Unit 4 – Inside Earth - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

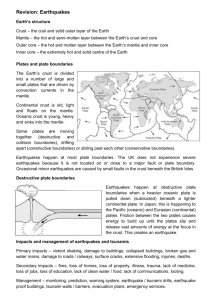
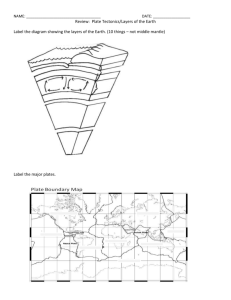
Name____________________ Test Date____________ Parent Signature____________________________ Unit 4 – Inside Earth OVERVIEW - Surface and subsurface processes that are involved in the formation and destruction of earth materials are identified in this unit. Standard for this unit Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface and climate of the Earth. ---------------------------------------------------------Questions – students will be asked to answer these during this unit of study #1 How are the earth’s layers alike and different? #2 What challenges stand in the way of sending explorers to the center of the earth? #3 How does the movement of lithospheric plates cause major events on earth’s surface? #4 What evidence do scientists have that continents were once joined together? #5 Why do mountains often occur in ranges thousands of kilometers long? #6 What can fossils tell us about movements of the plates in the past? 1. The earth is layered with __________________ metallic, inner core is____________, outer core is _______ __________________ solid but is hot enough to __________________ __________________ made of ________________ and __________________ 2. Draw a picture of Earth’s layers. 3. Each layer differs in __________________, __________________& _____________ 4. Complete the chart. Layer Composition Density Temperature 5. Temperature and density __________________ as __________________ increases. 6. The composition of the earth _______________ with _________________ and layers. 7. The crust is the ______________________ of the rigid__________________ and is of different composition under land as opposed to the ocean floor. 8. The__________ types of crust are the __________________ crust which is more __________________ and it is made primarily of __________________ . The __________________ crust is made up mainly of __________________. 9. Why is there different density between the types of crust? The oceanic crust is ______________________________________________________________________ above and the granite is transformed into __________________ 10. The_____________________________is the coolest layer of the earth. 11. Below the rigid lithosphere, the mantle consists of ___________________________ consistency, which ___________________________________ or flows. 12. Hot rocks rising and falling in the mantle/asthenosphere is called _______________. 13. The______________________is the smallest layer of the Earth and it comprise __ % of the Earth’s total mass. 14. The __________________ comprises ______% of the Earth’s total mass. 15. The____________is the hottest layer of the Earth and together they represent ____% of the Earth’s total mass. 16. The outer core is _________ and the inner core is a __________________________. 17. The mantle is solid but capable of _____________ (like hot asphalt or fudge). Under special conditions like at __________________ and along ___________________________________ the mantle or crust melt to make __________________ ,which may then rise to the surface to make a volcanic eruption. 18. Heat from the mantle and core creates __________________________________. 19. Lithospheric plates on the scales of continents and oceans _____________________. 20. The lithosphere is divided into ___________________________________ which move __________________ in response to the __________________. 21. Plate movement causes major geologic events such as __________________, __________________, and __________________________________ 22. At the edges or ___________________________________ of the plates, the earth's crust is in __________________. 23. The theory of _________________________________ connects the evidence for the ________________________, __________________, and _______________________ of the plates. 24. Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from these __________________________________. 25. Some changes in the earth’s surface are __________________ such as __________________ and ___________________________________ while other changes happen very __________________ such as __________________ and _________________________________ of mountains. 26. At __________________ plate boundaries such as the mid-Atlantic ridge, new ocean floor is created. 27. At __________________ plate boundaries known as subduction zones, a trench and deep earthquakes mark the zone where a slab of oceanic lithosphere descends into the mantle, and volcanoes and mountain ranges form on adjacent land. 28. When continental crust meets continental crust at a convergent boundary, a collision occurs, resulting in __________________, __________________, and ____________ __________________________________________ 29. __________________ boundaries are where plates slide past each other. They connect other plate boundaries and are characterized by earthquakes. 30. Earthquakes occur in the ___________________________________. 31. Geologists analyze ______________________________ (__________________ ) to determine the composition of the layers within Earth. 32. A machine that measures earthquakes is called a __________________ and the picture that this machine draws is called a __________________. 33. The __________________ is the exact location where an earthquake begins while the __________________ is the spot on the Earth’s surface immediately above where the earthquake hit. 34. There are ____ main types of earthquake waves: ____ wave, _____ wave, and __________________ wave 35. The ____ wave is the fastest wave and the__________________ destructive. 36. The __________________ wave is the slowest wave and the__________________ destructive. 37. S waves are blocked by __________________. Since seismographs on the opposite side of the Earth do not receive any S waves after an earth quake so scientists have concluded that the Earth has _________________________________. 38. A _________________________________ is formed on the opposite side of the Earth from where the earthquake occurred because _____________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 39. The __________________ scale measures the strength of earthquakes. 40. A 5.0 earthquake is approximately __________________ stronger than a 4.0 earthquake. 41. If you are inside a building, the best thing to do when an earthquake occurs is ___________________________________________________________________. 42. Moving plates cause ________________________________in a world map over __________________________________ of years. 43. ___________________________was the most recent of a succession of ___________________________________ that have formed and broken up over time. 44. Earthquakes represent ___________________________________ continuously stressed by plate movement. Gradually over time, the same movements result in __________________________________________________. Vocabulary Plate Tectonics Magma Continental Drift volcanic activities fossil evidence convection currents Subduction plate boundaries Rifting Transform faults Map of plate boundaries Earthquakes Volcanoes Seismogram Seismograph Shadow Zone Epicenter Focus