6. CULT 601-Contemporary Issues in ANTH
advertisement

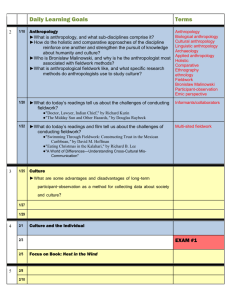
C-1 CULT 601 Contemporary Issues in Anthropology Full Course Title: Contemporary Issues in Anthropology Course Code: CULT 601 Course Level/BiH cycle: III Study cycle ECTS credit value: 6 ECTS Student work-load: For the whole semester: Lectures Practical training Assignment Individual learning TOTAL 45 15 30 60 150 Length: Spring 2013 Faculty/School/Department: Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences / Department of Cultural Studies Course leader: Assist. Prof. Dr. Tuba Boz Contact details: Office: F2.7 e-mail: tboz@ius.edu.ba Office hours: Monday 2-3pm Thursday 11am-12pm Phone: +387 33 957 404 Site: IUS Main Campus Host Study Program: Cultural Studies Course status: Elective Pre-requisites: None Access restrictions: III study cycle students only Assessment: Attendance and Participation, Research Project, Field work Presentation, Final Exam. Date validated: October 2013 Course aims: Learning outcomes: To introduce students to key anthropological theorists and theories To develop students’ observation and analytical skills To deepen student’s understanding of the culture in abstract and practical terms To develop academic communication skills, research skills and critical thinking After successful completion of this course, students will be able: To understand the historical socio-cultural context in which anthropology was employed; To connect anthropological theories to contemporary issues in as societies; To critically analyze and compare various cultures in society and across the globe; To observe cultures and social interaction with a particular attention to detail and reflexivity; To conduct research with a sophisticated consideration to issues concerning ethics and representation. 1 C-1 Indicative syllabus content: This course is designed for doctoral students in the field of Cultural Studies with a focus on classical and contemporary theories and issues in Anthropology. The politics and methods of ethnographic research is also central to this field. The main themes to be dealt with may include: Politics of Anthropology; beliefs and traditions, innovation, new technologies and culture; Globalization and Marginalization; Cultural Geography; Pluralism; Multiculturalism; Religion and; Cultural Integration, Cultural Assimilation; Hegemony and Resistance; Intercultural Exchange; Cross-cultural Communication; Migration and Citizenship; Ethnographic research and Ethics. Teaching occurs via lectures, seminars and tutorials, individual and team- work in-class activities Learning delivery: Assessment Rationale: Assessment Weighting: In order to provide solid foundation in Cultural Studies Program and to enable students to develop a critical and evaluative understanding of culture with the socio-political environment, and to demonstrate commitment and diligence at any time, different assessment methods are proposed for this module. Therefore, appropriate and diverse assessment methods include field-work project, presentations, group activities, consultations, exams and take-home exams with the aim to help students to stay focused and active, and fully benefit from the module. Attendance and Participation 10%, Research Project 30% Fieldwork 20% Presentation and Reflection 10% Final Exam 30% Essential Reading: Recommended readings: Beattie, John. (1966) Other Cultures: Aims, Methods and Achievements in Social Anthropology. U.K: Routledge and Kegan Paul Ltd. Barnard, A. (2004) History and Theory in Anthropology. U.K. Cambridge University Press. May, Tim. (2002). Qualitative Research in Action. London: SAGE. Wierzbicka, Anna. (1997). Understanding Cultures Through Their Key Words. New York: Oxford University Press. Ammerman, Nancy. (2007). Everyday Religion: Observing Modern Religious Lives. New York: Oxford University Press. Hall, Edward, Beyond Culture Hall, Edward, The Silent Language Additional articles and readings will be supplied in class for discussions Intranet web reference: N/A Important notes: Class absences should not exceed 20% of total class time. Students who exceed the limits without a medical certificate or emergency excuse acceptable to and approved by the Dean of the relevant faculty member shall not be allowed to take the final examination and shall receive a mark of N/A for the course. If the Dean approves the excuse, the student will be considered to have withdrawn from the course. Presentation of assignments - Your cover page must include: Your name Essay title Title of the subject Your lecture’s name Date of submission/Due date - Your paper: Font: Times New Roman Size: 12 You must use 1.5 spacing Include page numbers Staple the pages together Ensure that you use spell check and then check over your paper yourself again. 2 C-1 Double check over your grammar and expression You will use the in-text citations (APA) for your referencing You will NOT USE the following or similar websites in your academic writing: Wikipedia Answers.com Yahoo answers Plagiarism: Assignments must be the original work of the student. Sources must be acknowledged and cited. Plagiarism will result in an immediate fail. Submitting your work - You must submit your work on time in class. Email your assignment to tboz@ius.edu.ba In the subject section of the email, you must include: Your name Course title Assessment type Quality assurance: Student surveys, discussion on course, student appeals, e-mails, direct (formal) feedback at the end of the semester by students, assistants and other colleagues Course schedule: 3 C-1 Week 1. Lesson / Date 10/10 Topics to be covered Class activities Problems/ Assignments (Homework) Social and Cultural Anthropology Fieldwork report Chap. 1 and 2 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 3 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 6 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class 3. 24/10 Theorizing Culture 4. 31/10 Learning objectives (After this lesson student will be able to:) Introduction to the course, expectations and requirements 2. 17/10 Readings Ethnography in the 21st century 4 Understand the significance, relevance and applicability of social and cultural anthropology historically and in the 21st century Critically analyze and discuss culture in abstract and practical terms Conduct ethnographic research C-1 5. 7/11 Ethics and Representation Fieldwork report 6. Social Functions and Social Structure Chap. 4 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Beliefs and Values Fieldwork report Chap. 5 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 7 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report 14/11 7. 21/11 8. 28/11 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Kinship 5 Prepare documents to conduct ethical research and become sensitive to issues of representation when researching and writing about people and their cultures Discuss and analyse society and culture, agency and structure Critically analyze the connection between culture and religion and the role of religion in society Know the different types of kinship in different societies and its relevance to modern society C-1 9. 5/12 Marriage and Affinity Fieldwork report Chap. 8 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 9 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 10 Consultations and references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 11 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class 10. 12/12 Social Control and Political Organisation 11. 2/12 Law and Social Sanctions 12. 19/12 Economic and Property Relations 6 Have a cultural relativistic view of marriage and affinity in societies and its relevance to society as a whole Critically discuss and evaluate how culture is used as means of social control in the 21st century, culture of surveillance as a mean of political repression Understand different forms of social sanction in both Western and Eastern cultures and the challenges of diversity management in societies Critically discuss how culture affects economic and property relations C-1 13. 26/12 Rituals – Magic Fieldwork report Chap. 12 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 13 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class Fieldwork report Chap. 14 Consultations and additional references to the literature will be discussed and given during the class 14. 23/12 Rituals – Religion 15. 9/1 16. Social Change Final Exams 7 Recognize the manifest and latent functions of rituals and magic in society Study the significance of rituals in religion across cultures Appreciate the dynamic nature of culture and examine the relationship between culture and soil change in a globalised world