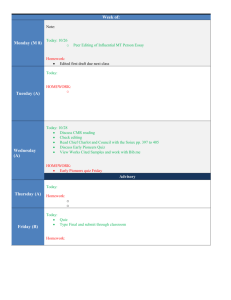
Block Environmental Science Pacing Guide
advertisement

Environmental Science Pacing Guide 2015-16 (Block) Week Standards (SEV) 1 1a, 1b 2 1d, 1e 3 2a, 2b 4 2c, 2d 5 3a, 3b, 3c 6 3d, 3e 7 4a, 4b Topics Covered 1a. Matter is recycled - biogeochemical cycles (H, N, P, O, C), Energy is not recycled Quiz 1 1b. Energy loss in food chains/webs through trophic levels due to entropy (10% rule) Quiz 2 (Week 2 should build on concepts from week 1) 1d. Relate cycling of matter and flow of energy to laws of conservation of mass and energy. Emphasize role of decomposers. Loop food webs. Quiz 3 1e. Distinguish between biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem, and describe how energy and matter move between these. Test 1 2a. Describe how abiotic components affect the biosphere. 2b. Describe levels of organization within the biosphere (organism, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere). Include which contain biotic and abiotic factors. Practice identification and distinguishing between biotic and abiotic factors. Quiz 4 2c. Characterize the factors that define a biome Abiotic Factors – to include precipitation, temperature, and soils. Biotic Factors – plant and animal adaptations that create success in that biome. Quiz 5 2d. Characterize the components that define fresh-water and marine systems. Abiotic Factors – to include light, dissolved oxygen, phosphorus, nitrogen, pH and substrate. Biotic Factors – plant and animal adaptations characteristic to that system. Test 2 3a. Describe interconnections between abiotic and biotic factors. (Loop concepts in weeks 2-4), climate change (include current events) Current Article Analysis as Quiz 6 3b. Primary & Secondary Succession, describing changes in biomass, diversity, and complexity/stability 3c. Traumatic events and succession: fires, floods, storms, earthquakes, etc… Refresh that early stages of primary succession are most sensitive. Quiz 7 3d. Explain how biotic and abiotic factors influence populations: density dependent/independent limiting factors, niche restriction, human activity, and… 3e. Interactions between individuals both interspecific and intraspecific: mutualism, commensalisms, parasitism, predation, and competition. Quiz 8 Test 3 4a. Differences between renewable and nonrenewable resources (especially energy): production, rates of use, renewal rates, limitations of resources (pollution, availability, damage to ecosystems) 4b. Describe how technology is increasing the efficiency and utilization of these resources. (Jevon’s paradox, hydraulic fracturing) Quiz 9 or Article Current Article Analysis as Quiz 9 Environmental Science Pacing Guide 2015-16 (Block) 8-9 10 4e, 4f 4c, 4d, 1c 11 12 4a, 4b, 4e, 4f, 5e 13 5a, 5b 14 5c, 5d 15 5f 4e. Describe the required technology, availability, and pollution/implementation problems of nonrenewable energy resources (fossil fuels, nuclear power) and renewable/alternative fuels (wind, solar, ethanol, etc…). Find new articles. Renewable energy has progressed well beyond what’s in the book. 4f. Describe the need for informed decision making for resource use (energy and water usage, allocation, conservation Quiz 10 or Article Current Article Analysis as Quiz 10 (Must be inverse of Quiz 9 assignment) Paper as Test 4 (based on resource consumption in Richland Reservoir project) 4d. Relationship of energy consumption and living standards (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/worldbalance/material.html) 1c.Relate food production and quality of nutrition to population growth and the trophic levels 4c. Impact of energy use and waste production on environment, focusing on positive steps that individuals and businesses can engage in to diminish these effects. Students should connect cause and effects when describing these actions. Quiz 11 (Given problems, students provide solutions) Water pollution – point-source vs nonpoint-source pollution, causes of these pollutants, and the effects on both natural ecosystems and human health Quiz 12 Air Pollution – primary vs secondary pollution (smog, ground level ozone, & acid rain), ozone depletion, indoor air pollutants, noise, and light pollution, causes of these pollutants, and the effects on both natural ecosystems and human health Quiz 13 Test 5 5a. Describe factors of exponential and logistic population growth on all organisms, including humans. Relate these to growth rates, carrying capacity, and population crashes. Article Analysis as Quiz 14 5b. Describe the effects of population growth, demographic transitions, cultural differences, emergent diseases, etc. on societal stability. Quiz 15 5c. Describe how human activities affect global and local sustainability through the lens of topics covered throughout standards 4 and 5, focusing on… 5d. The actual and potential effects of habitat destruction (loss of biodiversity, extinction), erosion/depletion of soil (loss of arable land exacerbated by urban sprawl and deforestation) Quiz 16 Test 6 5f. Describe how political, legal, social, and economic decisions may affect global and local ecosystems. (Since this standard is so broad, it serves as an excellent opportunity to revisit a topic of interest or one that you felt did not receive adequate attention Revisit Reservoir Papers to examine the influence of these elements on the progress of the Richland Creek Reservoir Project (Presentation as Test 7) Summary 22 Formative Grades 16 Quiz Grades o 13 quizzes, o 3 article analyses 6 Notebook Grades 7 Summative Grades 5 Tests 1 research paper 1 project