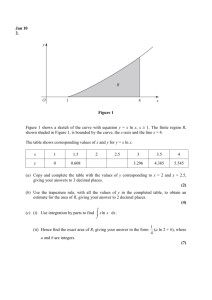
File

Question 1
The random variable X measures the time in months from the diagnosis age until death of
Tasmanian devils with a form of cancer:
0, 𝑓(𝑥) = {
0.036𝑥 0.2
𝑒 −0.03𝑥
1.2
} 𝑥 < 0 𝑥 ≥ 0 a.
Calculate, correct to three decimal places, that a randomly selected Tasmanian devil, once diagnosed, will survive for at least 12 months. b.
A group of 10 Devils have just been diagnosed with the cancer. What is the probability that exactly 6 of these 10 Devils will survive for at least 12 months? Give your answer correct to three decimal
places.
Question 2
The weekly repair cost of a machine is a random variable Y with a probability density function given by:
{ 𝑘𝑦(100 − 𝑦)
0
0 ≤ 𝑦 ≤ 100
otherwis𝑒 a.
Find the exact value of k to ensure that this is a valid pdf.
b.
Sketch the graph of this probability density function. c.
What is the probability that the repair cost will exceed $75 per week? d.
What is the probability that the repair cost will exceed $75, given that they will exceed $50?
Question 3
The effectiveness of solar energy heating units depends on the amount of radiation available from the sun. During a typical October day in Tampa, Florida, the total solar radiation S is a continuous random variable that approximately follows the probability density function (units are in hundreds of calories): 𝑓(𝑠) = {
3(𝑠−2)(6−𝑠)
32
0
, 2
≤ 𝑠 ≤ 6
0, otherwise
a.
Find the probability that the solar radiation will exceed 250 calories on a typical day in October. b.
Calculate the probability that in the month of October there will be at least 28 days in which the solar radiation exceeds 250 calories (there are 31 days in October).
Give your answer correct to 4 decimal places. (Assume that the solar radiation of each day is independent of the previous day).
c.
Find the median solar radiation for October, according to this model. d.
Calculate the mean solar radiation for October according to this model.
Question 3
The pH level, a measure of acidity, is important in studies of acid rain. For a certain lake, baseline measurements of acidity are made so that any changes caused by acid rain can be noted. The pH for water samples from the lake is a random variable X, with probability density function :
3 𝑓(𝑥) = {
8
(7 − 𝑥) 2 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 7
0
0, otherwise
a.
Sketch the pdf. b.
Find the probability that the pH for a sample of water taken from this lake will be less than 6.
c.
Find the probability that a sample of water taken from this lake will have a pH less than 5.5, given that it is known to have a pH less than 6.
Question 4
The proportion of impurities by weight W in certain copper ore samples is a continous random variable with probability density function: 𝑓(𝑤) = {12𝑤
2 (1 − 𝑤)
0
0 ≤ 𝑤 ≤ 1 𝑤 > 1 𝑜𝑟 𝑤 < 0
a.
Write down an integral which, when evaluated gives the probability that a randomly selected sample has a proportion of impurities exceeding 0.5. b.Evaluate this probability.
b.
If four such samples are independently selected, find the probability that i.
Exactly one of them has a proportion of impurities exceeding 0.5. Give your answer correct to 4 decimal places.
ii.
At least one of them has a proportion of impurities exceeding 0.5. Give your answer correct to 4 decimal places.
c.
What is the expected weight of impurities in a sample of this ore weighing 50 kg.
Question 5
The magnitudes of earthquakes recorded in a region of North America is a continuous random variable X which has a probability density function:
−𝑥 𝑓(𝑥) = { 𝑒 2.4
2.4
0
𝑥 ≥ 0
0, otherwise
Find the probabilities that the next earthquake to strike this region will have the following characteristics. Give your answers correct to four decimal places: a.
It will be no more than 2.5 on the Richter scale. b.
It will exceed 4.0 on the Richter scale. c.
It will fall between 2.0 and 3.0 on the Richter scale. d.
Find the probability that, of the next ten earthquakes to strike the region, at least one will exceed 5.0 on the Richter scale. Give your answer correct to four decimal places. (Assume that earthquakes occur independently of each other). e.
Calculate the mean magnitude of earth quakes for this region. f.
The variance of the magnitudes of earthquakes for this region. g.
The magnitude on the Richter scale that no more than 10% of earthquakes will be greater than. Give your answer correct to three decimal places.