Name
advertisement

Algebra 1
Name: _____________________________
Chapters 1 and 3
Unit rates, rate conversions, intro to functions, graphing linear equations, direct variation
Test review
Rates and unit rates
Unit conversions:
Convert the following quantities. Round to the nearest hundredth.
15. 25 miles per hour into feet per second
16. 110 feet per second into miles per hour
17. 48 yards per week into inches per hour
18. 550 lbs per week into ounces per hour
19. 63 inches per second into miles per day
20. 300 gallons per week into quarts per hour
Section 1.7: Representing functions as rules and tables
Tell whether the pairing is a function. If it is, state the domain and range.
21.
22.
23.
Input
Output
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
4.3
4.2
4.1
Input Output
25
14
30
13
30
12
35
11
Function
Not a function
Function
Not a function
Input Output
0.2
1.5
0.4
1.25
0.6
1.5
0.8
1.25
Function
Not a function
Domain: _________________
_________________
_________________
Range:
_________________
_________________
_________________
24. A baker has baked 10 loaves of bread so far today and plans on baking 3 loaves more each
hour for the rest of his shift. Write a rule for the total number of loaves baked as a function
of the number of hours left in the baker’s shift. Identify the independent and dependent
variables. How many loaves will the baker make if he has 4 hours left in his shift?
Section 1.8: Representing functions as graphs
25. Graph the function y 4 x 3 with domain {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
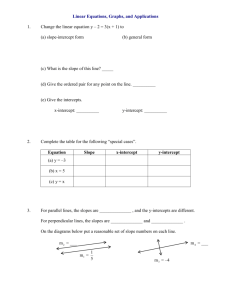
Section 3.2: Graphs of linear equations
Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the equation:
26. 5 x y 18 ; 5, 7
27. 7 x y 10 ;
1, 17
28. 2 x 6 y 14 ; (5, 4)
Tell whether the point lies on the graph of the line:
29. 2 x y 10 ; 4, 18
30. x 3 y 12 ;
6, 2
31. x 2 ; (0, 2)
Section 3.3: Graph linear equations using intercepts
Identify the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the graph.
32.
33.
The x-intercept is _____, which corresponds
The x-intercept is _____, which corresponds
to the point __________.
to the point __________.
The y-intercept is _____, which corresponds
The y-intercept is _____, which corresponds
to the point __________.
to the point __________.
Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of the equation. Graph the equation using
the x-intercept and y-intercept.
34. 6 x 3 y 18
35. 6 x 4 y 48
36. 4 x 9 y 16
x-intercept: __________
__________
__________
y-intercept: __________
__________
__________
Section 3.4: Find slope and rate of change
Find the slope of the line that passes through the points.
38. (5, 2) and (5, 8)
37. (7, 1) and (1, 5)
39. (5, 4) and (1, 2)
Find the value of x or y so that the line passing through the two points has the given slope.
40. (1, 4), ( x, 3), m
1
5
41. ( x, 8), (2, 1), m 3
42. (8, 1), (2, y ), m
3
5
For the following graphs,
a. state whether the slope is positive, negative, 0, or undefined and
y y
b. find the slope of the line using m 2 1 .
x2 x1
43.
44.
46. Given the equation of the line y 3 .
45.
47. Given the equation of the line x 5
a. What are the slope and the
y-intercept of this line?
a. What are the slope and the
y-intercept of this line?
b. Graph the line.
b. Graph the line.
Section 3.5: Graph using slope-intercept form
Rewrite the equations in slope-intercept form by solving for y. Then identify the slope and
the y-intercept of the graph of the equation.
48. 12 x 3 y 9
49. 8 x 4 y 1
50. 6 x 2 y 2
__________
__________
__________
y-intercept, b: __________
__________
__________
slope, m:
51.
5x 5 y 3
slope, m:
52. 4 x 6 y 2
53. 16 y 4
__________
__________
__________
y-intercept, b: __________
__________
__________
Tell whether the graphs of the two equations are parallel lines. Explain your reasoning.
54. y 5 x 7 and 5 x y 4
55. 6 x 2 y 10 and 3 x y 10
Graph the equations using the slopes and y-intercepts.
56. y
3
x6
4
57. y
3
x2
2
59. y
3
x2
2
60. y 1
58. y
4
x2
3
61. x 7
y
x
Answers:
15 dollars
2 inches
10 dollars
, $2.50/book ; 2.
, 0.29in./hr ;
, $1.43/chocolate bar ; 3.
6 books
7 hours
7 chocolate bars
15 dollars
40 dollars
12 dollars
4.
, $6.67/ticket ; 6.
, $1.20/battery ;
, $1.88/pencil ; 5.
6 tickets
10 batteries
8 pencils
150 miles
25 dollars
160 dollars
7.
, $40/calculator ; 9.
, 21.43 mi/gal ; 8.
, $4.17/yard ;
4 calculators
7 gallons
6 yars
9 dollars
10.
, $3.00/can ; 11. B; 12. D; 13. C; 14. A; 15. 36.67 ft/sec; 16. 75 mi/hr;
3 cans
17. 10.29 in./hr; 18. 52.39 oz/hr; 19. 85.91 mi/day; 20. 7.14 qt/hr; 21. Not a function;
22. Function, domain: {5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4}, range: {4.1, 4.2, .43};
23. Function, domain: {0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8}, range: {1.25, 1.5}
24. y 10 3 x , independent: number of hours left in shift, dependent: number of loaves baked,
The baker can make 22 loaves if he had 4 hours left in his shift.;
26. no; 27. yes; 28. yes; 29. yes; 30. no; 31. no;
25.
32. 3 , ( 3 , 0); 1, (0, 1); 33. 1, (1,0); 5, (0,5);
1.
34. 6 or (6, 0), 3 or (0, 3)
35. 8 or (8, 0) , 12 or (0, 12)
36. 4 or (4, 0),
16
16
or 0,
9
9
1
1
; 38. m is undefined ; 39. m ; 40. x 6 ; 41. x 1 ; 42. y 7 ;
3
2
4
1
43. positive, m ; 44. negative, m ; 45. 0
3
3
46. a. m 0, b 3 ; b. The graph is a horizontal line through (0, 3).
47. a. The slope is undefined; no y-intercept. b. The graph is a vertical line through (5, 0) .
1
1
48. y 4 x 3, m 4, b 3 ; 49. y 2 x , m 2, b ; 50. y 3x 1, m 3, b 1 ;
4
4
3
3
2
1
2
1
51. y x , m 1, b ; 52. y x , m , b ;
5
5
3
3
3
3
37. m
1
1
, m 0, b ; 54. Not parallel; slopes are different; 55. Parallel; same slopes
4
4
and different y-intercepts;
56.
57.
58.
53.
54.
53. y
59.
60.
61.