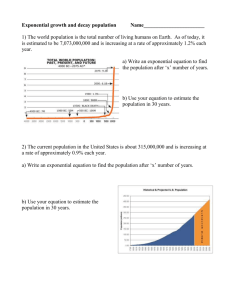
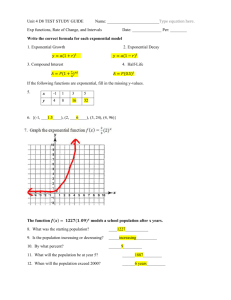
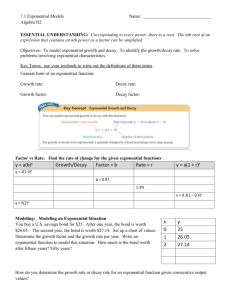
Coordinate Algebra Exponential Functions Day 2 Notes Date
advertisement

Coordinate Algebra Exponential Functions Day 2 Notes Date: _______ COMPLETED Exponential functions, just as any function, can be transformed by addition, subtraction, and multiplication. When this occurs in a problem the original function will shift left or right, up or down, and reflect. Vertical Shifts A function can travel along the y-axis by adding or subtracting within the function. Ex1) f(x) = 2x + 3 The adding 3 at the end of the function will shift the graph up three on the y-axis Original Function VS. Shifted Function Shifted Function Original Function Vertical Shifts change the asymptote! Ex2) What would happen to this function: f(x) = 2x – 3 This function will shift down 3 on the y-axis. Horizontal Shifts A function can travel along the x-axis by adding or subtracting within the function as well. Ex3) f(x) = 2x+3 The adding three in the exponent will shift the graph along the x-axis to the left. Ex4) f(x) = 2x – 3 The subtracting three in the exponent will shift the graph along the x-axis to the right. Reflections When a function is multiplied by a negative 1, the function will be reflected over the x-axis. This turns an exponential decay function into a reflected exponential decay and an exponential growth function into a reflected exponential growth. It is important to remember that these functions are still growth or decay; the reflection does not change that! 1 𝑥 Ex5) f(x) = −(2)x Ex6) f(x) = −(2) This is an exponential growth function reflected over the x-axis. This is an exponential decay function reflected over the x-axis. These transformations affect the characteristics such as Range, End Behavior, Increasing/Decreasing, and Asymptote. They will also affect the x-values we choose for the table if the graph is shifted horizontally. If the function has been shifted left or right by addition in the exponent then you need to adjust your table values. Instead of using the standard (-1, 0, 1) values you will use the adjusted values as seen in the example below. Ex7) f(x) = 2x+3 Instead of using -1, 0, 1 subtract 3 to all these values and use those in the table -1 − 3 = -4 0 − 3 = -3 1 − 3 = -2 x f(x) -4 ½ or 0.5 -3 1 -2 2 y=0 *We do this to make the table values easier points to graph. Circle One: Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Reflected Exponential Growth Reflected Exponential Decay Domain: _____ ℝ _________ Range: ____ y > 0 ________ Asymptote: _____ y = 0 _______ Increasing or Decreasing End Behavior: x ∞, y __ ∞ ___; x −∞, y __ 0 ____ 𝟕 Average Rate of Change for -3 ≤ x ≤ 0: ____ 𝟑 𝒐𝒓 𝟐. 𝟑𝟑 _______ (-3, 1) & (0, 8) 𝟖−𝟏 𝟕 = 𝟑 ≈ 𝟐. 𝟑𝟑 𝟎−−𝟑 3 𝑥 Ex8) f(x) = (2) + 4 x -1 𝟏𝟒 𝟑 or 4.67 0 1 y=4 f(x) 5 𝟏𝟏 𝟐 or 5.5 Circle One: Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Reflected Exponential Growth Reflected Exponential Decay Domain: _____ ℝ _________ Range: ____ y > 4 ________ Asymptote: _____ y = 4 _______ Increasing or Decreasing End Behavior: x ∞, y __ ∞ ___; x −∞, y __ 4 ____ 𝟏 Average Rate of Change for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1: _____ 𝟐 𝒐𝒓 𝟎. 𝟓 __________ (0, 5) & (1, 5.5) 𝟓.𝟓−𝟓 𝟎.𝟓 = 𝟏 = 𝟎. 𝟓 𝟏−𝟎 Ex9) f(x) = −(2)𝑥−3 Instead of using -1, 0, 1 add 3 to all these values and use those in the table -1 + 3 = 2 0+3=3 1+3=4 Circle One: Exponential Growth x f(x) 2 −½ or −0.5 3 −1 4 −2 Exponential Decay Reflected Exponential Growth y=0 Reflected Exponential Decay Domain: _____ ℝ _________ Range: ____ y < 0 ________ Asymptote: _____ y = 0 _______ Increasing or Decreasing End Behavior: x ∞, y __ −∞ ___; x −∞, y __ 0 ____ Average Rate of Change for 3 ≤ x ≤ 4: ______ -1 _________ (3, -1) & (4, -2) −𝟐−−𝟏 −𝟏 = 𝟏 = −𝟏 𝟒−𝟑 2 𝑥−2 Ex10) f(x) = (5) −3 Instead of using -1, 0, 1 add 2 to all these values and use those in the table x f(x) 1 −½ or −0.5 −2 2 -1 + 2 = 1 0+2=2 1+2=3 3 Circle One: Exponential Growth − 𝟏𝟑 𝟓 y = -3 or -2.6 Exponential Decay Reflected Exponential Growth Reflected Exponential Decay Domain: _____ ℝ _________ Range: ____ y > -3 ________ Asymptote: _____ y = -3 _______ Increasing or Decreasing End Behavior: x ∞, y __ −3 ___; x −∞, y __ ∞ ____ 𝟑 Average Rate of Change for 1 ≤ x ≤ 2: ______ − 𝟐 or −1.5 _________ (1, -0.5) & (2, -2) −𝟐−−𝟎.𝟓 −𝟏.𝟓 = 𝟏 = −𝟏. 𝟓 𝟐−𝟏 1 𝑥 Ex11) f(x) = −(3) + 2 x f(x) -1 −1 0 1 1 𝟓 𝟑 y=2 or 1.67 Circle One: Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Reflected Exponential Growth Reflected Exponential Decay Domain: _____ ℝ _________ Range: ____ y < 2 ________ Asymptote: _____ y = 2 _______ Increasing or Decreasing End Behavior: x ∞, y __ 2 ___; x −∞, y __ −∞ ____ Average Rate of Change for -2 ≤ x ≤ 0: ______ 4 _________ (-2, -7) & (0, 1) 𝟏−−𝟕 𝟖 =𝟐=𝟒 𝟎−−𝟐