RLF-LECTURE 14 ñ ANT#UNBR#
advertisement

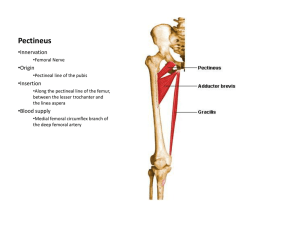
LECTURE 14 – ANTERIOR AND MEDIAL THIGH SPECIAL FEATURES: great sapheonous vein: located in superficial fascia of medial leg and thigh from. Begins at the dorsal venous arch of foot and empties into the femoral vein via the saphenous opening in the fascia lata. clinical note: valves of the superficial veins become incompetent this can result in varicose veins. fascia lata: the deep fascia of the thigh is a dense layer of connective tissue deep to the superficial fascia and overlying the muscles. Attaches to and is continuous with inguinal ligament. Laterally thickens to for iliotibial tract. intermuscular septa: septa pass from the fascia lata to attach to the femur to create anterior and posterior compartments of the thigh. femoral triangle: located inferior to inguinal ligament bound by: Sartorius m. laterally adductor longus m. medially inguinal ligament m. superiorly pectineus, iliopsoas and adductor longus mm. floor fascia lata roof contains from lateral to medial: femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein and deep inguinal lymphnodes (NAVL). femoral sheath: fascial tube containing the artery and vein (not the nerve). femoral canal: medial space within femoral sheath that allows for the femoral vein to expand; occupied by lnguinal lymph nodes; site for femoral hernias. femoral ring: is the superior abdominal opening of femoral canal. Outlines a weak spot in the anterior abdominal wall that is a frequent site for femoral hernias. Hernias can protrude the saphenous opening. adductors canal: (aka Hunter’s or subsartorial canal) Fascial tunnel covered by middle third of sartorius m. that conveys femoral vessels from femoral triangle to adductor hiatus where they enter the popliteal fossa. Contains to branches of femoral nerve: 1. nerve to vastus medialis 2. saphenous nerve SKELETAL FEATURES: 1. os coxa: anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS): attachment for sartorius and tensor fascia latae m. and superior end of inguinal ligament anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS): attachment for rectus femoris pubic tubercle: inferior attachment for inguinal ligament; pubic crest is medial to it pecten pubis: ridge on superior ramus of pubis, lateral to pubic tubercle; attachment for pectineus m. obturator foramen: conveys obturator vessels and nerve from pelvis pubic arch: formed by two inferior ishiopubic rami; attachments for adductors body of pubis: adjacent to the pubic symphysis Ischial tuberosity: attachment for hamstring mm. 2. Femur: lesser trochanter: attachment for iliopsoas m. linea aspera: vertical, roughened line on midposterior surface; attachment for the following muscles from medial to lateral: vastus medialis, pectineus & adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gluteus max, biceps femoris (short head) and vastus lateralis. adductor tubercle: superior aspect of medial epicondyle; attachment for adductor magnus 3. Tibia: shaft is triangular in cross section with medial, lateral, and posterior surface tibial tuberosity: attachment for patellar ligament Gerdy’s tubercle: located on lateral condyle, is the attachment of tensor fascia lata MUSCLES: ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT: 1. Iliopsoas: (see posterior abdominal wall notes) attachments: superior part of iliac fossa (illiacus) and transverse processes, bodies and intervertebral discs of T12 through L5 (psoas) to lesser trochanter. innervation: femoral n (L2-L4, illiacus) and anterior primary rami L2-L4 (psoas) actions: flexion of thigh at hip 2. Sartorius: attachments: from ASIS to medial superior surface of tibia innervation: femoral n. - L2-4 actions: flexion of leg at knee; flexion of thigh at hip 3. Tensor fasciae latae attachments: from ASIS and adjacednt iliac crest to iliotibial tract (which attach to the lateral condyle of tibia innervation: superior gluteal n. L4-S1 actions: thigh abductor; stabilizes extended knee and trunk on hip joint Quadriceps femoris group: attach to tibial tuberocity via a common tendon (quadriceps tendon) with sesamoid bone (patella); known beyond patella as patellar ligament all innervated by femoral n. L2-4 action of all is extension of leg at knee 4. Rectus femoris: attachment: AIIS to tibial tuberocity innervation: femoral n. action: extension of leg at knee AND flexion of femur at hip 5. Vastus lateralis: attachment: greater trochanter and lateral lip of linea aspera to tibial tuberocity innervation: femoral n. action: extension of leg at knee 6. Vastus medialis: attachment: medial lip of linea aspera to tipial tuberocity innervation: femoral n. action: extension of leg at knee 7. Vastus intermedius: attachment: anterolateral femoral shaft to tibial tuberocity innervation: femoral n. action: extension of leg at knee Clinical note: runner’s knee is a soreness due to hyperflexion of the knee or a blow to the patella pulling the patella sideways MEDIAL THIGH COMPARTMENT: 8. Pectineus: attachment: pecten pubis to pectineal line at top of linea aspera innervation: femoral n. (occasionally obturator) L2-4 actions: flexion of femur at hip; adduction of thigh 9. Gracilis: attachments: body & inferior ramus of pubis to superior medial surface of tibia, below Sartorius innervation: obturator n. L2-L4 actions: adduction of thigh, flexion of leg at knee 10. Adductor longus: attachments: from body of pubis to middle third of linea aspera innervation: obturator n. L2-L4 actions: adduction of thigh and flexion of thigh at hip 11. Adductor brevis: attachments: from body of pubis to superior third of linea aspera innervation: obturator n. L2-L4 actions: adduction of thigh 12. Adductor magnus: attachments: inferior ramus of pubis, ramus and tuberosity of ischium to linea aspera and adductor tubercle of femur innervation: obturator n. L2-L4 actions: adduction of thigh, extension of thigh at hip 13. Obturator externus: attachments: from border of obturator foramen and obturator membrane to intertrochanteric fossa of femur innervation: obturator n. L2-L4 actions: lateral rotation of thigh; stabilizes hip joint Clinical note: pulled groin is caused by strain or stretching of superior attachments of medial thigh muscles NERVES (from lumbar plexus) 1. femoral nerve: L2 - L4; supplies mm. noted above and cutaneous branches (anterior and medial femoral cutaneous and saphenous n.) 2. obturator nerve: L2 - L4; supplies adductors and obturator externus and small cutaneous field of medial thigh 3. lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: L2 - L3 ; supplies skin of lateral thigh VESSELS: 1. femoral artery: from external iliac a.; changes to femoral a. after passing deep to inguinal ligament, thru femoral triangle, deep to sartorius in adductor canal, traverses adductor hiatus to become popliteal a. supplies anterior and medial thigh mm. main branch is the profunda femoris a. (deep femoral a.) 2. profunda femoris artery: supplies deep anterior & posterior thigh mm. 3. lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries: which supply hip and knee joints (medial passes between pectineus & iliopsoas mm.) 4. obturator artery: from internal iliac a. via obturator foramen to medial thigh; supplies adductor mm. and obturator externus 5. great saphenous v.: see above