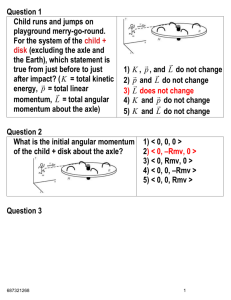
Worksheet - PHYS 172 Fall 2014
advertisement
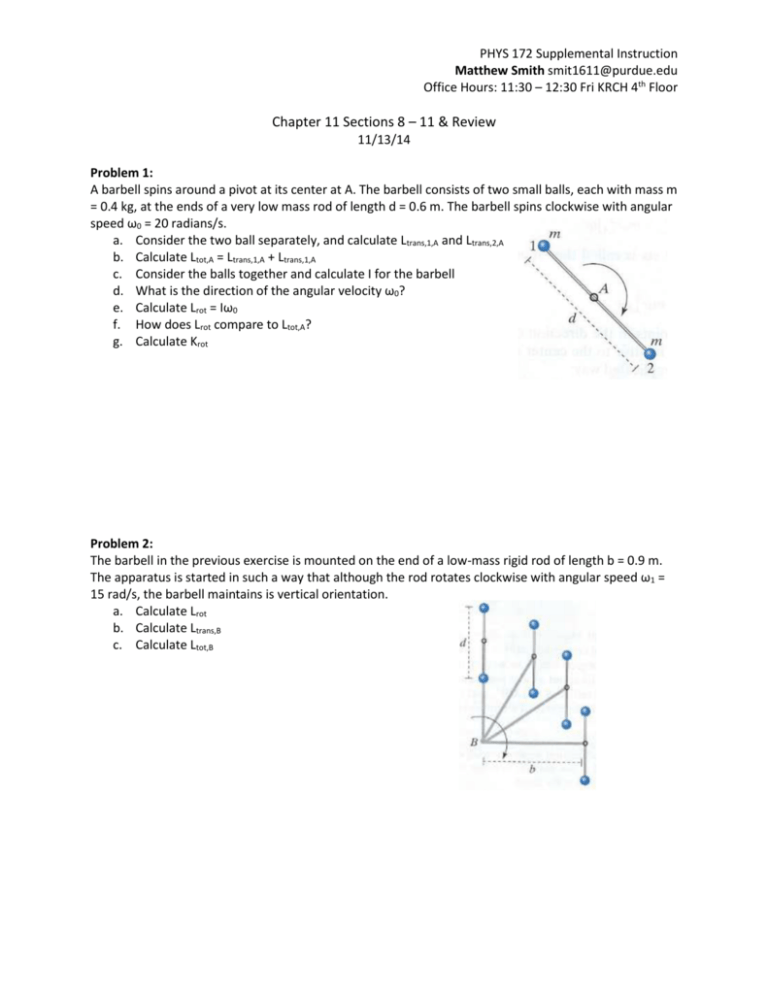
PHYS 172 Supplemental Instruction Matthew Smith smit1611@purdue.edu Office Hours: 11:30 – 12:30 Fri KRCH 4th Floor Chapter 11 Sections 8 – 11 & Review 11/13/14 Problem 1: A barbell spins around a pivot at its center at A. The barbell consists of two small balls, each with mass m = 0.4 kg, at the ends of a very low mass rod of length d = 0.6 m. The barbell spins clockwise with angular speed ω0 = 20 radians/s. a. Consider the two ball separately, and calculate Ltrans,1,A and Ltrans,2,A b. Calculate Ltot,A = Ltrans,1,A + Ltrans,1,A c. Consider the balls together and calculate I for the barbell d. What is the direction of the angular velocity ω0? e. Calculate Lrot = Iω0 f. How does Lrot compare to Ltot,A? g. Calculate Krot Problem 2: The barbell in the previous exercise is mounted on the end of a low-mass rigid rod of length b = 0.9 m. The apparatus is started in such a way that although the rod rotates clockwise with angular speed ω1 = 15 rad/s, the barbell maintains is vertical orientation. a. Calculate Lrot b. Calculate Ltrans,B c. Calculate Ltot,B PHYS 172 Supplemental Instruction Matthew Smith smit1611@purdue.edu Office Hours: 11:30 – 12:30 Fri KRCH 4th Floor Problem 3: The apparatus in the previous exercise is restarted in such a way that it again rotates clockwise with angular speed ω1 = 15 rad/s, but in addition, the barbell rotates clockwise about its center, with an angular speed ω2 = 20 rad/s. a. Calculate Lrot b. Calculate Ltrans,B c. Calculate Ltot,B Problem 4: Two people are sitting on a seesaw as shown. The person on the left has mass M1 =90 kg and sits at a distance d1 = 1.2 m from the nearly frictionless axle. The person on the right has mass M2 = 40 kg. What is the upward force that the axle must exert? Where must the person on the right sit in order that the seesaw not rotate? Problem 5: A uniform-density wheel of mass 6 kg and radius 0.3 m rotates on a low-friction axle. Starting from rest, a string wrapped around the edge exerts a constant force of 15 N for 0.6 s. a. What is the final angular speed? b. What is the average angular speed? c. Through how big an angle did the wheel turn? d. How much string came off the wheel? PHYS 172 Supplemental Instruction Matthew Smith smit1611@purdue.edu Office Hours: 11:30 – 12:30 Fri KRCH 4th Floor Problem 6: A playground ride consists of a uniform-density disk of mass 300 kg and radius 2 m mounted on a low friction axle. Starting from a distance of 5 m from the disk, a child of mass 40 kg runs at 3 m/s on a line tangential to the disk and jumps onto the outer edge of the disk. If the disk was initially at rest, how fast does it rotate just after the collision? Problem 7: What is the difference between an elastic collision and an inelastic collision? What is a maximally inelastic collision? Problem 8: What is the difference between a bound and unbound system? Problem 9: How much energy is at the lowest three levels of a hydrogen atom? (N = 1, 2, 3) Problem 10: When and where is your exam 3?