Chapter 21 review sheet
advertisement

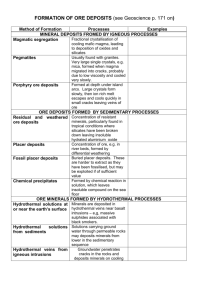
Earth Systems 3209 Chapter 21 - Review Sheet Key Terms Economic mineral Hydrothermal deposit (vein) Metamorphism Open pit mine Crude oil Diagenesis Anticline trap Stratigraphic trap Ore Placer deposit Diamond Underground mine Hydrocarbons Catagenesis Fault trap Magmatic deposit Secondary enrichment (sedimentation) Kimberlite Petroleum Kerogen Metagenesis Salt dome trap Key Topics p. 580-581: Understand that mineral resources are the basis of modern civilization: everything that does not come from a living thing has to be removed from the solid Earth. See Fig. 21.2 for a list of the most commonly used minerals by all Canadians. p. 583: Understand what is meant by the term ore and why finding ore deposits is the key to the mining industry. p. 585: Explain how magmatic deposits form and the types of minerals that can be found in them. p. 587-590: Explain how mineral veins form from hydrothermal deposits and the types of minerals that can be found in them. p. 594: Explain how placer deposits form and the types of minerals that can be found in them. p. 595-596: Explain how metamorphic deposits form and the types of minerals that can be found in them. p. 598-600: Explain how diamonds are found in deposits of Kimberlite. p. 602-603 and notes: Explain the formation of petroleum from ancient organic matter including: kerogen, diagenesis, catagenesis, and metagenesis. p. 603 – 604: describe the components involved in the formation of petroleum traps. Include: A. source rock B. reservoir rock C. cap rock p. 603-609 and notes: describe the processes and techniques involved in extracting and refining hydrocarbons.describe the methods of refining petroleum. Include: (i) distillation (ii) cracking (iii) reforming