YEAR 10 GEOGRAPHY Population Distribution and Density
advertisement
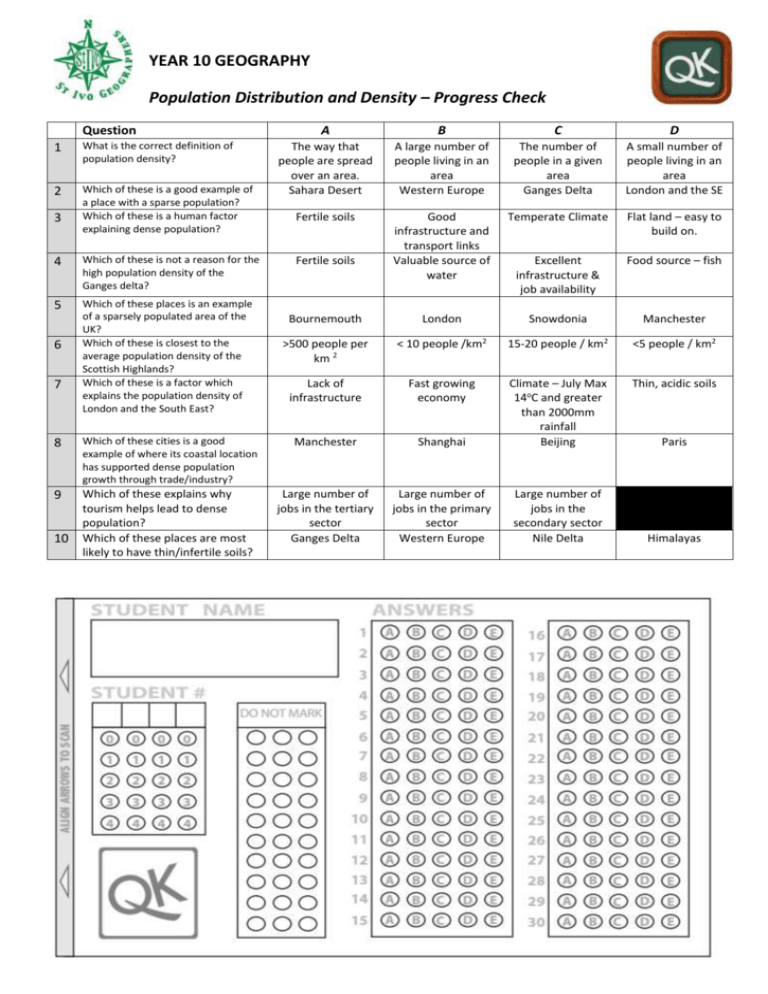
YEAR 10 GEOGRAPHY Population Distribution and Density – Progress Check Question 1 What is the correct definition of population density? 2 Which of these is a good example of a place with a sparse population? Which of these is a human factor explaining dense population? 3 4 Which of these is not a reason for the high population density of the Ganges delta? 5 Which of these places is an example of a sparsely populated area of the UK? Which of these is closest to the average population density of the Scottish Highlands? Which of these is a factor which explains the population density of London and the South East? 6 A B C D The way that people are spread over an area. Sahara Desert A large number of people living in an area Western Europe The number of people in a given area Ganges Delta A small number of people living in an area London and the SE Fertile soils Good infrastructure and transport links Valuable source of water Temperate Climate Flat land – easy to build on. Excellent infrastructure & job availability Food source – fish Bournemouth London Snowdonia Manchester >500 people per km 2 < 10 people /km2 15-20 people / km2 <5 people / km2 Lack of infrastructure Fast growing economy Thin, acidic soils Fertile soils 8 Which of these cities is a good example of where its coastal location has supported dense population growth through trade/industry? Manchester Shanghai Climate – July Max 14oC and greater than 2000mm rainfall Beijing 9 Which of these explains why tourism helps lead to dense population? Which of these places are most likely to have thin/infertile soils? Large number of jobs in the tertiary sector Ganges Delta Large number of jobs in the primary sector Western Europe Large number of jobs in the secondary sector Nile Delta 7 10 Paris Himalayas