Subject Knowledge Audit – Primary Computer Science
advertisement

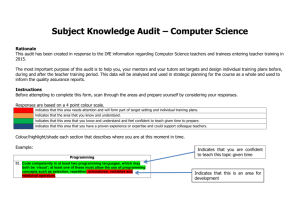
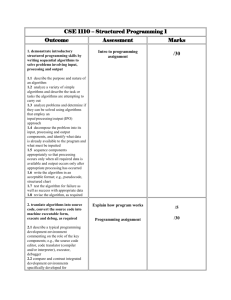
Subject Knowledge Audit – Primary Computer Science Rationale This audit has been created in response to the DfE information regarding Computer Science teachers and trainees entering teacher training. The most important purpose of this audit is to help you, your mentors and your tutors set targets and design individual training plans before, during and after the teacher training period. This data will be analysed and used in strategic planning for the course as a whole and used to inform the quality assurance reports. Instructions Before attempting to complete this form, scan through the areas and prepare yourself by considering your responses. Responses are based on a 4 point colour scale. indicates that this area needs attention and will form part of target setting and individual training plans. indicates that the area that you know and understand. indicates that this area that you know and understand and feel confident to teach given time to prepare. indicates that this area that you have a proven experience or expertise and could support colleague teachers. Colour/highlight/shade each section that describes where you are at this moment in time. Example: Programming B1. Code competently in at least two programming languages, which may both be ‘visual’; at least one of these must allow the use of programming concepts such as selection, repetition, procedures, variables and relational operators. Indicates that you are confident to teach this topic given time Indicates that this is an area for development Once you have identified the areas for development, create an action plan using the Subject Knowledge: Computing Action Plan as a template. You will need to copy the relevant statements from this audit to the Area for Improvement column and set yourself a SMART target to develop and enhance your subject knowledge in this particular area. As shown below: Computers & Social Informatics D1. Explain what a computer is and give examples of devices that include computers Communications and the Internet E1. Explain what the World Wide Web and the Internet are, and the difference. C2. Explain how the same binary data can be interpreted in different ways e.g. an 8-bit value could be a character or a number. D2. Explain and describe the key characteristics of basic computer architecture (eg CPU, memory, hard disk, mouse, display etc) . E2. Outline the key features of the World Wide Web and their relationships– eg browsers, URLs, navigation methods C3. Explain how the same information can be represented in a computer in a variety of ways e.g. sound as mp3 or MIDI. D3. Explain why there are sometimes different operating systems and application software for the same hardware. E3. Outline how data are transported on the Internet, including packets and the notion of a protocol. Range and Content Algorithms Programming Data Training as a primary teacher you should know, understand and be able to: A1. Explain that an algorithm is a precise way of solving a problem which can be followed by humans and computers. B1. Code competently in at least two programming languages, which may both be ‘visual’; at least one of these must allow the use of programming concepts such as selection, repetition, procedures, variables and relational operators. C1. Explain how computers represent all data in binary, with a variety of examples: unsigned integers, text representation (e.g. ASCII), different sound file data/types, and different graphics data/file types. A2. Give examples algorithms met everyday life. of in B2. Explain and use programming concepts such as selection, repetition, procedures, variables, and relational operators. A3. Explain that computers need more precise instructions than humans and the need for precision to avoid errors. B3. Review and assess the quality of code. Find and correct errors in syntax and meaning. Training as a primary Computer Science specialist, you should know, understand and be able to: B1. Range and Content Training as a primary teacher you should know, understand and be able to: Training as a primary Computer Science specialist, you should know, understand and be able to: Algorithms Programming Data A4. Explain and show how B4. Explain that computers algorithms can use are controlled by selection (if), sequences of precise repetition (loops), instructions known as procedures (sub programs algorithms within an algorithm). C4. Explain that data can have errors, how this might affect results and decisions based on the data and how errors can be reduced. A5. Explain the need for B5. Explain that computers accuracy of follow instructions/ algorithms. blindly; hence the need for care and precision. C5. Explain the need for and content of the Data Protection Act, Computer Misuse Act and Copyright legislation (and other relevant legislation). A6. Distinguish between an algorithm and the programs that implements that algorithm B6. Represent algorithmic steps in multiple programming languages (e.g. logo, Scratch). Computers & Social Informatics D4. Explain and use common troubleshooting techniques. Communications and the Internet E4. Explain the role of search engines and what happens when a user requests a web page in a browser. D5. Explain Moore’s Law and multitasking by computers. E5. Explain the technological perspective on safety and security. D6. Discuss social and ethical issues raised by the role of computers in the world. B7. Explain how and use programs to simulate environments to test hypothesis. D7. Explain the importance of humancomputer interface design B8. Explain and show how programs can be planned, tested and corrected and documented B9. Explain how HTML constructs the rendering of a web page D8. Discuss career paths for those studying Computing.