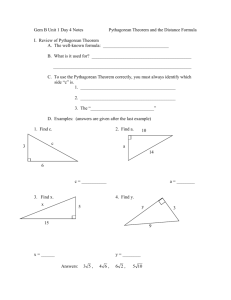
Tri. 3: 8.G.6
advertisement
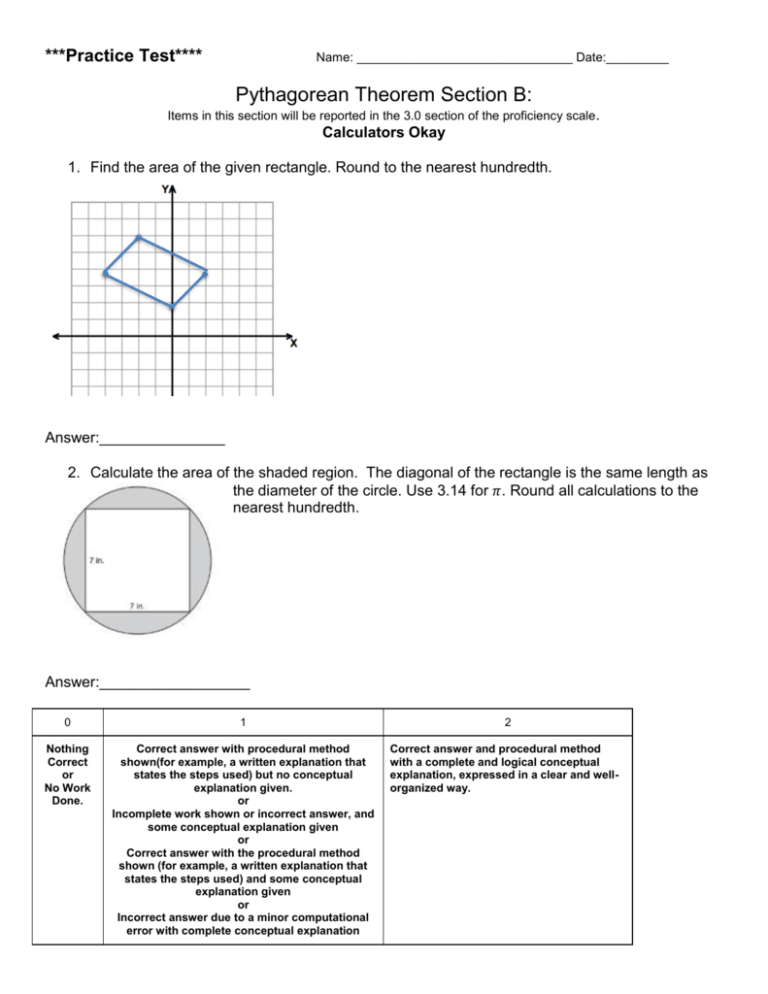
***Practice Test**** Name: _______________________________ Date:_________ Pythagorean Theorem Section B: Items in this section will be reported in the 3.0 section of the proficiency scale . Calculators Okay 1. Find the area of the given rectangle. Round to the nearest hundredth. Answer:_______________ 2. Calculate the area of the shaded region. The diagonal of the rectangle is the same length as the diameter of the circle. Use 3.14 for 𝜋. Round all calculations to the nearest hundredth. Answer:__________________ 0 1 Nothing Correct or No Work Done. Correct answer with procedural method shown(for example, a written explanation that states the steps used) but no conceptual explanation given. or Incomplete work shown or incorrect answer, and some conceptual explanation given or Correct answer with the procedural method shown (for example, a written explanation that states the steps used) and some conceptual explanation given or Incorrect answer due to a minor computational error with complete conceptual explanation 2 Correct answer and procedural method with a complete and logical conceptual explanation, expressed in a clear and wellorganized way. 3. Students in a class are using their knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem to make conjectures about triangles. A student makes the conjecture shown below. A triangle has side lengths x, y and z. If x < y < z and x2 + y2 > z2, the triangle is an acute triangle. Use Pythagorean theorem to develop a chain of reasoning to justify or refute the conjecture. You must demonstrate that the conjecture is always true or that there is at least one example in which the conjecture is not true. 4. Students in a class are using their knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem to make conjectures about triangles. A student makes the conjecture shown below. A triangle has side lengths x, y and z. If x < y < z and x2 + y2 < z2, the triangle is an obtuse triangle. Use Pythagorean theorem to develop a chain of reasoning to justify or refute the conjecture. You must demonstrate that the conjecture is always true or that there is at least one example in which the conjecture is not true.