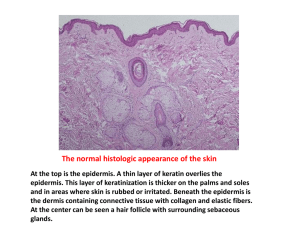
Public Health Issue – Skin Cancer
advertisement

It is no secret that there is a serious chronic disease epidemic in the United States. Chronic disease comes in many forms: obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. The second leading cause of death is cancer, accounting for about 23% of all deaths nationwide (Resnick & Siegel, 2013). Because chronic illness accounts for so many deaths, it is urgent that public health address these issues and find ways to prevent them. As Resnick and Siegel state, “The primary and most urgent challenge to public health today is to find a way to halt the epidemic of chronic disease that threatens to dominate the population in the 21st century (2013).” Among all cancer incidences, skin cancer is by far the most common type (American Cancer Society, 2013). There are three different types of skin cancer: (1) basal and squamous cell skin cancers, (2) melanoma skin cancer, and (3) lymphoma of the skin. Basal and squamous cell cancers are the most common types of cancer and are developed within the layers of the skin. About 8 out of 10 skin cancer types are the basal cell carcinoma skin cancers (ACS, 2013). Basal cell carcinomas tend to develop on sun-exposed areas such as the head or neck. Squamous cell carcinomas account for about 2 out of 10 skin cancers and also usually show up on sun-exposed areas of the body and are also found in scars or skin sores. Squamous cell carcinomas tend to spread and grow more than the basal cell carcinomas and are more likely to spread into the lymph nodes and other systems of the body, although it is fairly uncommon for that to happen. With early treatment, the prognosis for these two types of skin cancer is pretty good (ACS, 2013). Melanoma skin cancer is a specific type of skin cancer found in the melanocytes, responsible for the brown pigment, known as melanin. Moles are a type of benign tumor developed from melanocytes. Most of these are benign and harmless, but having a certain type of them can make one more prone to developing melanoma. Melanoma tumors are brown or black, usually, as the melanocytes are still producing the melanin. It can occur anywhere on the skin, but they are most commonly found in the trunk area for men and in the legs for women, but they are also sometimes found on the neck or face. While anyone can develop this type of skin cancer, one’s risk will generally go down if they have darker skin, meaning their skin generally produces more melanin than others. While melanoma is much less common than the basal and squamous cell carcinomas, they are far more dangerous. The prognosis is usually good if melanoma is detected early enough, but it is much more likely to spread to the other systems of the body than the other carcinoma types of skin cancers (ACS, 2013). Finally, lymphoma of the skin is a type of cancer of the lymph system. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can start in the skin and is therefore known as lymphoma of the skin. It is a cancer of the lymphocytes, which is a type of cell that is used in the body’s immune system and these cell types can be found in various parts of the body, including the skin. There are many different types of lymphoma of the skin depending on how they look in the microscope and what specific type of lymphocyte they start in and each type will behave differently than the others (ACS, 2013). Skin cancer affects all ages and sizes and all skin types. It is estimated that about 1 in 5 Americans will get skin cancer in their life (Skin Cancer Foundation, 2013). Out of all cancers, skin cancer is the most common and the most rapidly increasing. “From 1970 to 2009, the incidence of melanoma increased by 800 percent among young women and 400 percent among young men (SCF, 2013).” While skin cancer used to just be an issue for middle aged persons, it is becoming more of a problem for younger people every year. “Melanoma is the most common form of cancer for young adults 25-29 years old and the second most common form of cancer for young people 15-29 years old (SCF, 2013).” Because, most instances of skin cancer, particularly melanoma, is due to prolonged sun or UV ray exposure, it is probably one of the most easily preventable forms of cancer that plagues our nation. Because of the high incidence of skin cancer in the United States and that it affects all individuals regardless of age, ethnicity, sex, etc., that makes it a top priority for public health officials. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, skin cancer is the most common type of cancer affecting all individuals and is also the easiest to cure, if diagnosed early enough (2013). Therefore, assisting individuals and educating them on how they can help detect any changes in their skin is crucial for public health and something that can be done through a social marketing strategy. The challenge being: How can public health officials not just educate individuals but provide the right kind of tools through a marketing strategy to influence and motivate people to take part in early detection? References American Cancer Society (2013). Learn about Cancer: Skin Cancer. Retrieved September 8, 2013 from http://www.cancer.org/cancer/skincancer/index Resnick, E.A. & Siegel, M. (2013). Marketing Public Health. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning. Skin Cancer Foundation (2013). Skin Cancer Facts. Retrieved September 8, 2013 from http://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts