Mineral Identification Data Sheet 7
advertisement
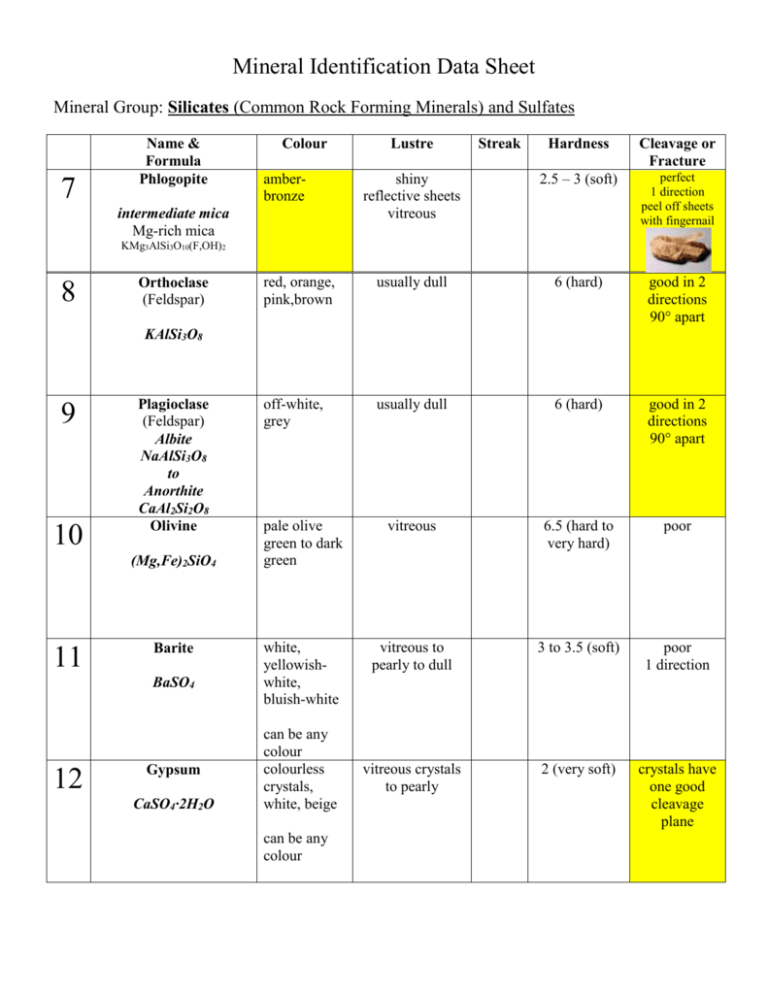
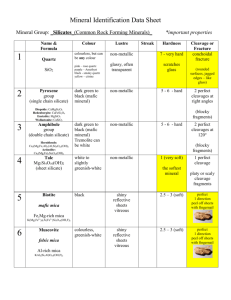
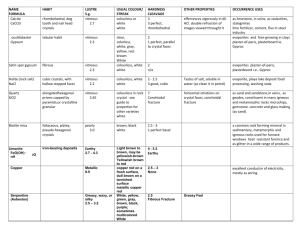
Mineral Identification Data Sheet Mineral Group: Silicates (Common Rock Forming Minerals) and Sulfates 7 Name & Formula Phlogopite Colour Hardness Cleavage or Fracture shiny reflective sheets vitreous 2.5 – 3 (soft) perfect 1 direction peel off sheets with fingernail red, orange, pink,brown usually dull 6 (hard) good in 2 directions 90° apart off-white, grey usually dull 6 (hard) good in 2 directions 90° apart pale olive green to dark green vitreous 6.5 (hard to very hard) poor white, yellowishwhite, bluish-white vitreous to pearly to dull 3 to 3.5 (soft) poor 1 direction vitreous crystals to pearly 2 (very soft) crystals have one good cleavage plane amberbronze intermediate mica Mg-rich mica Lustre Streak KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2 8 Orthoclase (Feldspar) KAlSi3O8 9 10 Plagioclase (Feldspar) Albite NaAlSi3O8 to Anorthite CaAl2Si2O8 Olivine (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 11 Barite BaSO4 12 Gypsum CaSO4∙2H2O can be any colour colourless crystals, white, beige can be any colour Mineral Group: Silicates (Common Rock Forming Minerals) and Sulfates Crystal Habit (draw picture) hexagonal “books” Crystal Drawing Density Special Properties above average for a nonmetallic mineral (3.3) flake off sheets of mica in hand sheets are “elastic/flexible” Uses Geological Environment electrical and heat insulation found in granites with quartz, feldspar and hornblende usually massive, rare blocky crystals average (2.5) most common mineral. unusual “wormy” perthite intergrowth no uses found in felsic rocks with quartz and mica usually massive, rare blocky crystals average (2.5) “record grooves” from twinning found in all types of rocks and is often the main constituent of intermediate and mafic rocks. usually vitreous, sugary grains or massive above average (3.8) some Labradorite samples show the Schiller effect Peridot gems – August birthstone found with pyroxenes and serpentines in ultramafic rock and basalt (never found with quartz). There are green olivine beaches in Hawaii. Oxidizes easily to form serpentine massive or radiating blades very heavy for a non-metallic (4.7) looks like calcite but doesn’t fizz, heavier and harder than gypsum main ore of barium (to make paper, glass, rubber); used for X-raying the digestive system; used as drilling mud usually white masses; colourless crystals – tabular or prismatic 2.3 (light) very soft CaSO4 is called Anhydrite or Alabaster (much harder and denser) Used to make wallboard (Gyprock) – it is dehydrated to make it harder an more absorbent – Ontario is a major producer; A major evaporate mineral found with limestone