Instructor Guide
advertisement

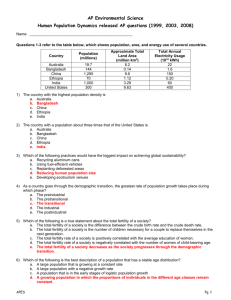
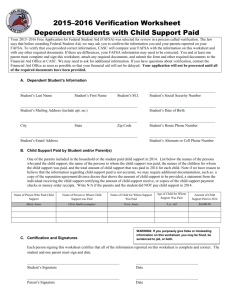
Human Population M. Merrill Human Population and Demographics Instructor Guide Objectives Practice basic numeracy using relevant, large numbers Relate population size and growth to student’s life experiences Introduce basic population growth concepts Explore and compare online numeracy and population resources Materials At least 3 sheets of Flip Chart or larger paper (depending on class size) Colored dot stickers, at least 7 per student in each of two colors Markers Tape 3-page worksheet on Human Demographics and Population – one per student Computer with internet access and projector Camera/smartphone Procedure Begin by collecting some quick data on your students and their ideas about population. Do not start the worksheet until after students have done this “pre-test.” Before class, write the following three tables on the flip charts. There should be sufficient space in each row for several students (maybe most) to have the same estimate. Post these around the room. Instruct students to put one dot in each row that reflects their estimates (you can make the table without columns, to suggest more of a continuum). All students should use the same color for the estimates. Table 1 (vertical): 0 1 2 3 4+ How many kids do you have now? How many kids do you plan to have? What do you think is the average number of kids per woman now in the US? What do you think is the average number of kids per woman now in the world? 8 February 2016 1 Human Population M. Merrill Table 2 (horizontal): It already has 10 years from now 15 yrs 20 yrs 25 yrs 30 yrs 40 yrs 50 or more Never When do you think world population will reach 8 billion (how many years from now)? Table 3 (horizontal): Less than 1B 1B 2B 3B 4B 6B 7B 8B 9B 10B 15B 20B More What do you think the maximum global population will be? What do you think is the maximum sustainable global population? Now have the students complete the 3-page worksheet on Human Demographics and Population. Use the references provided on the worksheet to get the needed numbers. Depending on the average numeracy capabilities of your class, you may need to help students to choose formulas and calculate their answers. After students have completed the worksheet, give them the second color of dots, and invite them to post their opinion. (You might have a second set of tables for a large class.) Photograph or record the before and after as a pre- and post-activity assessment. Additional Info Note that average fertility is calculated as number of children per woman. Male fertility is generally much more variable than female fertility in primates.1 You may share the following information with your students after they complete the pre-test. You may also show how to use Wolfram Alpha (http://www.wolframalpha.com) and look at some of the graphics related to population you can produce there. You can use the table “World Population, 1950-2010” in the downloadable data from http://www.earth-policy.org/books/fpep/fpep_data#3 or a similar source for students to determine the population in the year they were born, or you can use http://galen.metapath.org/popclk.html and allow students to enter their exact birthdate. One estimate of when population will reach 8 billion is March 15, 2029 by 11:48GMT. 2 1 2 Boyd & Silk, 2012, How Humans Evolved (6th Ed.) Based on population estimates from http://galen.metapath.org/popclk.html (10/24/11) 8 February 2016 2 Human Population M. Merrill Average US fertility was 2.05 children per woman in 2009 (http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=average+us+fertility 11/7/12) Average global fertility was 2.59 in 2009 population | 6.79 billion people (2009 estimate) population density | 118 people/mi^2 (people per square mile) (2009 estimate) population growth | 1.14 %/yr (2006 estimate) life expectancy | 64.8 years (2009 estimate) median age | 27.6 years (http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=average+global+fertility 11/7/12) Countries with the fastest population growth: 1 | Qatar | 12.6 %/yr | 2 | Liberia | 4.58 %/yr | 3 | Niger | 3.99 %/yr | 4 | French Guiana | 3.74 %/yr | 5 | Syria | 3.53 %/yr | 6 | Afghanistan | 3.49 %/yr | 7 | Burkina Faso | 3.48 %/yr | 8 | Gaza Strip | 3.35 %/yr | 9 | Uganda | 3.33 %/yr | 10 | Mayotte | 3.32 %/yr | (http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=countries+with+fastest+population+growth 11/7/12) Countries with the lowest population growth: 1 | Georgia | -1.17 %/yr | 2 | Lithuania | -1.05 %/yr | 3 | Moldova | -0.93 %/yr | 4 | Ukraine | -0.642 %/yr | 5 | Bulgaria | -0.635 %/yr | 6 | Belarus | -0.466 %/yr | 7 | Latvia | -0.443 %/yr | 8 | Romania | -0.414 %/yr | 9 | Russia | -0.385 %/yr | 10 | Dominica | -0.331 %/yr | (http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=countries+with+lowest+population+growth 11/7/12) Additional Resources: Population Reference Bureau http://www.prb.org; Pan Earth http://www.PanEarth.org; 6 Degrees of Population http://populationgrowth.org/ 8 February 2016 3 Human Population M. Merrill Population (in Millions), 10,000BC-2050AD 10000 9000 8000 Population (in Millions), 1600-2050 10000 9000 7000 8000 7000 6000 6000 5000 5000 4000 4000 3000 2000 3000 1000 0 1600 2000 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 -2000 -1000 2050 1000 0 -10000 -9000 8 February 2016 -8000 -7000 -6000 -5000 -4000 -3000 0 1000 2000 4 Human Population M. Merrill http://phys.org/news196489543.html 8 February 2016 5