Science Monday
advertisement
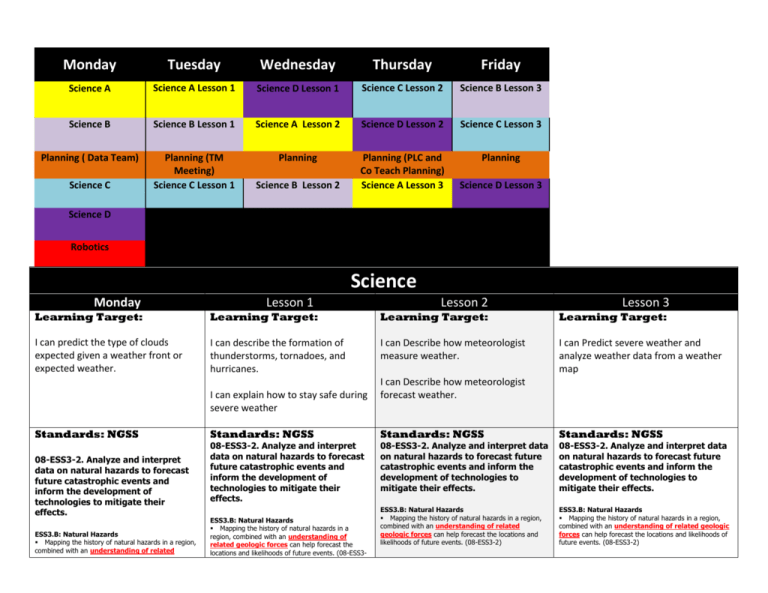
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Science A Science A Lesson 1 Science D Lesson 1 Science C Lesson 2 Science B Lesson 3 Science B Science B Lesson 1 Science A Lesson 2 Science D Lesson 2 Science C Lesson 3 Planning ( Data Team) Planning (TM Meeting) Science C Lesson 1 Planning Planning (PLC and Co Teach Planning) Science A Lesson 3 Planning Science C Science B Lesson 2 Science D Lesson 3 Science D Robotics Science Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Learning Target: Monday Learning Target: Lesson 1 Learning Target: Learning Target: I can predict the type of clouds expected given a weather front or expected weather. I can describe the formation of thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. I can Describe how meteorologist measure weather. I can Predict severe weather and analyze weather data from a weather map I can explain how to stay safe during severe weather Standards: NGSS 08-ESS3-2. Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. ESS3.B: Natural Hazards Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related I can Describe how meteorologist forecast weather. Standards: NGSS Standards: NGSS Standards: NGSS 08-ESS3-2. Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. 08-ESS3-2. Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. 08-ESS3-2. Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. ESS3.B: Natural Hazards Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. (08-ESS3-2) ESS3.B: Natural Hazards Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. (08-ESS3-2) ESS3.B: Natural Hazards Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. (08-ESS3- geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. (08-ESS3-2) 2) Instructional Method Instructional Method Instructional Method Instructional Method Bellringer: Bellringer: Bellringer: Bellringer: Prove it “atmospheric instability” Prove It strategy on evacuate, updrafts, downdrafts Prove it strategy on forcasting Prove it strategy on isobar and isotherm What is the difference between measuring and forecasting something? Craft: Craft: Workshop: Craft: Review cloud formation, cloud types, air masses, and front movement What is lightning? What is thunder? What is a cyclone? Craft: 1. Workshop: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Three Main Type Y chart Cloud weather chart Finish Front Foldable Air Mass and Cloud practice packet Group Weather prediction worksheet Weather Data Graphing practice 2. Confer: While the students are working on the activity I will be walking around assessing if they are correctly connecting the cloud type to front type. I will also be walking around with a formative assessment powerpoint on my Reflection: Students will reflect on the complexity of what a weather 3. 4. Ask what observations can we make during a thunderstorm. Show thunderstorms on radar and talk about relative size compared to the system it is in. Introduce Statement for them to do Prove It. Hurricane: Ask the students the Cardinal Direction of where the storm wind is coming from using a drawing to show how the direction of wind changes as a cyclone passes over. Introduce statement for prove it Show where tornado alley is. Show a risk map of tornados in the U.S. compared to the rest of the world. Introduce statement for prove it. Show pictures of damage done by severe weather. Explain the importance of safety education from severe weather. Explain the next workshop activity. Workshop: 1. What does the weather feel like today? What would you use to describe the weather? (wind speed, temp, pressure) How can we see future weather systems coming 2. Use gizmo (edgenuity) to show how radar shows weather fronts Workshop: 1. Students will do a matching activity where they match the description of the instrument to the picture of the instrument. Students will work as a group to build a weather prediction presentation for the class 1. 2. 3. Quiz Reflections Assessment Earthquake Assessment Reflection 1. 2. 3. 4. Prove It: Statement: Thunderstorms form when cool air pushes up warm humid air to create a cumulonimbus cloud with electrical charges that create lightning which will sometimes come into contact with the ground. Prove It: Statement: Hurricanes in the United States form in the Atlantic Ocean and are tropical storms that turn into hurricanes that draw its energy from the warm humid air at the ocean’s surface and spiral around a low pressure area to create a cyclone. Prove It: Statement: Tornado alley has weather patterns that are more likely to create tornados than any other place on earth. Pair Work-Graphic organizer to organize safety precautions for the different severe weathers’. Then they will make a brochure to support a state: a. reference state and % of getting severe weather b. Must be for Hurricane or Tornado c. discuss how you would know if one is coming. (evidence) d. Confer: 1. During the prove it’s I will traveling around ensuring that the students are able to pick out of the text the information needed to prove statement. Confer: 1. This is an opportunity for me to walk around and show video of different instruments Reflection: 1. Students will reflect on : What can we measure in the weather to identify the fronts coming and leaving? Weather balloons Radar Satellites (Doppler Radars) Barometer Thermometer Wind Sock or Wind Vein Anemometer NWS (national weather service) 2. Practice Reading the EF scale. I will have question for small groups to answer Reflection: 1. Reflection will be the three Teacher generated statement with evidence statements and vocabulary used. Instructional Strateges: Instructional Strategies: Instructional Strategies: Instructional Strategies: Pair work, direct instruction, journaling, reading and writing strategies Pair work, direct instruction, journaling, reading and writing strategies Pair work, direct instruction, journaling, reading and writing strategies Pair work, direct instruction, journaling, reading and writing strategies Vocabulary: Stratus, cumulus, cirrus, Air mass, tropical, polar, maritime, continental, , front, occluded, cyclone, anticyclone Vocabulary: Storm, thunderstorm, lightning, hurricanes, storm surge, tornado, evacuate Vocabulary: Meteorologist, isobars, anemometer, barameter Vocabulary: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Students will look at the weather map and solve for expected weather and cloud types using their knowledge on fronts. 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify which state has the most likely chance of developing a tornado (analyzing data tables and graphs) Multiple choice question that ask where not to hide for a tornado Most common severe weather Cloud formations that are indicators of severe thunderstorms 1. Students can describe how weather fronts are tracked and we can see precipitation Students will predict the type of weather a region will have based on the types of fronts Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: text book, journal, lab equipment, conferring items, graphic organizers Both test Text book, journal Text book, journal Text book, journal Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: None None None None Differentiated: Differentiated: Differentiated: Differentiated: All: Pair Share ( add one from your partner) .. This will help those that need extended time to complete strategy. All: Pair Share ( add one from your partner) .. This will help those that need extended time to complete strategy. A block GT students: A block GT students: Read an article on the importance of weather safety Read an article on the importance of weather safety C block collaboration: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing 2. JM (edgenuity on forecasting weather C block collaboration: 3. Grouping, prompting and cueing 4. JM (edgenuity on forecasting weather D block IEP students: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing 2. NC and JS : D block IEP students: 3. Grouping, prompting and cueing 4. NC and JS : D block GT students: D block GT students D block GT students Those that get done with the strategies early can work on Prove It from statements made from an article called ZAPPED from National Geographic. Read an article on the importance of weather safety Read an article on the importance of weather safety All: Pair Share ( add one from your partner) .. This will help those that need extended time to complete strategy. A block GT students: 1. Cyclones vs Anticyclones reading on page 440 C block collaboration: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing, graphic oragizers 2. JM (student will start a folder and keep the folder in special place): edgenuity –graphic organizer- all vocab word and definition, cornell notes on direct instruction, journal activity on worksheet, cornell lab lecture 3. D block IEP students: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing 2. NC and JS : Have students show work in order and neat in journal D block GT students: All: Pair Share ( add one from your partner) .. This will help those that need extended time to complete strategy. A block GT students: Those that get done with the strategies early can work on Prove It from statements made from an article called ZAPPED from National Geographic. C block collaboration: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing, graphic oragizers 2. JM (edgenuity on forecasting weather D block IEP students: 1. Grouping, prompting and cueing 2. NC and JS : Graphic Organizers SGG Items Have students make a data table with different temperatures and pressure readings. Work on basic Data Tables Robotics: 1. 2. 3. All students work on finding the manual Question board Class challenge Make robot follow a black tape SGG Items SGG Items: SGG Items: