Name: Date: Period: ______ Chapter 11.2: Fossil Fuels Fossil Fuels
advertisement

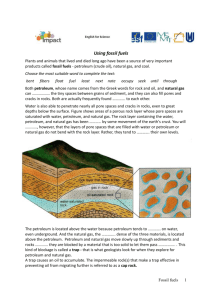
Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ Chapter 11.2: Fossil Fuels 1. Fossil Fuels a. ________ formed from the remains of ____________ organisms, such as ________, ___________________, and ______________ gas. b. __________ fuels consist primarily of ____________________ called ___________________________. i. Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of _________ of carbon and __________________. 1. These __________________ contain ________________ originally obtained from __________________ by plants and animals that lived _________________ of years ago. 2. When _______________________ are burned, energy is _______________ as heat and ________ that we can use. 2. Formation of Coal a. ____________ is a dark colored, _____________ rock formed from __________________ and __________________ changes of plant material over ______________ of years. b. ______________________ is the process by which ______________ decomposed _________ and other plants are buried in ______________ mud and transformed into ______________. i. The process of _____________________ occurs when bacteria ______________ the plant material and release ____________ and carbon dioxide ______. When these gases _____________ the swamp, only the ______________ is left. 3. Types of Coal a. ________ is the partial ______________________ of brownish–black plant remains. Peat is the ________________ that all ___________ is formed from. b. The ____________ main types of coal are _____________________, ________________________, and _________________________. i. ____________ is the first type of __________ formed from the __________. As layers of __________________ cover the peat, depleting the ______________ so decomposition can’t continue, they cause ______________, which squeeze out the ______________ and _______, which then becomes a denser, ______________ lignite. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ 1. ___________________________ coal, also called black ____________, is generally dark brown to ___________ coal, and falls between lignite and bituminous ________. ii. The added ________________ of more ___________________ sediments further ___________________ the lignite to form bituminous coal, or __________ coal. 1. Bituminous __________ is the most ______________ type of coal. iii. Where the ______________ of the earth’s crust ____________ extremely high ____________________ and ______________, bituminous coal is changed into _______________, the hardest of all coal. iv. Bituminous coal and anthracite consists of _____ to ____ carbon, which makes them a great ______________ resource. 4. Petroleum and Natural Gas a. ______________ and natural ______ are mixtures of ____________________. i. Petroleum _____ consists of _______________ hydrocarbons. ii. _______________ gas consists of ___________ hydrocarbons. b. Formation of petroleum and Natural Gas i. When ________________________ died in shallow prehistoric ___________ and ______________, their remains accumulated on the ocean floor and lake _______________ which were then covered and buried by ___________________. ii. As the amount of sediments ________________, so did the __________ and ______________ on the microorganisms. This added __________ and pressure was enough to cause a ______________ change to form petroleum and natural gas. 5. Petroleum and Natural Gas Deposits a. Sedimentary _________ has many _______________ spaces between the rock _________________. This allows ______________ and gases to flow ___________ through the rock. b. As sedimentary __________ becomes deeply ______________ under overlying sediments, ________________ increases. This increasing pressure causes the ___________ and ____________________ out of the rock and up through the layers of __________________ rock until they come to a layer of _________________________ rock. i. This impermeable __________ of rock is called ______ rock. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ c. The ____________, _____, and natural gas separate under the ______ rock due to their _________________. Natural gas is _____ dense, then oil, then water. d. Rock that _____________ can easily ___________ through is called _____________________ rock. e. Rock that liquids ____________ easily flow through is called ______________________ rock. f. ____________ oil is unrefined _____ and has many uses. g. _________________________ are chemicals derived from _________________ and are the main component in over _________ products. i. These products include ________________, synthetic fabrics, ________________, tars, waxes, synthetic ________________, insecticides, chemical ____________________, detergents, and ____________________. 6. Fossil Fuel Supplies a. Fossil _________ are a _____________________________ resource. b. __________ is the most abundant __________ fuel in the word, occurring on every _______________________. i. While coal is very __________________, scientists predict that world wide coal _____________ will only last another _______ years. ii. However, _________________ of it are deposited in ________ countries: the ______, ____________, and _____________. c. Scientists estimate that _____ of all the ________________ in the US has already been __________________, however, much of the undiscovered _____________ is thought to be under the ___________ floor along the edges of North __________________. 7. Fossil Fuels and the Environment a. The use of any __________ fuels has an _______ on the environment. i. Strip mining 1. __________ mining coal leaves deep _______________ where coal is __________________. 2. ____________ and _______________ that are displaced to expose the coal are left in _______ slopes, and without plants and topsoil to ______________ it, the exposed land will ________________ away. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ 3. ______ rocks that are exposed during __________ can give off acids. a. These _________ can be carried to nearby ______ and streams causing ___________ to aquatic life. 4. Since _________ mining can be so _________________ to the environment, the US _____________________ has place many regulations to __________________ and/or ________________ the damaging of our environment. ii. Air Pollution 1. The ________________ of any fossil fuel ____________ pollution in the _____. While some fuels may be ______ damaging such as _______________ gas, they do still __________________ the environment. a. Much of this _____ pollution can contribute to ___________ rain iii. Spills 1. Fossil fuel _____________ happen rarely, but have a _______________ and sudden _______________ on the environment when they do. a. Examples include spills from _______, ________________, and ____________________.