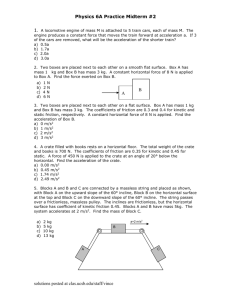
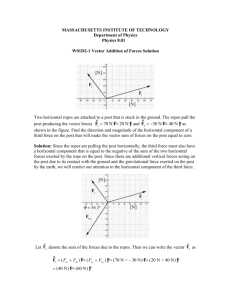
1) In a collision between a huge SUV and a small hybrid car, the
advertisement

1) In a collision between a huge SUV and a small hybrid car, the SUV exerts a larger force on the hybrid than the hybrid exerts on the SUV. A) True B) False C) It depends on whether the collision is a head-on collision or a rear-end collision. 2) A box is placed on a table which rests on the floor. The box pushes on the table; the reaction force to the box's push on the table is the table's push on the floor. A) True B) False 3) A girl attaches a rock to a string, which she then swings counter-clockwise in a horizontal circle. The string breaks at point P in the figure, which shows a bird's-eye view (as seen from above). Which path (A-E) will the rock follow? A) Path A B) Path B C) Path C D) Path D E) Path E 4) A satellite is in orbit around the earth. Which one feels the greater force? A) the satellite because the earth is so much more massive B) the earth because the satellite has so little mass C) Earth and the satellite feel exactly the same force. D) It depends on the distance of the satellite from Earth. 5) You are in a train traveling on a horizontal track and notice that a piece of luggage starts to slide directly toward the front of the train. From this observation, you can conclude that this train is A) speeding up. B) slowing down. C) changing direction. D) speeding up and changing direction. E) slowing down and changing direction. 6) A crate is sliding down an inclined ramp at a constant speed of 0.55 m/s. The vector sum of all the forces acting on this crate must point A) down the ramp. B) up the ramp. C) perpendicular to the ramp. D) vertically downward. E) None of the above choices is correct. 7) An object is moving with constant non-zero velocity. Which of the following statements about it must be true? A) A constant force is being applied to it in the direction of motion. B) A constant force is being applied to it in the direction opposite of motion. C) A constant force is being applied to it perpendicular to the direction of motion. D) The net force on the object is zero. E) Its acceleration is in the same direction as it velocity. 8) A fireman is sliding down a fire pole. As he speeds up, he tightens his grip on the pole, thus increasing the vertical frictional force that the pole exerts on the fireman. When the force on his hands equals his weight, what happens to the fireman? A) The fireman comes to a stop. B) The fireman descends with slower and slower speed. C) The fireman descends with a smaller but non-zero acceleration. D) The fireman continues to descend, but with constant speed. E) The acceleration of the fireman is now upward. 9) Two blocks, A and B, are being pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a horizontal 100-N pull, as shown in the figure. Both of them are moving together at a constant velocity of 2.0 m/s to the right, and both weigh the same. Which of the figures below shows a correct free-body diagram of the horizontal forces acting on the upper block, A? A) B) C) D) E) 10) Two boxes P and Q on a perfectly smooth horizontal surface are connected by a light horizontal cord. The mass of P is greater than that of Q. A horizontal force is applied to box Q as shown in the figure, accelerating the bodies to the right. The magnitude of the force exerted by the connecting cord on body P is A) zero. B) less than F but not zero. C) equal to F. D) greater than F. 11) Two boxes are connected to each other by a string as shown in the figure. The 10-N box slides without friction on the horizontal table surface. The pulley is ideal and the string has negligible mass. What is true about the tension T in the string? A) T = 10 N B) T = 20 N C) T = 30 N D) T < 30 N E) T > 30 N 12) Two blocks, A and B, are being pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a horizontal 100-N pull, as shown in the figure. Both of them are moving together at a constant velocity of 2.0 m/s to the right, and both weigh the same. Which of the figures below shows a correct free-body diagram of the horizontal forces acting on the lower block, B? A) B) C) D) E) None of these diagrams is correct. 13) A push of magnitude P acts on a box of weight W as shown in the figure. The push is directed at an angle θ below the horizontal, and the box remains a rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to A) P sin θ B) P cos θ C) 0 D) P cos θ + W E) P + W 14) Two boxes P and Q on a perfectly smooth horizontal surface are connected by a light horizontal cord. The mass of P is greater than that of Q. A horizontal force is applied to box Q as shown in the figure, accelerating the bodies to the right. The magnitude of the force exerted by the connecting cord on body P is A) zero. B) less than F but not zero. C) equal to F. D) greater than F. 15) The figure shows a block of mass M hanging at rest. The light wire fastened to the wall is horizontal and has a tension of 38 N. The wire fastened to the ceiling is also very light, has a tension of and makes an angle θ with the ceiling. Find the angle θ. A) 50° B) 40° C) 33° D) 65° E) 45° 41) A very light wire is used to hang a series of 8.0-kg bricks. This wire will break if the tension in it exceeds 450 N. The bricks are hung one below the other from a hook in the ceiling using this wire, as shown in the figure. (a) How many whole bricks can be hung without breaking the wire? (b) If you add one more brick to the number found in part (a), which string will break? (a) 5 (b) the top wire 49) Three boxes rest side-by-side on a smooth, horizontal floor. Their masses are 5.0 kg, 3.0 kg, and 2.0 kg, with the 3.0-kg mass in the center. A force of 50 N pushes on the 5.0-kg box, which pushes against the other two boxes. What magnitude force does the 5.0-kg box exert on the 3.0kg box? A) 0 N B) 10 N C) 25 N D) 40 N E) 50 N Answer: C 61) A 55-kg box rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface is 0.30, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. What horizontal force must be applied to the box to cause it to start sliding along the surface? Answer: 160 N 63) An object slides on a level floor. It slows and comes to a stop with a constant acceleration of magnitude 2.4 m/s2. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the floor? A) 0.24 B) 0.48 C) 0.12 D) It is impossible to determine without knowing the mass of the object. Answer: A 85) A system consisting of blocks, a light frictionless pulley, a frictionless incline, and very light connecting wires is shown in the figure. The wires pull on the left-hand blocks parallel to the surface of the ramp. The 9.0-kg block accelerates downward when the system is released gently from rest. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the 9.0-kg block? (b) What is the tension in the wire connecting the two blocks on the incline? Answer: (a) 2.1 m/s2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. B B B C B E D D E B D B B B A (b) 42 N