File
advertisement

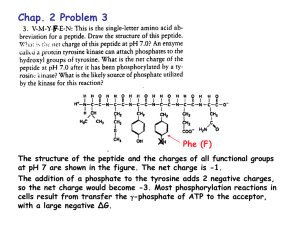
New Biology Textbook (Biology by Miller & Levine) Chap 1 – Science of Biology What is Science – what science is and is not Science in Context – discovery, ideas, communicating, sharing, theories, society Studying Life – characteristics of living things, big ideas, fields of bio, performing biological investigations Chap 2 – Chemistry of Life Nature of matter – atoms, elements, isotopes, chemical compounds, bonds, technology & biology Properties of Water – water molecule, solutions and suspensions, acids, bases, pH Carbon Compounds – chemistry of carbon, macromolecules Chemical Reactions and Enzymes – chemical reactions, energy in reactions, enzymes Chap 3 – The Biosphere What is Ecology – studying our living planet, biotic and abiotic factors, ecological methods Energy, Producers and Consumers – producers and consumers Energy Flow in Ecosystems – food chains and webs, trophic levels and ecological pyramids Cycles of Matter – recycling in biosphere, water cycle, nutrient cycles, nutrient limitation, technology, and biology Chap 4 – Ecosystems & Communities Climate – weather and climate, factors that affect climate Niches & Community Interactions – the niche, competition, predation, herbivory and keystone species, symbioses, careers and biology Succession – primary and secondary succession, climax communities Biomes – major biomes, other land areas Aquatic Ecosystems – conditions underwater, freshwater ecosystems, estuaries, marine ecosystems Chap 5 – Populations How Populations Grow – describing populations, population growth, exponential growth, logistic growth Limits to Growth – limiting factors, density-dependent & density-independent factors Human Population Growth – historical overview, patterns of human growth Chap 6 – Humans in the Biosphere A Changing Landscape – effect of human activity, sustainable development Using Resources Wisely – soil, freshwater and atmospheric resources Biodiversity – what is biodiversity, conserving biodiversity Meeting Ecological Challenges – ecological footprints, ecology in action Chap 7 – Cell Structure & Function Life is Cellular – discovery of the cell, exploring the cell, prokaryotes and eukaryotes Cell Structure – cell organization, organs that store, clean up and support, organelles that build proteins, organelles that capture and release energy, cellular boundaries Cell Transport – passive and active transport Homeostasis and Cells – the cell as an organism, multicellular life Chap 8 – Photosynthesis Energy & Life – chemical energy and ATP, heterotrophs and autotrophs An Overview of Photosynthesis – chlorophyll and chloroplasts, high-energy electrons, an overview of photosynthesis The Process of Photosynthesis – light-dependent (generating ATP and NADPH), lightindependent reactions (producing sugars), factors affecting photosynthesis Chap 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation An Overview of Cellular Respiration – chemical energy and food, overview, comparing photosynthesis and cellular respiration The Process of Cellular Respiration – glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport and ATP synthesis, the totals Fermentation – fermentation, energy and exercise Chap 10 – Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction – limits to cell size, cell division and reproduction Process of Cell Division – chromosomes, the cell cycle, mitosis, cytokinesis Regulating the Cell Cycle – controls on cell division, cancer, uncontrolled cll growth Cell Differentiation – from one cell to many, stem cells and development, frontiers in stem cell research Chap 11 – Introduction to Genetics Work of Mendel - the experiments of Mendel, segregation Applying Mendel’s Principles – probability and Punnett squares, independent assortment, summary of Mendel’s principles Other Patterns of Inheritance – beyond dominant and recessive alleles, genes and the environment Meiosis – chromosome number, phases of meiosis, comparing meiosis and mitosis, gene linkage and gene maps Chap 12 – DNA Identifying the Substance of Genes - - bacterial transformation, bacterial viruses, role of DNA Structure of DNA – components of DNA, solving the structure of DNa, doubles-helix model DNA Replication – copying the code, replication in living cells Chap 13 – RNA and Protein Synthesis RNA – role of RNA, RNA synthesis Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis – the genetic code, translation, molecular basis of heredity Mutations – types of mutations, effects of mutations Gene Regulation & Expression – prokaryotic gene regulation, eukaryotic gene regulation, genetic control of development Chap 14 – Human Heredity Human Chromosomes – karyotypes, transmission of human traits, human pedigrees Human Genetic Disorders – from molecule to phenotype, chromosomal disorders Studying the Human Genome – manipulating DNA, the Human Genome Project Chap 15 – Genetic Engineering Selective Breeding – selective breeding, increasing variation Recombinant DNA – copying DNA, changing DNA, transgenic organisms Applications of Genetic Engineering – agriculture and industry, health and medicine, personal identification Ethics and Impacts of Biotechnology – profits and privacy, safety of transgenics, ethics of the new biology Chap 16 – Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Darwin’s Voyage of Discovery – Darwin’s Epic Journey, observations aboard the Beagle Ideas That Shaped Darwin’s Thinking – an ancient, changing Earth, Lamarck’s hypotheses, population growth, artificial selection Darwin Presents His Case – evolution by natural selection, common descent Evidence of Evolution – biogeography, age of Earth and fossils, comparing anatomy and embryology, genetics and molecular biology, testing natural selection Chap 17 –Evolution of Populations Genes & Variation – genetics joins evolutionary theory, sources of genetic variation, single-gene and polygenic traits Evolution as Genetic Changes in Populations – how natural selection works, genetic drift, evolution vs. genetic equilibrium Process of Speciation – isolating mechanism, speciation in Darwin’s Finches Molecular Evolution – timing lineage splits (molecular clocks), gene duplication, developmental genes and body plans Chap 18 – Classification Finding Order in Diversity – why classify, assigning scientific names, Linnaean classification system Modern Evolutionary Classification – evolutionary classification, cladograms, DNA in classification Building the Tree of Life – changing ideas about kingdoms, the tree of all life Chap 19 – History of Life The Fossil Record – fossils and ancient life, dating Earth’s history, geologic time scale, processes affecting life’s history Patterns & Processes of Evolution – speciation and extinction, rate of evolution, adaptive radiation and convergent evolution, co-evolution Earth’s Early History –the mysteries of life’s origins, origin of eukaryotic cells, sexual reproduction and multicellularity, Chap 20 – Viruses & Prokaryotes Viruses – discovery of viruses, viral infections Prokaryotes – classifying prokaryotes, structure and function, importance of prokaryotes Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses – bacterial diseases, viral diseases, emerging diseases Chap 21 – Protists & Fungi Protist Classification – the first eukaryotes, protists – ancestors and descendants Protist Structure & Function – how protists move, protest reproduction Ecology of Protists – autotrophic and heterotrophic protists, symbiotic – mutualists and parasites Fungi – what are fungi, the ecology of fungi Chap 22 – Introduction to Plants What is a Plant – characteristics of a plant, history and evolution of plants, the plant life cycle Seedless Plants – green algae, mosses and other bryophytes, vascular plants Seed Plants – importance of seeds, life cycle of a gymnosperm Flowering Plants – flowers and fruits, angiosperm diversity Chap 23 – Plant Structure & Function Specialized Tissues – seed plant structure, plant tissue systems, plant growth and meristems Roots – root structure and growth, root functions Stems – stem structure and function, growth of stems Leaves – leaf structure and function, gas exchange and homeostasis Transport in Plants – water transport, nutrient transport Chap 24 – Plant Reproduction & Response Reproduction in Flowering Plants – structure of flowers, angiosperm life cycle, vegetative reproduction Fruits & Seeds – seed and frit development, seed dispersal, seed dormancy and germination Plant Hormones – hormones, tropisms and rapid movements, response to seasons Plants & Humans – agriculture, fiber, wood and medicine Chap 25 - Introduction to Animals What is an Animal – characteristics of animals, types of animals, what animals do to survive Animal Body Plans & Evolution – features of body plans, cladogram of animals Chap 26 – Animal Evolution & Diversity Invertebrate Evolution & Diversity – origins of invertebrates, cladogram of invertebrates Chordate Evolution & Diversity – origin of chordates, cladogram of chordates Primate Evolution – what is a primate, evolution of primates, hominine evolution, the road to modern humans Chap 27 – Animal Systems I Feeding & Digestion – obtaining food, processing food, specializations for different diets Respiration – gas exchange, respiratory surfaces of aquatic animals, respiratory surfaces of terrestrial animals Circulation – open and closed circulatory systems, single- and double-loop circulation Excretion – ammonia problem, excretion in aquatic animals, excretion in terrestrial animals Chap 28 – Animal Systems II Response – how animals respond, trends in nervous system evolution, sensory systems Movement & Support – types of skeletons, muscles and movement Reproduction – asexual and sexual reproduction, internal and external fertilization, development and growth, reproductive diversity in chordates Homeostasis – inter-relationship of body systems, body temperature control Chap 29 – Animal Behavior Elements of Behavior – behavior and evolution, innate behavior, learned behavior, complex behaviors Animals in Their Environments – behavioral cycles, social behavior, communication Chap 30 – Digestive & Excretory Systems Organization of the Human Body – organization of the boy, homeostasis Food & Nutrition – food and energy, nutrients, nutrition and a balanced diet The Digestive System – functions of the digestive system, process of digestion, absorption and elimination The Excretory System – structures of the excretory system, excretion and the kidneys, the kidneys and homeostasis Chap 31 – Nervous System The Neuron – functions of the nervous system, neurons, the nerve impulse The CNS – the brain and spinal cord, addiction and the brain The PNS – sensory division, motor division The Senses – touch and related senses, smell and taste, hearing and balance, vision Chap 32 – Skeletal, Muscular, & Integumentary System The Skeletal System – the skeleton, bones, joints The Muscular System – muscle tissue, muscle contraction, muscles and movement Skin – The Integumentary System – functions and structures of the integumentary system, skin problems Chap 33 – Circulatory & Respiratory Systems The Circulatory System – functions of the circulatory system, the heart, blood vessels Blood and the Lymphatic System – blood, the lymphatic system, circulatory system diseases, understanding circulatory disease The Respiratory System – structures of the respiratory system, gas exchange and transport, breathing, smoking and the respiratory system Chap 34 – Endocrine & Reproductive Systems The Endocrine System – hormones and glands, hormone action Glands of the Endocrine System – human endocrine glands, control of the endocrine system The Reproductive System – sexual development, the male and female reproductive systems, STDs Fertilization & Development – fertilization and early development, later development Chap 35 – Immune System & Disease Infectious Disease – causes of infectious diseases, how disease spread Defenses Against Infection – nonspecific, specific, the immune system, the immune system in action Fighting Infections Disease – acquired immunity, public health and medication, new and re-emerging diseases Immune System Disorders – when the immune system “misfires”, HIV and AIDS