Test A
advertisement

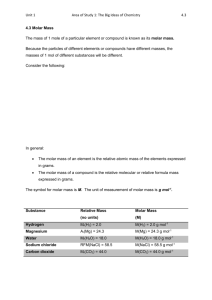
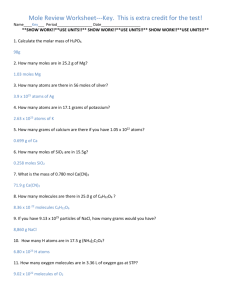
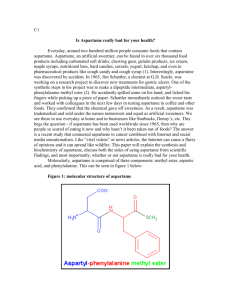
LLG Paris–Abu Dhabi Advanced Math and Science Pilot Class Academic year 2014-2015 Short Test - Chemistry Test A I. Pure substances. Data: Under atmospheric pressure and at room temperature, • Sucrose is a solid. Molecular formula: C12H22O11 • Aspartame is a solid. Molecular formula: C14H18N2O5 Aspartame is a sugar substitute 200 times sweeter than sucrose. • Olive oil is a liquid. Molecular formula: C57H104O6 Density: d = 0.92 g/mL Note: For each question, give a formula (using only letters) before calculating the value. a) Calculate the molar mass of each compound. Check that the molar mass of olive oil is 884 g.mol-1 , aspartame 294 g.mol-1 and sucrose 342 g.mol-1 b) We take a sample containing 250 mL of olive oil? What is the corresponding mass? What is the corresponding amount of substance? What is the corresponding number of C57H104O6 molecules in the sample? c) What is the mass of sucrose to be taken to get 0.1 mol of sucrose? What is the amount of substance in 6.84 g of sucrose? What is the corresponding number of sucrose molecules? d) What is the mass of aspartame needed to have the same sweetener effect as 6.84 g of sucrose? II. Solutions. a) What is the difference between aspartame as a pure substance and an aqueous solution of aspartame? b) What is the mass of aspartame to dissolve into a 500mL volumetric flask to obtain an aspartame solution whose molar concentration is 2×10-2 mol.L-1. c) Starting from this solution, what is the procedure to prepare 100 mL of aspartame solution at concentration 4×10-4 mol.L-1. d) What is the amount of substance of aspartame in 10 mL of aspartame solution at 5×10-3 mol.L-1? What is the corresponding number of aspartame molecules? Data: NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Molar mass: M (C ) = 12 g.mol-1 M (O ) = 16 g.mol-1 M (N ) = 14 g.mol-1 M (H ) = 1 g.mol-1 LLG Paris–Abu Dhabi Advanced Math and Science Pilot Class Academic year 2014-2015 Short Test - Chemistry Test B I. Pure substances. Data: Under atmospheric pressure and at room temperature, • Sucrose is a solid. Molecular formula: C12H22O11 • Aspartame is a solid. Molecular formula: C14H18N2O5 Aspartame is a sugar substitute 200 times sweeter than sucrose. • Olive oil is a liquid. Molecular formula: C57H104O6 Density: d = 0.92 g/mL Note: For each question, give a formula (using only letters) before calculating the value. a) Calculate the molar mass of each compound. Check that the molar mass of olive oil is 884 g.mol-1 , aspartame 294 g.mol-1 and sucrose 342 g.mol-1 b) We take a sample containing 500 mL of olive oil? What is the corresponding mass? What is the corresponding amount of substance? What is the corresponding number of C57H104O6 molecules in the sample? c) What is the mass of sucrose to be taken to get 0.2 mol of sucrose? What is the amount of substance in 3.42 g of sucrose? What is the corresponding number of sucrose molecules? d) What is the mass of aspartame needed to have the same sweetener effect as 3.42 g of sucrose? II. Solutions. a) What is the difference between aspartame as a pure substance and an aqueous solution of aspartame? b) What is the mass of aspartame to dissolve into a 500mL volumetric flask to obtain an aspartame solution whose molar concentration is 3×10-2 mol.L-1. c) Starting from this solution, what is the procedure to prepare 100 mL of aspartame solution at concentration 1.5×10-3 mol.L-1. d) What is the amount of substance of aspartame in 20 mL of aspartame solution at 2×10-3 mol.L-1? What is the corresponding number of aspartame molecules? Data: NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Molar mass: M (C ) = 12 g.mol-1 M (O ) = 16 g.mol-1 M (N ) = 14 g.mol-1 M (H ) = 1 g.mol-1