Quiz 2B Answer Key
advertisement
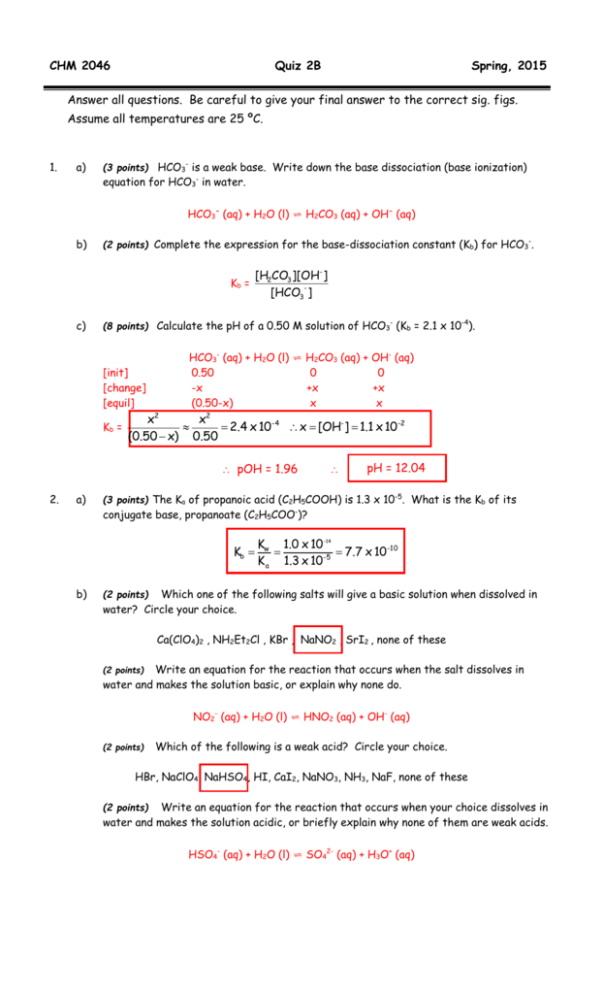
CHM 2046 Quiz 2B Spring, 2015 Answer all questions. Be careful to give your final answer to the correct sig. figs. Assume all temperatures are 25 ºC. 1. a) (3 points) HCO3- is a weak base. Write down the base dissociation (base ionization) equation for HCO3- in water. HCO3- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H2CO3 (aq) + OH- (aq) b) (2 points) Complete the expression for the base-dissociation constant (Kb) for HCO3-. Kb = c) [H2CO3 ][OH- ] [HCO3 ] (8 points) Calculate the pH of a 0.50 M solution of HCO3- (Kb = 2.1 x 10-4). [init] [change] [equil] Kb = HCO3- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ 0.50 -x (0.50-x) H2CO3 (aq) + OH- (aq) 0 0 +x +x x x x2 x2 2.4 x 10- 4 x [OH- ] 1.1 x 10-2 (0.50 x) 0.50 pOH = 1.96 2. a) pH = 12.04 (3 points) The Ka of propanoic acid (C2H5COOH) is 1.3 x 10-5. What is the Kb of its conjugate base, propanoate (C2H5COO-)? Kb b) Kw 1.0 x 10 -14 7.7 x 10 -10 -5 K a 1.3 x 10 Which one of the following salts will give a basic solution when dissolved in water? Circle your choice. (2 points) Ca(ClO4)2 , NH2Et2Cl , KBr , NaNO2 , SrI2 , none of these Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when the salt dissolves in water and makes the solution basic, or explain why none do. (2 points) NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ HNO2 (aq) + OH- (aq) (2 points) Which of the following is a weak acid? Circle your choice. HBr, NaClO4, NaHSO4, HI, CaI2, NaNO3, NH3, NaF, none of these Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when your choice dissolves in water and makes the solution acidic, or briefly explain why none of them are weak acids. (2 points) HSO4- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ SO42- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) 3. a) What is the pH of a buffer solution prepared from adding 60.0 mL of 0.22 M nitrous acid (HNO2) solution to 50.0 mL of 0.24 M sodium nitrite (NaNO2) solution? (Ka for HNO2 is 7.1 x 10-4). (60.0mL)(0.22M) [HNO2 ] 0.120M (extra sig. fig.) 110.0mL (50.0mL)(0.24M) [NO2 ] 0.109M 110.0mL (10 points) HNO2 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + NO2- (aq) [init] 0.120 0 0.109 [change] -x +x +x [equil] (0.120-x) x (0.109+x) Ka x(0.109 x 0.109x 7.1 x 10 -4 (0.120 - x) 0.120 x = 7.82 x 10-4 [H+] = x = 7.82 x 10-4 M = 7.8 x 10-4 M (sig. figs.) pH = -log (7.8 x 10-4) pH = pKa + log [base] [acid] pH = 3.11 pH = 3.15 + (-0.04) pH = 3.11 b) (10 points) What is the new pH if 10.0 mL of a 0.20 M solution of NaOH is now added? n(HNO2) = MV = (0.120 M)(110.0 x 10-3 L) = 0.0132 mol n(NO2-) = MV = (0.109 M)(110.0 x 10-3 L) = 0.0120 mol n(OH-) added = MV = (0.20 M)(10.0 x 10-3 L) = 0.0020 mol HNO2 + OH- NO2- + H2O n(init) 0.0132 0.0120 addition 0.0020 n(new) 0.0112 new [HNO2] = new [NO2-] = 0 0.0112mol 120x10 0.0140 120x10 3 3 0.0140 = 0.0933M OR OR METHOD (2): pH = pKa + log [base] [acid] OR METHOD (3): use number of moles = 0.1167M pH = pKa + log n(base) n(acid) METHOD (1): HNO2 ⇌ H+ + NO2[init] 0.0933 0 0.1167 [change] -x +x +x [equil] (0.0933)-x x (0.1167)+x + -4 [H ] = x = (7.1 x 10 )(0.0933)/(0.1167) [H+] = 5.7 x 10-5 pH = 3.25 4. pH = 3.15 + 0.097 pH = 3.25 (4 points) Calculate the solubility of the salt MX2 (containing M2+ and X- ions) in water (Ksp = 4.4 x 10-8). MX2 (s) ⇌ M3+ (aq) + 2 X- (aq) I (solid) 0 0 C -x +x +2x E (solid) x 2x 5. Either way, Ksp = 4.4 x 10-8 = [M2+][X-]2 Ksp = x(2x)2 4.4 x 10-8 = 4x3 x3 = 1.1 x 10-8 x = 2.2 x 10-3 M solubility of MX2 = 2.2 x 10-3 M (4 points) Now calculate the solubility of the same salt MX2 in an aqueous solution containing 0.10 M NaX, where NaX is a very soluble salt. MX2 (s) ⇌ M3+ (aq) + 2 X- (aq) I (solid) 0 0.10 C -x +x +2x E (solid) x (0.10 + 2x) Ksp = 4.4 x 10-8 = [M2+][X-]2 Ksp = x(0.10 + 2x)2 4.4 x 10-8 ≈ x (0.10)2 = x(1.0 x 10-2) x = 4.4 x 10-8 /1.0 x 10-2 = 4.4 x 10-6 solubility of MX2 = 4.4 x 10-6 M