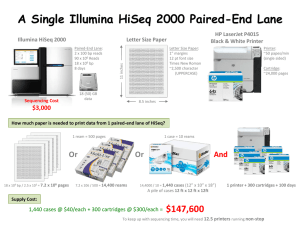
Experimental Procedures for Grant Write
advertisement

Sequencing Procedure on Illumina GAIIx and HiSeq Prior to initiating sequencing procedure, the quality of the DNA or RNA sample is analyzed on Agilent Bioanalyzer and is then processed for sequence library construction. Currently, at YCGA single-end, paired-end and barcoded sequence libraries are constructed for genomic DNA, ChIP-DNA, amplicons, mRNA, small RNA, and exome capture. Briefly, the DNA sample is fragmented to appropriate size and end repaired to generated polished blunt ends. In case of mRNA, poly A selection is made and resulting mRNA is fragmented to appropriate size prior to its conversion to cDNA. After polishing the ends, adenine base is added at the 3’ ends following which Illumina supplied specific adaptors are ligated. The adaptor ligated DNA is amplified by PCR. The PCR DNA is then purified on Qiagen PCR purification kit to get the final seq library ready for sequencing. The insert size and DNA concentration of the seq library is determined on Agilent Bioanalyzer. For sequencing, each seq library is layered on one of the eight lanes of the Illumina flow cell at appropriate concentration and bridge amplified to get around 40- 45 million raw reads for GAIIx and 8000 million raw reads for HiSeq. The DNA reads on the flow cell are then sequenced on Genome Analyzer IIx or HiSeq using appropriate base pair sequencing recipe. At the current rate, on an average 30-35 million passing filter reads per lane on GAIIx and 70-80 million passing filter reads on HiSeq are obtained, which yield 3 to 3.5 billion and 7-8 billion sequenced bases on GAIIx and HiSeq, respectively using 100 bp single end sequencing recipe. The rate of sequencing is around 1.2 hours per base. Basically, sequencing by synthesis procedure is followed by incorporation of one fluorescent labeled base at a time. At the addition of each base, the fluorescence images are captured by the in situ camera. The images are converted into intensities that in turn are called for bases. The entire process of imaging to base calling is carried out real time on the computer attached to the genome analyzer. The data is then transferred and stored in Yale HPC server Bulldog-N. The quality of the sequence and its alignment to reference genome is carried out by the Illumina supported Consensus Assessment of Sequence and Variation (CASAVA) software program. At this point the sequence data is sent to the user to download from the Bulldog N server.