Structures, 2. Analogous Structures, & 3. Vestigial Structures 7. Know that DNA is the MOST RELIABLE form of evidence when comparing ancestral history. 8. Know that each generation of an organism in a population shows some type of variation due to any of the following & know how to evaluate their effects: 1. mutations, 2. genetic recombination in meiosis, 3. Genetic Drift, & 4. Gene Flow 9. Know Lamark and his early theories and beliefs: 1. Theory of Use and Disuse & 2. Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics 10. Know Charles Darwin and His Theory of Natural Selection (“survival of the fittest) = opposed Lamark. 12. Know Charles Darwin traveled the world on the HMS Beagle and be familiar with his findings and work from his book The Origin of Species. 13. Be familiar with Darwin’s Finches example and why he saw the different morphological changes in beaks be able to apply this concept to the Theory of Natural Selection in different Examples. 14. Know that all organisms originate from a COMMON ANCESTOR. 15. Know the evolution of a new species = SPECIATION. Know the following causes of speciation and their definitions: 16. Geographic Isolation, 2. Reproductive Isolation, & 3. Polyploid Speciation 17. Know what the bottleneck effect is and how it affects evolutionary mechanisms. 18. Know individuals DO NOT evolve but POPULATIONS EVOLVE over time. 19. Know Divergent vs. Convergent evolution 20. Know mimicry vs. camouflage 21. Know the following types of selections: 1. Artificial, 2. Sexual, 3. Directional, 4. Diversifying, 5. Stabilizing 22. Know what a cladogram is and how to read one. UNIT 8 EVOLUTION OVERVIEW Biology Textbook: Chapters 14 - 16 Essential Terms: Definitions- Know what the term means and be able to use this information to apply the term to various circumstances. A. B. C. D. E. Evolution Theory Fossil Artificial selection Struggle for existence F. Fitness G. H. I. J. Adaptation Survival of the fittest Natural selection Homologous structure K. Analogous Structure L. Vestigial organ M. Common descent N. Descent with modification O. Genetic Drift P. Gene Flow Q. Embryology R. Species What I Need to Know/Be able to do: 1. Know the Theory of Evolution = species have changed gradually over time 2. Be familiar with the history of Earth, “primordial soup”, and eras of that time period. Know earliest life forms they believe were similar to bacteria and then know how life gradually changed overtime into how we know Earth today: (From Heterotrophs Autotrophs more complex organisms). 3. Know the 4 types & definitions of Indirect Evidence for the Theory of Evolution: Fossil Record, Comparative Anatomy, Comparative Embryology, & Comparative Biochemistry. Know how to read and compare these types of evidence and their examples. 4. Know the 1 type and definition of the Direct Evidence for the Theory of Evolution: Current Observations 5. Know what Fossils are and how to read what layers of sediment are oldest vs youngest = Relative Dating = Law of Superposition 6. Know the Definitions, examples of each, and how to compare the following anatomical structures: 1. Homologous Structures, 2. Analogous Structures, & 3. Vestigial Structures 7. Know that DNA is the MOST RELIABLE form of evidence when comparing ancestral history. 8. Know that each generation of an organism in a population shows some type of variation due to any of the following & know how to evaluate their effects: 1. mutations, 2. genetic recombination in meiosis, 3. Genetic Drift, & 4. Gene Flow 9. Know Lamark and his early theories and beliefs: 1. Theory of Use and Disuse & 2. Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics 10. Know Charles Darwin and His Theory of Natural Selection (“survival of the fittest) = opposed Lamark. 12. Know Charles Darwin traveled the world on the HMS Beagle and be familiar with his findings and work from his book The Origin of Species. 13. Be familiar with Darwin’s Finches example and why he saw the different morphological changes in beaks be able to apply this concept to the Theory of Natural Selection in different Examples. 14. Know that all organisms originate from a COMMON ANCESTOR. 15. Know the evolution of a new species = SPECIATION. Know the following causes of speciation and their definitions: 16. Geographic Isolation, 2. Reproductive Isolation, & 3. Polyploid Speciation 17. Know what the bottleneck effect is and how it affects evolutionary mechanisms. 18. Know individuals DO NOT evolve but POPULATIONS EVOLVE over time. 19. Know Divergent vs. Convergent evolution 20. Know mimicry vs. camouflage 21. Know the following types of selections: 1. Artificial, 2. Sexual, 3. Directional, 4. Diversifying, 5. Stabilizing 22. Know what a cladogram is and how to read one.