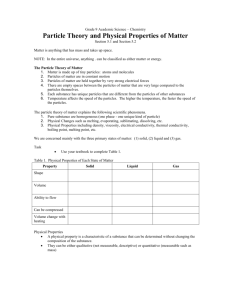
Fluid Examples
advertisement

Fluids and Viscosity Chapter One: Viscosity Describes a Fluid=s Resistance to Flow. SECTION 7.1: DESCRIBING FLUIDS Fluid any form of matter that flows. can be a liquid or a gas. Examples: water, syrup, compressed air in tires Question: Why can you pour sand, but it is not considered a fluid? Sand has a definite shape so it cannot Aflow@. The sand will not take the shape of the container. Fluid Examples Food Fluids Cleanin Body g Fluids Fluids Industrial Fluids -syrup - honey molasses - water - oil - shampoo - blood - liquid - mucus soap - saliva - hair gel - Vim - motor oil - compressed air in tires States of Matter SOLIDS LIQUIDS GASES SHAPE definite shape no definite shape no definite shape VOLUME definite volume definite volume no definite volume PARTICLE ARRANGE MENT PARTICLE MOVEMEN T particles particles particles are close are close are distant particles free random only flowing movem vibrate ent Note: Since solids and liquids both have a definite shape, they are able to flow, so by definition they are fluids. Changes of State FROM / TO SOLID SOLID LIQUID GAS ---------- Melting Sublimation LIQUID Solidification ---------- Evaporation GAS Deposition Condensatio n ---------- Particle Theory Of Matter 1. All matter is made up of tiny particles 2. All the particles in a substance are the same; different substances are made up of different particles. 3. There are attractive forces among particles - these attractions may be weak or strong. 4. These particles are always moving; the more energy the particles gain, the faster they move. 5. There are spaces among the particles. Worksheet #1: Describe what happens to water particles as water changes from solid ice to liquid water to vapor gas. Fill in the blanks SECTION 7.2 VISCOSITY AND FLOW RATE Viscosity the measure of a liquid=s resistance to flow. it=s the Athickness@ or Athinness@ of a fluid. (How runny a fluid is). describes how easily a fluid flows. Friction the rubbing of one object against another. A force that resists movement. Viscosity and Friction the more the friction, the higher the viscosity. Said to be Aviscous@ determined by the size, shape, and attraction of the particles of the substance Viscosity of Products (1) Must be easy to use (2) Must fulfill the need (3) Food and personal care products must have tactile / sensually pleasing texture and consistency Everyday Examples Many substances require the proper degree of viscosity to perform their intended function. Most times money is a factor associated with quality in any product. A good ice cream is creamy and melts in your mouth, but a cheap ice cream will be chunky and icy. Pancake batter must be of the right consistency or they would not form yummy pancakes. Too solid or runny would ruin pancake day!!!!! High Viscosity Examples Hand cream rich (viscous) to be creamy but not gummy and gross Wood Glue must adhere to surface Cough Medicine must cling to throat, but not choke you Shampoo must cling to hair, but at the same time rinse easily Paints require right viscosity in order to spread properly Low Viscosity Examples Motor Oil lubricate parts easy to apply Mouth Wash must swirl around in mouth Hand Soap must be runny in order to be pumped out of bottle Flow Rate the speed at which a fluid flows from one point to another. often used in comparing viscosity. (viscosity is hard to measure) liquids flow at different rates. Water (fast), dishwashing liquid (medium), and pancake syrup (slow) Peanut butter kept in the fridge is often too viscous to spread. So......High Flow Rate = Low Viscosity Low Flow Rate = High Viscosity Core Lab: Flow Rate of Liquids Question: What others ways could you determine the viscosity of liquids, besides the lab? (Answer: syringe with constant pressure, splatter test, measure a circular spread test) 7.3: FACTORS AFFECTING VISCOSITY The factors listed below have a bigger impact on liquids than on gasses because of the spaces between the particles. (1) Temperature A liquid=s viscosity decreases as the fluid is heated A liquids viscosity increases as the fluid is cooled. A gases=s viscosity increases as the gas is heated A gases=s viscosity decreases as the fluid is cooled. As heat is added to a liquid the particles have more energy and pull away from neighboring particles and slide past them more easily. This increases the liquid=s ability to flow, so we can state that its viscosity is lower. If heat is taken away from a liquid, the particles lose energy and move slower. Because they have less energy, it is harder for the particles to pull away from other nearby particles. The liquid loses some of its ability to flow and its viscosity becomes higher. The particle theory states that the particles in gases are already very far apart. When energy is added, gas particles speed up and collide with each other more often, causing an increase in internal friction, and therefore an increase in viscosity. Cooler temperatures in gases keep the internal friction of particles (and the viscosity) low. (2) Concentration the amount of a substance dissolved in a specific volume. generally, by increasing the concentration of a substance, the viscosity is also increased. Example; purity syrup or 2% milk vs skim milk (3) Attractive Forces Between Particles Attractive forces among particles of a substance have a major effect on the viscosity of the substance If the attractive forces between particles are strong, it=s difficult for the particles to pull away from each other, so the liquid flows slowly, and therefore has a high viscosity. If the attractive forces among the particles are weak, the particles pull apart easily, and the liquid flows easily, so the viscosity is low. (4) Particle Size and Shape Fluids that are made of small particles can flow faster (have a low viscosity) because their particles are able to move more easily and quickly. Some particles in certain fluids are bigger than others. This means that the fluid they make up flows much slower (has a higher viscosity) the shape of particles also affects their ability to slide past one another.