Name: Class:___Earth Science_______ Period/Block: Date: Class
advertisement
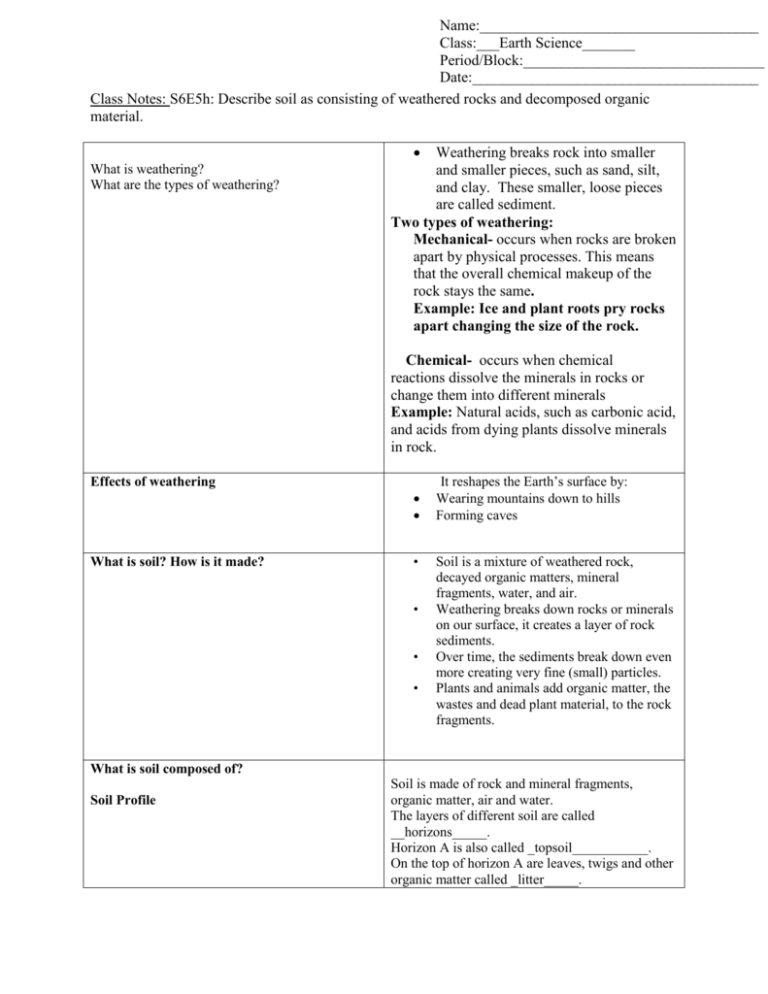
Name:_____________________________________ Class:___Earth Science_______ Period/Block:________________________________ Date:______________________________________ Class Notes: S6E5h: Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material. What is weathering? What are the types of weathering? Weathering breaks rock into smaller and smaller pieces, such as sand, silt, and clay. These smaller, loose pieces are called sediment. Two types of weathering: Mechanical- occurs when rocks are broken apart by physical processes. This means that the overall chemical makeup of the rock stays the same. Example: Ice and plant roots pry rocks apart changing the size of the rock. Chemical- occurs when chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them into different minerals Example: Natural acids, such as carbonic acid, and acids from dying plants dissolve minerals in rock. Effects of weathering What is soil? How is it made? • • • • It reshapes the Earth’s surface by: Wearing mountains down to hills Forming caves Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, decayed organic matters, mineral fragments, water, and air. Weathering breaks down rocks or minerals on our surface, it creates a layer of rock sediments. Over time, the sediments break down even more creating very fine (small) particles. Plants and animals add organic matter, the wastes and dead plant material, to the rock fragments. What is soil composed of? Soil Profile Soil is made of rock and mineral fragments, organic matter, air and water. The layers of different soil are called __horizons_____. Horizon A is also called _topsoil___________. On the top of horizon A are leaves, twigs and other organic matter called _litter_____. Horizon _A_ has the darkest soil because of the decayed organic matter. B Horizon has soil that is lighter in color because less __ORGANIC_____ matter. B Horizon gets materials from the A horizon by the process of _LEACHING________. C Horizon is the lightest and __THICKEST_____ soil layer. The C Horizon contains partially weathered _ROCK____ and very little organic matter. What is found beneath the horizons? _BEDROCK_________: a layer of solid rock that contributes/adds to soil; also called __PARENT____ rock. List in order from largest to smallest. SAND, SILT, CLAY Sediment (weathered rock/mineral) sizes in soil 4 factors that affect soil formation Words to know: Mechanical weathering Chemical weathering Soil, humus, litter, horizon, soil profile, and leaching 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Climate Slope Vegetation Types of rock Amount of time rock has been weathering Directions: Vocabulary Flip book









