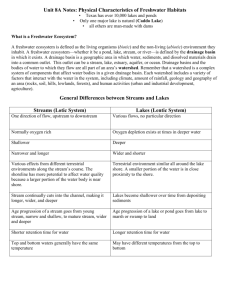
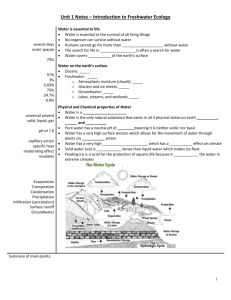
The Basics of Freshwater Ecosystems
advertisement
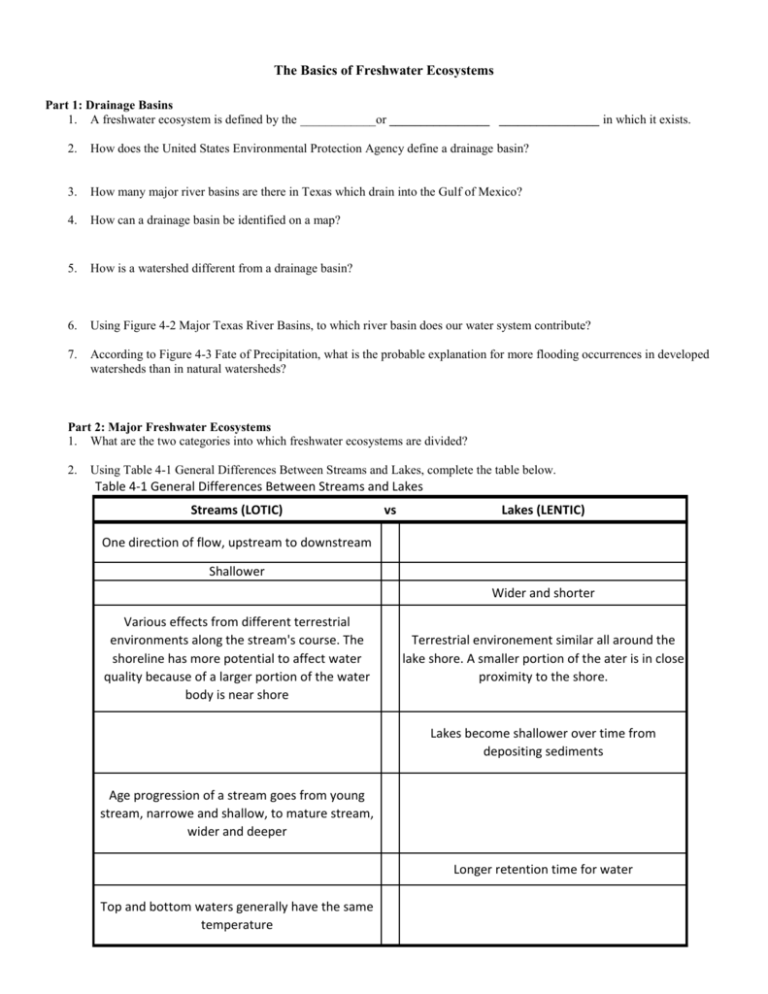
The Basics of Freshwater Ecosystems Part 1: Drainage Basins 1. A freshwater ecosystem is defined by the ____________or ________________ ________________ in which it exists. 2. How does the United States Environmental Protection Agency define a drainage basin? 3. How many major river basins are there in Texas which drain into the Gulf of Mexico? 4. How can a drainage basin be identified on a map? 5. How is a watershed different from a drainage basin? 6. Using Figure 4-2 Major Texas River Basins, to which river basin does our water system contribute? 7. According to Figure 4-3 Fate of Precipitation, what is the probable explanation for more flooding occurrences in developed watersheds than in natural watersheds? Part 2: Major Freshwater Ecosystems 1. What are the two categories into which freshwater ecosystems are divided? 2. Using Table 4-1 General Differences Between Streams and Lakes, complete the table below. Table 4-1 General Differences Between Streams and Lakes Streams (LOTIC) vs Lakes (LENTIC) One direction of flow, upstream to downstream Shallower Wider and shorter Various effects from different terrestrial environments along the stream's course. The shoreline has more potential to affect water quality because of a larger portion of the water body is near shore Terrestrial environement similar all around the lake shore. A smaller portion of the ater is in close proximity to the shore. Lakes become shallower over time from depositing sediments Age progression of a stream goes from young stream, narrowe and shallow, to mature stream, wider and deeper Longer retention time for water Top and bottom waters generally have the same temperature Lotic Systems 3. What types of bodies of water are included in lotic environments? 4. Define the following terms: First order streams (headwater streams): Second order streams: Third order streams: 5. How are steams categorized if a second-order stream flows into a third order stream? 6. Describe the following stream types: Perennial: Intermittent: Ephemeral: 7. Why are urban streams considered effluent dominated? 8. What is an aquifer and how is it formed? 9. What is the water table? 10. What is the difference between losing streams and gaining streams? 11. Complete the table below: Table 4-2 Aquatic Stream Habitats Characteristics Flow Lotic-erosional Relatively shallow area of a stream. Three areas defined by flow: Riffle: Run: Glide: Lotic-depositional Relatively deep and wide with slow moving water compared to riffles, runs, or glides *Primarily found in pools and backwater areas or streams Sediment * Fine sediment comprised of sand and silt Aquatic Plants (macrophytes) Aquatic animals Plants typically grow on or in coarse sediment (pondweed) * Organisms similar to those found in lakes and pond systems (dragonflies, damselflies, water Aquatic insects and small fish that require high striders) oxygen levels, flowing water fro feeding, and are adapted to living in swift water through the ability to swim or cling to rocks in riffle areas Organis materials(detrius) 12. How are meanders created and why do they change? Comprised of leaf litter and other particulate matter found at the bottom of pools and backwater areas of streams 13. Define the following terms: Erosional Zone: Depositional Zone: Riparian Zone: 14. Why are riffle areas in the erosional zone important? 15. Within depositional zones, what are the areas that are relatively deep and wide with slow-moving water called? 16. How are riparian zones important? 17. Which three abiotic factors determine the quality of a stream? 18. Using Figure 4-6 on page 26, label the diagram below of stream habitats. Lentic Systems 19. What type of environments are included in lentic environments? 20. Name the three types of lakes and describe how they are formed. 21. With the exception of playa lakes, ____________, and Caddo Lake in East Texas, lakes in Texas are ___________________________, ___________________________________________________, or _______________________________________________. 22. Approximately how many reservoirs and lakes does Texas have and how much surface area do they cover? 23. What are wetlands? 24. Describe the following categories of wetlands: Marshes: Swamps: Bogs: Fens: 25. Describe the following three major zones (habitats) within lentic systems. Littoral Limnetic Profundal 26. Which zone does not allow any photosynthesis at all? 27. Which zone is shallow enough to allow light penetration to the bottom? 28. Which zone is characterized by the lack of rooted plants? 29. List and describe the three categories of plants found in the littoral zone. 30. For the following categories of aquatic animals found in the littoral zone, describe the category and give an example: Neuston: Nekton: Periphyton: Benthos: Plankton: 31. Use Figure 4-8 on page 30 to label the diagram below. 32. What is succession? 33. What happens to ponds and lakes during succession?