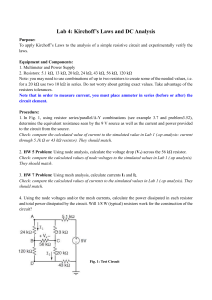
Mixed Series-Parallel Combination
advertisement

Characteristics of Series and Parallel Circuits In this laboratory exercise you will measure the characteristic voltages and currents in series, parallel, and mixed series-parallel circuits. You will compare your experimental results with the formulas and principles that govern those circuits. 1. You will be using three resistors whose marked values are: 𝑅1 = 220 Ω, 𝑅2 = 330 Ω, and 𝑅3 = 470 Ω. Use your multimeter to measure the resistance of each of these resistors. Note units carefully, and write your results with units in the table provided. Series Combination On the attached, sheet find the diagram of a series combination of three resistors with several labeled points identified. A series combination like this can be included as part of a more complex circuit. The equivalent resistance of a series combination is given by the formula𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 + 𝑅3 . If a power supply is connected across the points F and E a the resulting circuit will have the following properties. 2a) b) I. The current will be the same throughout the circuit II. The sum of the voltages across the three resistors the same as the voltage across points F and E. Use the formula for equivalent resistance to calculate the equivalent resistance of your three resistors. In doing the calculation use your measured values rather than the marked values. Show your work Now wire your three resistors into a series combination on your breadboard. Let your instructor check the circuit if you have any doubts. Use the multimeter to measure the equivalent resistance. Now connect a power supply across points F and E and set it accurately to 5.00 V. Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to point F. You may need to readjust the 5.00 V voltage to that value from time to time. 3a) Use your multimeter to measure the currents at points A, and B. Be careful to read the units correctly and indicate the direction of the current at each of the point. b) What current would you expect to measure at points C and D. What directions do you expect? Explain your reasoning. Use your multimeter to check. Let you instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. In a previous experiment you used a multimeter to measure the voltage difference across a resistor. Here are some more details. Every point of a circuit has a voltage, and a voltmeter can be used to measure the difference in voltage between any two points in a circuit. To be specific, when used as a voltmeter, the number displayed on the multimeter is the voltage at the point connected to the 𝑉Ω terminal minus the voltage at the point connected to the COM terminal. That number may be positive or negative. Voltage reading = 𝑉VΩ − 𝑉COM 4a) b) 5. Rotate your multimeter dial into the voltage range, and measure the voltage differences indicated. What voltages differences would you expect to measure across the points indicated? Explain your reasoning in each case. Then make measurements and let you instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. You should expect that the equivalent resistance of your series combination will follow Ohm’s law, 𝑉𝐹𝐸 = 𝐼𝑅𝑒𝑞 . Use your experimental values for those three quantities to check that result. Parallel Combinations On the attached sheet find the diagram of three resistors in series with several points identified with letters. A parallel combination like this can be included as part of a more complex circuit. When resistors are configured in parallel they have an equivalent resistance given by 1 𝑅𝑒𝑞 1 1 1 =𝑅 +𝑅 +𝑅 . 1 2 3 If a power supply is connected across points G and H the resulting circuit will have the following properties. 6a) b) I. The sum of the currents through the resistors is the same as the current at points G or H, II. The voltage across each of the resistors is the same as the voltage across points G and H. Use the formula to calculate the equivalent resistance of your three resistors in parallel. In doing the calculation use your measured values rather than the marked values. Now wire your three resistors into a parallel combination on your breadboard. Use the multimeter to measure the equivalent resistance and compare with your calculated value. Connect the power supply across points G and H and set it accurately to 5.00 V. Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to point G. You may need to readjust the 5.00 V voltage to that value from time to time. 7a) Measure the voltage across the points indicated. b) Try to anticipate what voltage will be measured across the points indicated. Explain your reasoning in each case. Then measure. Let your instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. 8a) Measure the currents at the points indicated and indicate the direction of the currents at those points. Take care about units. b) What currents would you expect to be measured at the points indicated. Explain your reasoning in each case. Then measure. Let your instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. You should expect the equivalent resistance of your parallel combination will follow Ohm’s law, 𝑉𝐺𝐻 = 𝐼𝐺 𝑅𝑒𝑞 . Use your experimental values for those three quantities to check that result. 9. Mixed Series-Parallel Combinations On the attached sheet, find the diagram of a mixed series-parallel combination. Combinations like this can be included as part of a more complex circuit. The effective resistance of combinations like this can be found by repeated application of the series and parallel formulas for equivalent resistance. If a power supply is connected across points A and D the voltages and currents in the various resistors can be found by application of the loop and junction rules. 10a) b) Use the series and parallel formulas to calculate the equivalent resistance of your three resistors in this combination. In doing the calculation use your measured values of resistance rather than the marked values. Now wire your three resistors on your breadboard. Use the multimeter to measure the equivalent resistance. Connect the power supply across points A and D and set it accurately to 5.00 V. Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to point A. You may need to readjust the 5.00 V voltage to that value from time to time. 11a) b) Use your multimeter to measure the voltage differences indicated. What voltage differences do you expect across the points indicated. Explain your reasoning in each case. Then measure the voltages to check. Let your instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. 12a) b) Use your multimeter to measure the currents at the points indicated. What currents would you expect to be measured at the points indicated. Explain your reasoning in each case. Then measure the currents to check. Let your instructor know if your measurements differ from your expectations. 13. Based on your data, what are the currents through the three resistors? 14. You should expect the equivalent resistance of your mixed combination will follow Ohm’s law, 𝑉𝐴𝐷 = 𝐼𝐷 𝑅𝑒𝑞 . Use your experimental values for those three quantities to check that result. Series and Parallel Combinations of Resistors 1. Marked Resistance Measured Values 𝑅1 = 220 Ω 𝑅2 = 330 Ω 𝑅3 = 470 Ω Series Combination 2a) Calculated equivalent resistance: ______________________ Show your work b) Measured equivalent resistance: _______________________ 3a) b) 𝐼𝐴 = _____________________ Direction (Circle one.) toward B away from B 𝐼𝐵 = _____________________ Direction (Circle one.) toward C away from C 𝐼𝐶 = _____________________ Explain your reasoning. Direction (Circle one.) toward D away from D 𝐼𝐷 = _____________________ Explain your reasoning. Direction (Circle one.) toward E away from E Your expectations 4a) 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐵 = ______________________________ 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐶 = ______________________________ 𝑉𝐶 − 𝑉𝐷 = ______________________________ b) 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐷 = ______________________________ Explain your reasoning. 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐶 = ______________________________ Explain your reasoning. 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐹 = ______________________________ Explain your reasoning. 5. Measured value of 𝑉𝐹𝐸 ______________________________________ Measured I times measured 𝑅𝑒𝑞 __________________________ Parallel Combination 6a) Calculated equivalent resistance: ______________________ Show your work. b) Measured equivalent resistance: _______________________ 7a) 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐵 = ________________________________ 𝑉𝐶 − 𝑉𝐷 = ________________________________ b) 𝑉𝐸 − 𝑉𝐹 = ________________________________ Explain your reasoning. 𝑉𝐸 − 𝑉𝐷 = ________________________________ Explain your reasoning. 𝑉𝐻 − 𝑉𝐶 = ________________________________ Explain your reasoning. 8a) b) 9. 𝐼𝐴 = _____________________________________ Direction: toward B away from B 𝐼𝐶 = _____________________________________ Direction: toward D away from D 𝐼𝐸 = _____________________________________ Direction: toward F away from F 𝐼𝐺 = _____________________________________ Direction: Explain toward H Measured value of 𝑉𝐺𝐻 ______________________________________ Measured IG times measured 𝑅𝑒𝑞 __________________________ away from H Mixed Series-Parallel Combination 10a) Calculated equivalent resistance: ______________________ Show your work b) Measured equivalent resistance: _______________________ 11a) 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐵 = _____________________________________ 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐶 = _____________________________________ b) 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐶 = _____________________________________ Explain your reasoning 𝑉𝐸 − 𝑉𝐷 = _____________________________________ Explain your reasoning 12a) 𝐼𝐴 = ___________________________________________ 𝐼𝐵 = ___________________________________________ 𝐼𝐶 = ___________________________________________ b) 𝐼𝐸 = ___________________________________________ Explain your reasoning 𝐼𝐷 = ___________________________________________ Explain your reasoning 13. 𝐼𝑅1 = ___________________________________________ 𝐼𝑅2 = ___________________________________________ 𝐼𝑅3 = ___________________________________________ 14. Measured value of 𝑉𝐴𝐷 ______________________________________ Measured IA times measured 𝑅𝑒𝑞 __________________________ Series Combination Parallel Combination Mixed Series-Parallel