MasterProjectProposal - College of Engineering and Applied
advertisement

DCSPM: Develop and Compile Subset of PASCAL
Language to MSIL
Master Proposal
by
Abdullah Sheneamer
Master of Computer Science
University Of Colorado, Colorado Springs
1. Committee Members and Signatures:
Approved by
Date
Advisor: Dr.Albert Glock
Committee member: Dr. Edward Chow
Committee member: Albert Brouillette
1
2. Introduction
In the computer world, techniques evolve rapidly from theories, algorithms, programming
languages, software systems, and software engineering. Fortunately, compilers allow
programmers to write at a high level, and automated processing take care of creating the
machine-specific instructions. My project will design and create a compiler which translates
PASCAL source code into Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL). MSIL includes
instructions for loading, storing, initializing, and calling methods on objects, as well as
instructions for arithmetic and logical operations. There is currently no PASCAL compiler which
compiles to MSIL. The Just-in-time (JIT) compiler will convert the MSIL to CPU- Specific code
[1]. The advantage in compiling to MSIL is that 1) legacy PASCAL can now be run on modern
machines, 2) MSIL is platform independent and 3) JIT compilers can be optimized for specific
machines and architectures. The JIT compiler can also do aggressive optimizations specifically
for the machine where the code is running.
Program HelloWorld; Begin
Writeln (‘ Hello World’);
End .
Compilation
PASCAL
Compiler
Execution
MSIL
JIT
Compiler
.method public static void Main() cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 1
IL_00: ldstr "Hello World"
IL_05: call
void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_10: ret
} // end of method HelloWorld::Main
Figure 1: The compilation and execution process of PASCAL programs.
2
Native
Code
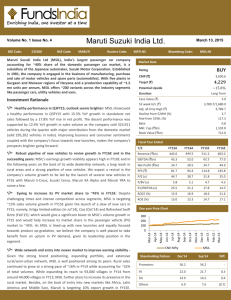
-Compilation process: takes PASCAL source code and produces MSIL. The PASCAL compiler
includes lexical and syntax analysis, and the creation of the symbol table. MSIL is created when
compiling to manage native code. MSIL is a CPU-independent set of instructions that can be
efficiently converted to native code. Such as in Figure 2.
-Execution process: MSIL must be converted to CPU-specific code, usually by a just-in-time
(JIT) compiler. Native code is computer programming (code) that is compiled to run with a
particular processor (such as an Intel x86-class processor) and its set of instructions.
Source code of PASCAL
Lexical
Analysis
Parser
Symbol Table
MSIL
.method public static void Main() cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 1
IL_00: ldstr
"Hello World"
IL_05: call
void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_10: ret
} // end of method HelloWorld::Main
Figure 2: Compilation process
3
Error
Handler
3. Project Plan
As part of this project, I will design the Intermediate language (IL or MSIL) for PASCAL
Language. I plan to design a compiler that can handle subset of PASCAL Language to compile
to MSIL including, assignment statement, Writeln instructions, if statement, if/else statement, for
statement and switch statement. Also, I will design an algorithm that implements the lexical
analysis and another algorithm for syntax analysis and semantic analysis then improve these
algorithms and evaluate these different algorithms for their performance. By observing the
performance I will try to improve the compiler.
ILAsm has the instruction set same as that the native assembly language has. You can write code
for ILAsm in any text editor like notepad and then can use the command line compiler
(ILAsm.exe) provided by the .NET framework to compile that. ILAsm.exe is a command line tool
shipped with the .NET Framework and can be located at
<windowsfolder>\Microsoft.NET\Framework\<version> folder. You can include this path in
your path environment variable. When you have finished compiling your .IL file, then it will
output the exe with the same name as that of .IL file. You can specify the output file name using
/OutPut=<filename> switch like ILAsm Test.il /output=MyFile.exe. To run the outputted exe
file, just type the name of the exe and hit return. Output will be before you on the screen. [11]
So, my project will include:
1- Design and Implement subset of Pascal Language Lexical analysis, Syntax analysis and
Semantic analysis.
2- Design Assignment statement that an arithmetic expression is an expression using
additions +, subtractions -, multiplications *, and divisions /. A single
mode arithmetic expression is an expression all of whose operands are of the
same type (i.e. INTEGER, REAL or COMPLEX). However,
only INTEGER and REAL will be covered in this project. Therefore, those
values or variables in a single mode arithmetic expression are all integers or
real numbers. such as a:=b+c/d-e OR an assignment statement gives a value to
a variable such as x:=5; and compile that to Intermediate language.
3- The PASCAL compiler is structured in such a way that a write, and writeln statements
containing more than one argument is compiled into several write statement with only
one argument. For writeln, these statements are followed by a statement that writes the
end-of-line. So for example the writeln statement: “ Prgoram Write; Begin
writeln('This writeln is compiled into MSIL '); End . ” So,I will Design and Compile
“Writeln” instruction to MSIL
4
4- Design and Compile “if” Statement to MSIL
a- If variable1 > , < ,= ,>=,<= variable2 Then Begin variable3 :=
variable1*variable2; End;
b- If variable1 > , < ,= ,>=,<= variable2 Then Begin Writeln(‘ Conditional statement
End;
c- If variable1 > , < ,= ,>=,<= Number Then Begin Writeln(‘ Conditional statement
End;
5- Design and Compile “if/Else” Statement to MSIL
a- If variable1 > / < / = / >=/<= variable2 Then Begin variable3 := variable1+,-,*,/
variable2; End Else Begin variable2 := variable1 +,-,*,/ variable3 End
b- If variable1 > / < / = / >=/<= variable2 Then Begin variable3 := variable1+,-,*,/
variable2; End Else Begin Writeln(‘ Condtitional statement’); End
c- If variable1 > / < / = / >=/<= Number Then Begin variable3 := variable1+,-,*,/
variable2; End Else Begin Writeln(‘ Condtitional statement’); End
6- Design and Compile “ While” Statement to MSIL
a- While Variable1 >,<.,=,<=,>= Variable2 Do
Begin Writeln(‘ While Statement’); Variable1:= Variable1 + 1; End;
b- While Variable1 >,<.,=,<=,>= Number Do
Begin Writeln(‘ While Statement’); Variable1:= Variable1 + 1; End;
c- While Variable1 >,<.,=,<=,>= Variable2 Do
5
Begin Variable3: = Variable1 *,+,/,- Variable2 ….; Variable1:= Variable1 + 1;
End;
d- While Variable1 >,<.,=,<=,>= Number Do
Begin Variable3: = Variable1 *,+,/,- Variable2 ….; Variable1:= Variable1 + 1;
End;
7- Design and Compile “For” Statement to MSIL
a- For I:= Number To Number Do Begin Writeln(‘ For Statement’); End;
b- For I:= Number To Number Do Begin Variable3: = Variable1 *,+,/,- Variable2
….; End;
c- For I:= Number To Number Do Begin If variable1 > , < ,= ,>=,<= variable2
Then Begin Writeln(‘ Conditional statement ‘) End;
8- Design and Compile “Switch” Statement to MSIL
a- Case Variable of Value1 Writeln(‘A’);
Case Variable of Value2 Writeln(‘B’);
Case Variable of Value3 Writeln(‘C’);
Else Writeln(‘D’); End
9- Evaluation of the algorithms
6
For example of Compile Pascal program to MSIL:
“ Program HelloWorld;
Begin
Writeln (‘ Hello World’);
End . “
The output of MSIL:
// Metadata version: v4.0.30319
.assembly extern mscorlib
{
.publickeytoken = (B7 7A 5C 56 19 34 E0 89 )
// .z\V.4..
.ver 2:0:0:0
}
.assembly HelloWorld
{
.hash algorithm 0x00008004
.ver 0:0:0:0
}
.module expression.dll
.imagebase 0x00400000
.file alignment 0x00000200
.stackreserve 0x00100000
.subsystem 0x0003
// WINDOWS_CUI
.corflags 0x00000001
// ILONLY
// Image base: 0x00820000
// =============== CLASS MEMBERS DECLARATION ===================
.class public auto ansi HelloWorld
extends [mscorlib]System.Object
{
.method public static void Main() cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 1
IL_00: ldstr
"Hello World"
IL_05: call
void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_10: ret
} // end of method HelloWorld::Main
.method public specialname rtspecialname
instance void .ctor() cil managed
{
.maxstack 2
IL_00: ldarg.0
IL_01: call
instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor()
IL_06: ret
} // end of method HelloWorld::.ctor
} // end of class HelloWorld
3.1 Tasks:
3.1.1 Already Complete - done during fall 2011 to present
Designed and implemented lexical Analysis [2],[4],[5],[6]
Built Assembly and Compile “Writeln” instruction to MSIL[7],[8],[9]
3.1.2 In Progress - should finish in spring 2012
Design and Implement Syntax “ Parser” [4], [7],[8],[9]
Design and Compile Assignment Statement [7],[8],[9]
7
Design and Compile subset of “if” Statement to MSIL [7],[8],[9]
Design and Compile subset of “if/Else” Statement to MSIL [7],[8],[9]
3.1.3 Future - complete during summer2012/fall 2012 (Listed from highest to lowest
priority)
Design and Compile subset of “For” Statement to MSIL [7],[8],[9]
Design and Compile subset of “ While” Statement to MSIL[7],[8],[9]
Design and Compile subset of “Switch” Statement to MSIL [7],[8],[9]
Evaluation the algorithms.
3.2 Deliverables:
1- A working c# based PASCAL compiler.
2- A master report documenting the design and implementation of the subset of PASCAL
compiler. Additionally, improvements in the compilation process will be demonstrated and
documented.
4.0 References
1. http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/c5tkafs1(v=vs.71).aspx
2. C# To Program By H.M Deitel & P.J.Deitel& J.Listfield & T.R. Nieto & C.Yaeger &
M.Zlatkina.
3. Compiler Construction principles and practice by Kennth C.louden
4. Data Structure using Java By D.S.Malik & P.S.Nair.
5. An introduction to formal languages and automata. Fourth Edition. Peter Linz
6. Compilers Principles, Techniques and Tools by Alfred V.Aho, Ravi Sethi and Jeffrey D.
Ullman. 1985
7. Develop a Compiler in Java for a Compiler Design Course Abdul Sattar and Torben
Lorenzen
8. Guide to assembly language [electronic resource] : a concise introduction / James T.
Streib.Streib, James T. London ; New York : Springer, c2011.
9. Using a Stack Assembler Language in a Compiler Course by Dr. Gerald Wildenberg St .
John Fisher College, Rochester, NY Bristol Polytechnic, England (1989-1990 )
10. Expert .NET 2. IL assembler/ Serge Lidin. Lidin, Serge. 1956- Berkeley, CA
11. http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/3778/Introduction-to-IL-Assembly-Language
8
Appendix A:
<program> ::= Program <identifier> ; <block> .
<block> ::= <variable declaration part>
<procedure declaration part>
<statement part>
variable declaration part> ::= <empty> |
var <variable declaration> ;
{ <variable declaration> ; }
<variable declaration> ::= <identifier > { , <identifier> } : <type>
<type> ::= <simple type>
<simple type> ::= <type identifier>
<type identifier> ::= <identifier>
<statement part> ::= <compound statement>
<compound statement> ::= begin <statement>{ ; <statement> } end
<statement> ::= <simple statement> | <structured statement>
<simple statement> ::= <assignment statement> |
<read statement> | <write statement>| <if statement> | <for statement>
<assignment statement> ::= <variable> := <expression>
<read statement> ::= read ( <input variable> { , <input variable> } )
<input variable> ::= <variable>
<write statement> ::= write ( <output value> { , <output value> } )
<output value> ::= <expression>
<structured statement> ::= <compound statement> | <if statement> |
<while statement>
<if statement> ::= if <expression> then <statement> |
if <expression> then <statement> else <statement>
<while statement> ::= while <expression> do <statement>
<for statement> ::= for <variable identifier > ::= <expression> to <expression> do <
statement>
<expression> ::= <simple expression> |
<simple expression> <relational operator> <simple expression>
<simple expression> ::= <sign> <term> { <adding operator> <term> }
<term> ::= <factor> { <multiplying operator> <factor> }
<factor> ::= <variable> | ( <expression> )
9
<relational operator> ::= = | <> | < | <= | >= | >
<adding operator> ::= + | <multiplying operator> ::= * | /
<variable> ::= <entire variable>
<entire variable> ::= <variable identifier>
<variable identifier> ::= <identifier>
<identifier> ::= <letter> { <letter or digit> }
<letter or digit> ::= <letter> | <digit>
<integer constant> ::= <digit> { <digit> }
<character constant> ::= '< any character other than ' >' | ''''
<letter> ::= a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o |
p|q|r|s|t|u|v|w|x|y|z|A|B|C|
D|E|F|G|H|I|J|K|L|M|N|O|P
|Q|R|S|T|U|V|W|X|Y|Z
<digit> ::= 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
<special symbol> ::= + | - | * | = | <> | < | > | <= | >= |
( | ) | := | . | , | ; | : | if | then | else | of | while | do |
begin | end | read | write | var | | program | switch| for | to
<predefined identifier> ::= integer | Boolean
10