Group E Snell`s Law Handout By: William Wysession and Jack
advertisement

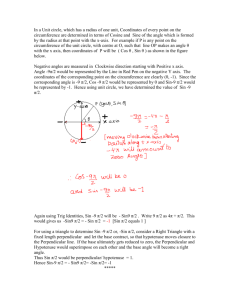
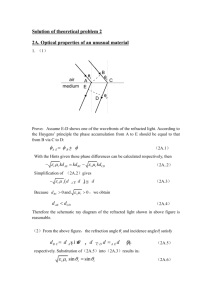
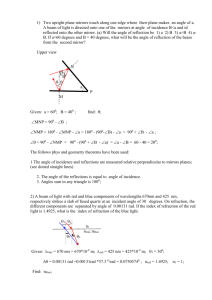
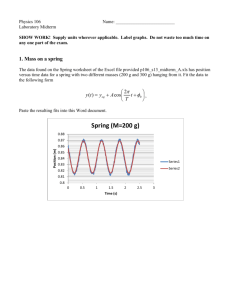
Group E Snell’s Law Handout By: William Wysession and Jack Klamer Purpose: The purpose of this experiment was to investigate the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction for an air-plastic and an air-water interface. Hypothesis: We predicted that the refracted angle squared would be directly proportional to the incident angle. Equipment: Plexiglas Semi-Cylinder Paper with 10 degree markings Laser pointer Source of water Pencil Vertical Cylindrical Water Laser Apparatus Computer with LoggerPro Plexiglas and Air Setup: Take your Plexiglas semi-cylinder and place it on your paper with 10-degree markings along one of the diameter lines (leaving the markings open). Take your laser point and place the beam along the 10-degree marking lines toward the center and observe the effect through the apparatus, recording the angle of refraction. Now flip the Plexiglas onto the markings, keeping the laser pointer in the same place in order to test Plexiglas to air refractions. You will notice something strange happen. We will discuss this. Water and Air Setup: Take your vertical cylindrical water laser apparatus and fill it halfway with water. Start by shooting the laser into the water from 0 to 90 degrees in 10-degree increments, measuring the refraction angle as you go. You will notice something strange after a little while, and we will discuss this at the end. To observe air to water refraction, move the laser pointer to the top and do the same, shooting the laser into the water and recording the refraction angle. Raw Data Air and Plexiglas Air and Water: Formal Data Table Air and Plexiglas: Air and Water: Mathematical Analyses Air to Plexiglass Semichord of Refraction vs. Semichord of Incident Semichord of Refraction SR Semichord of IncidentSI SR α SI SR =K* SI ∆SR SR K= ∆SI SI K= .672 (Slope calculated by LoggerPro) SR = .672 * SI Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Refracted Angle) Sin (Θr) Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) α Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) =K* Sin (Θi) ∆Sin (Θr) K= ∆Sin (Θi) K= .671 (Slope calculated by LoggerPro) Sin (Θr) = .671 * Sin (Θi) Plexiglass to Air Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Refracted Angle) Sin (Θr) Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) α Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) =K* Sin (Θi) ∆Sin (Θr) K= ∆Sin (Θi) K= 1.46 (Slope calculated by LoggerPro) Sin (Θr) = 1.46 * Sin (Θi) Air to Water Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Refracted Angle) Sin (Θr) Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) α Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) =K* Sin (Θi) ∆Sin (Θr) K= ∆Sin (Θi) K= .774 (Slope calculated by LoggerPro) Sin (Θr) = .774 * Sin (Θi) Water to Air Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Refracted Angle) Sin (Θr) Sin (Incident Angle) Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) α Sin (Θi) Sin (Θr) =K* Sin (Θi) ∆Sin (Θr) K= ∆Sin (Θi) K= 1.32 (Slope calculated by LoggerPro) Sin (Θr) = 1.32 * Sin (Θi) Error Analyses Air to Plexiglass Semichord of Refraction vs. Semichord of Incident Accepted Value= .672 Experimental Value= .672 Absolute Error=|𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒| Absolute Error=|. 672 − .672| Absolute Error=0 𝐴𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 Percent Error=(𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒)*100 0 Percent Error=(.6722)*100 Percent Error=0% Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Accepted Value= .672 Experimental Value= .671 Absolute Error=|𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒| Absolute Error=|. 671 − .672| Absolute Error= .001 𝐴𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 Percent Error=(𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒)*100 .001 Percent Error=(.672)*100 Percent Error=.149% Plexiglass to Air Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Accepted Value= 1.49 Experimental Value= 1.46 Absolute Error=|𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒| Absolute Error=|1.46 − 1.49| Absolute Error= 0.03 𝐴𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 Percent Error=(𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒)*100 0.03 Percent Error=(1.49)*100 Percent Error=2.01% Air to Water Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Accepted Value= 0.751 Experimental Value= .774 Absolute Error=|𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒| Absolute Error=|. 774 − .751| Absolute Error= 0.023 𝐴𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 Percent Error= (𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒) *100 0.023 Percent Error=( .751 )*100 Percent Error=3.06% Water to Air Sin (Refracted Angle) vs. Sin (Incident Angle) Accepted Value= 1.33 Experimental Value= 1.32 Absolute Error=|𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒| Absolute Error=|1.32 − 1.33| Absolute Error= 0.01 𝐴𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 Percent Error(𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒)=*100 0.01 Percent Error=(1.33)*100 Percent Error=.752% Important Terms to Know Critical Angle- The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which total internal reflection occurs. Total Internal Reflection- Total internal reflection is a phenomenon that happens when a propagating wave strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. Index of Refraction- In optics the refractive index or index of refraction n of a substance (optical medium) is a dimensionless number that describes how light, or any other radiation, propagates through that medium. Snell’s Law-