CUSTOMER_CODE
SMUDE
DIVISION_CODE
SMUDE
EVENT_CODE
SMUAPR15
ASSESSMENT_CODE EM0006_SMUAPR15
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
41905
QUESTION_TEXT
Describe the major sources of air pollution.
SCHEME OF
EVALUATION
Some major sources of air pollution are as follows:
• Industrial sources (3 marks – with explanation)
• Mobile sources (3 marks – with explanation)
• Other sources of air pollution (4 marks – with
explanation)
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
41909
QUESTION_TEXT
What are the significance of spatial technology in disaster management?
SCHEME OF EVALUATION
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Early warning (2 marks)
Disaster magnitude estimation (2 marks)
Communication (1.5 marks)
City planning (1.5 marks)
Monitoring and mitigation (1.5 marks)
6.
Models and demonstrations (1.5 marks)
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
41910
QUESTION_TEXT
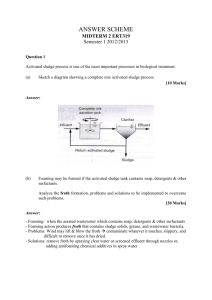
Explain the types of sludge treatment process. Describe different uses
of treated wastewater.
SCHEME OF
EVALUATION
Types of sludge treatment process (1.25X4=5)
Anaerobic Digestion: It is the process of treating sludge without the
presence of oxygen. The bacteria used in this process do not need
oxygen supply to function. They teed off the organic matter in the
sludge, using it as food and producing similar bacteria to help hasten
the process. For anaerobic digestion, sludge is left for fermentation.
The bacteria can do their job well in the fermented sludge. This
process of sludge treatment creates high amounts of methane which
is used as an extra energy supply to power generators and boilers
for heat. The treatment process can be thermophilic or mesophilic.
Most sludge treatment processes are mesophilic because
thermophilic processes require higher amounts of energy, thus
increasing the cost of sludge treatment. Anaerobic digestion may
also be used in combination with aerobic digestion to get good
results. This reduces the biochemical oxygen demand to almost 40
per cent.
Aerobic Digestion: In this process, the bacteria used for sludge
treatment require oxygen to function. In the presence of oxygen, the
bacteria use up organic matter quickly and produce large amounts of
carbon dioxide. This process costs more than anaerobic digestion
because of the added cost of air pumps, blowers and motors needed
to induce oxygen into the process.
Compositing: This process, is initiated when a large amount of
sludge is mixed with a small amount of carbon content like
sawdust or woodchips. In compositing, the bacteria digest the
oxygen as well as the organic matter in the sludge like other
processes. But they also digest the carbon content in the sludge and
produce large amounts of heat which can be transported and used
as energy elsewhere in the plant.
Incineration: It is the least used sludge treatment process because of
its high cost. The high cost arises because of the fuel required to
burn the low-calorific value sludge and remove residual water. Also,
air emissions are a cause of concern in using incineration for sludge
treatment.
The treated wastewater is used for many purposes some of which
are described below: ( 5 marks )
Urban Reuse: Wastewater after treatment is used in water public
parks, school yards, flushes, drain cleaning and in a number of
commercial buildings. It is also used for landscaping in houses and in
public and commercial air conditioners which need large amounts of
hydration.
Agricultural reuse: It is used in the irrigation of non-food crops. It is
not used for food crops because it is not completely treated and is
not fit to be mixed with anything which will be consumed by
humans. However, after high-quality treatment, wastewater could
be fit for food crops as well as used in local nurseries and small
plantations.
Recreational impoundment; Wastewater can be used to rebuild
small water bodies in certain areas where drought has destroyed the
natural and scenic beauty.
Environment reuse: Wastewater can be used in the construction of
wetlands and for enhancing existing natural and man-made
wetlands. It is also used to regulate water flow in a number of
streams.
Industrial reuse: Wastewater is pumped into cooling towers to
maintain a certain temperature of machinery or it is used in makeup
water.
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
125725
QUESTION_TEXT
How do landslides impact the social, economic and natural
environment of the affected area?
Loss of lives: (1X10=10)
Landslides can severely affect human settlements in the area of their
impact. They can lead to the death of a large number of people apart from
injuries to scores of others.
Lower human settlement: An area already gone through a landslide
has reduced chances of new human settlements coming up for the
fear of being caught in a landslide again.
Destruction of infrastructure: Landslides take a heavy toll on the
economy because of their destructive consequences for the economic
infrastructure in the affected area. They lead to the damage or
destruction of a number of homes, offices and buildings.
Huge cost of recovery: The economy has to incur huge costs to carry
out rescue and evacuation activities in the landslide-affected areas
and also on redevelopment/relocation activities.
SCHEME OF
EVALUATION
Disruption of dams: Landslides which occur near rivers and are
drained into rivers may lead to the collection of their mass near a
dam which can block the flow of water to the dam. This can severely
damage the dam machinery.
Terrain modification: The run-off and mixing of different kinds of
mass following a landslide may lead to a collection at the bottom of
the slope. This collection would cover the fertile soil with the
infertile, loose and bad- quality soil that came down with the
landslide.
Environmental deterioration: The natural environment is adversely
affected by landslides which uproot existing vegetation on the slope
as well as at its bottom. It can also make the land infertile, leading to
lesser plantations in the area.
Loss of wildlife: Strong landslides may also destroy habitats of a
number of animals in the affected area, thus substantially reducing
the wildlife population in the area.
Fires: Landslides can lead to forest fires because of the friction that
occurs during the run-off between trees. This is particularly seen in
the dry soil run-off and it can cause large-scale destruction in the
slope as well as the area around it.
Obstruction of rivers: Landslides that drain into rivers may obstruct
the river flow leading to floods in the surrounding areas.
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
125727
QUESTION_TEXT What is grey water management?
SCHEME OF
EVALUATION
The grey water management is the process of managing wastewater
from households apart from the one mixed with human waste. In
other words, the grey water management is the process of reduction,
treatment, disposal and reuse of grey water which has been collected
in a community. Grey water is not very high in nutrients or toxins. It
contains a certain amount of dirt and impurities. Its pH level is basic
because of the dominance of soap water in it. Grey water has small
amounts of organic wastes which can be easily decomposed by
micro-organisms. It is due to the organic waste that the stagnant grey
water or the one that has been stored for too long develops a pungent
smell. For grey water
management, a large, common pipe is attached to every household to
direct its grey water output to the locality’s main storage. All this
collection is taken for treatment. The treatment is mostly conducted
using soil filters or bio-rotors. In both cases, grey water is allowed to
pass through a substrate which is the habitat to a number of microorganisms. They attach themselves to the organic waste and
decompose the same. This treatment is sometimes used in
combination with processes like sedimentation and skimming to get
the water which can be reused in agriculture and for irrigation in
cities and ground water restoration.
QUESTION_TYPE
DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION
QUESTION_ID
125728
QUESTION_TEXT
Describe the types of cyclones.
The types of cyclones are described below;
1. Polar cyclone: Various types of cyclones like polar, subpolar or arctic cyclones take place in vast
SCHEME OF
EVALUATION
areas of low pressure. These types of cyclones weaken in summer
and strengthen in winter. A polar
cyclone can cover areas ranging between one thousand and two
thousand kilometers. When polar
cyclones are weak, there are chances of cold outbreaks.
2. Polar low cyclone: This type of cyclone occurs for a short
duration of time, covers less area and is low-
pressure cyclone. It generally occurs in oceans near the Polar
Regions. The horizontal length of this
type of cyclone is less than one thousand kilometers and it lasts
only a couple of days.
3. Extra-tropical cyclone: This cyclone does not form near the
poles or tropic regions and thus can be
unexpected and unpredictable. It forms along zones of change in
temperature and dew point.
4. Subtropical cyclone: It is a weather system which has a few
characteristics of both a tropical cyclone
and an extra tropical cyclone. This cyclone is formed in areas
where sea temperatures are slightly
lower. Generally, it rises in coastal regions.
5. Tropical cyclone: A tropical cyclone is characterized by
thunderstorms and heavy winds which cause
sea storm, tropical storms and flooding rains. It fuels itself
through the heat being released when moist
air rises.
 0
0