Homework 1
advertisement

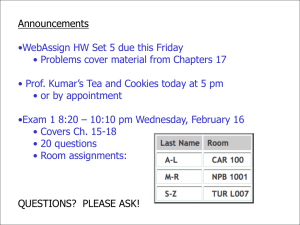
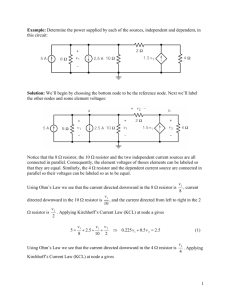
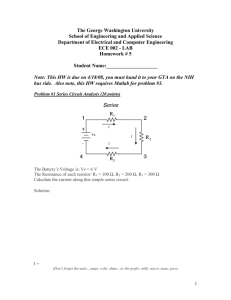
ECE 252 Introduction to Electrical Engineering Lesson 1. Basic Elements and Circuit Laws Homework Version S16 Homework partner name: _______________________Homework partner name: ________________________ Important: Sketch each circuit. Label all circuits with appropriate currents and voltages. 1. Homework policy: Copying homework and all other forms of academic dishonesty are forbidden. Use of homework assignments from previous terms is forbidden, as is looking up solutions on line, looking at the papers of others, showing others your papers, and comparing answers. Getting aid from other students on homework is acceptable if limited to general solution concepts and methods. The team members must work together, face-toface, on all parts of the assignment, that is, dividing up the work is not permitted. To verify that you have worked together, each team member must sign each problem solution at the time the problem is solved. If it is impossible for the team members to work together, each individual should turn in a separate homework assignment. Please carefully read the above policy, and then comment below. You will be given credit so long as your comments are thoughtful and sincere. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Quickies a) A +3 coulomb charge is moved from point A, which has a voltage of 15 V with respect to ground, to point B, which has a voltage of 25 V with respect to ground. The work done on the charge is _________ J. The answer is an integer. b) 480 coulombs of charge flows through a wire at a constant rate over a period of 4 minutes. The current in the wire is _______________ A. The answer is an integer. c) A 120 V toaster carries a current of 15 A when it toasts a slice of bread for 3 minutes. The power consumed by the toaster is _________ W. The resistance of the coils in the toaster is _______ Ω. The energy consumed by the toaster is ___________ J or ________ kWh. d) For an ideal independent _____________________ source, the voltage is independent of the current. It can deliver any current (from 0 to infinity) in either direction. e) For an ideal independent _____________________ source, the current is independent of the voltage. It can have any voltage (from 0 to infinity) with either polarity. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 3. E = 20 V, R1 = 800 Ω, R2 = 1200 Ω. Do not solve by combining resistors in series. a) Define and label a current for the circuit. Define and label a voltage across each resistor. b) Write Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) for the circuit. c) Write an Ohm’s Law equation for each resistor. d) Solve these three equations to find the current in the circuit. Give your answer in mA. The answer is an integer. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 4. E = 9 V, R1 = 60 Ω, R2 = 180 Ω. Do not solve by combining resistors in parallel. a) Define and label currents in R1 and R2. Define and label voltages across R1 and R2. b) Write a Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) equation at one of the essential nodes. c) Write a KVL equation for the left mesh. Write a KVL equation for the right mesh. d) Write an Ohm’s Law equation for each resistor. e) Solve these 5 equations to find I. Give your answer in mA. The answer is an integer. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 5. E = 240 V, R1 = 16 Ω, R2 = 36 Ω, R3 = 72 Ω. Do not combine resistors in series and parallel. a) Define and label a current in each resistor and a voltage across each resistor. b) Write a Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) equation at one of the essential nodes. c) Write a KVL equation for the left mesh. Write a KVL equation for the right mesh. d) Write an Ohm’s Law equation for each resistor. e) Solve these 6 equations to find the current in each resistor. The answers are integers. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 6. C1 = 15 A, C2 = 4 A, E1 = 20 V, E2 = 30 V, R1 = 40 Ω, R2 = 50 Ω. Find I2. The answer is an integer. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 7. E1 = 25 V, E2 = 72 V, R1 = 27 Ω, R2 = 100 Ω, I1 = 4.5 A. Find V1. The answer is an integer. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 8. E1 = 9 V, E2 = 10 V, R1 = 5 Ω, R2 = 11 Ω, R3 = 8 Ω, I1 = 1 A, Ix = 3 A, Iy = 6 A. Find the voltage at point A with respect to ground. The answer is an integer. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ BONUS (no partial credit). It is wise to become adept at solving simultaneous equations using modern tools. Advanced calculators have this capability, as do computer algebra systems, such as Maple. Use either a calculator with equation-solving capability or a computer algebra program to find V1, V2, V3, and V4 in the following simultaneous KVL equations. The answers will not be integers. 5V1 – 3V2 + 8V3 + 9V4 + 17 = 0 10V1 – 12V3 – 4V4 – 6 = 0 -2V2 + 7V3 – 14V4 – 16 = 0 17V1 + 18V2 – V3 – 13V4 = 0 Describe the tools you use and how to use them to solve this problem. Give your answers in decimal form. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________