Group 2 V1 - WordPress.com
advertisement

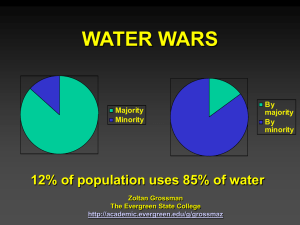
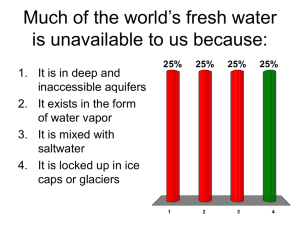
EVS Group - 2 Question bank and Answers 1. Give a brief account of problems associated with over utilization of surface and ground water Water resources are sources of water potentially useful to humans. Sources of fresh water can be classified as surface water and groundwater. Surface water is water on the surface of the planet such as in a stream, river, lake, wetland, or ocean. Groundwater is the water located beneath Earth's surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock ground water or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. Over utilization of surface and ground water results in: (i) Loss of integrity of freshwater ecosystems: Human activities for infrastructure development like creation of dams, land conversion, etc. are responsible for this loss of integrity of freshwater ecosystems. (ii) Risk to ecosystem functions: Population and consumption growth increases water abstraction and acquisition of cultivated land. Virtually all ecosystem functions including habitat, production and regulation functions are at risk. (iii) Depletion of living resources and biodiversity Overharvesting and exploitation causes groundwater depletion, collapse of fisheries. Production of food, quality and quantity of water and supply of water gets badly affected by these depletions of living resources and biodiversity. (iv) Pollution of water bodies: Release of pollutants to land, air or water alters chemistry and ecology of water bodies. Greenhouse gas emissions produce significant changes in runoff and rainfall patterns. Because of water pollution, water supply, habitat, water quality, food production, climate change, etc. are at risk. 2. How can we tackle the twin problems of floods and droughts ? Methods to tackle the problems associated with drought: • Dams - many dams and their associated reservoirs supply additional water in times of drought. • Cloud seeding - intentional weather modification to induce rainfall. • Desalination - of sea water for irrigation or consumption. • Drought monitoring – continuous observation • Land use- Carefully planned crop rotation can help to minimize erosion. • Outdoor water-use restriction - Regulating the use of sprinklers, hoses or buckets on outdoor plants, filling pools, and other waterintensive home maintenance tasks. • Rainwater harvesting - Collection and storage of rainwater from roofs or other suitable catchments. • Recycled water - Former wastewater (sewage) that has been treated and purified for reuse. Methods to tackle the problems associated with floods: • Radar estimates of rainfall and general weather forecasting techniques are also important components of good flood forecasting. • Defenses such as detention basins, levees, bunds, reservoirs, and weirs are used to prevent waterways from overflowing their banks. When these defenses fail, emergency measures such as sandbags or portable inflatable tubes are often used to try and stem flooding. • Flood controls, such as dams, can be built and maintained over time to try and reduce the occurrence and severity of floods as well. 3. What are the benefits and problems associated with dams? A dam is a barrier that divides waters. It serves the purpose of retaining water. Classified according to their size , purpose or structure. Large dams which are higher than 15m. Major dams which are higher than 150m. Based on material used dams are also classified as timber dams , masonry dams. Purposes of dams: • Providing water for irrigation or city water supply. • Improving navigation. • Creating a reservoir of water to supply industrial uses. • Generating hydroelectric power. • Creating recreation areas or habitat for fish and wildlife • Flood control Problems associated with dams: • Inundation of vast areas of forest • Soil erosion • Species extinction • Spread of disease • Changes to earth rotation 4. Explain the use and exploitation , environmental effects of extracting mineral resources. Naturally occuring substances formed through geological processes. Possess characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structures and specific physical properties. They are non-renewable. Minerals are extracted by mining. India produces 89 minerals: 4 fuel minerals , 11 metallic minerals , 52 non-metallic and 22 minor minerals. Forests are rich in mineral resources. In 1998-2005 about 1,50,700 acres of forest land was converted for mining. If forests are converted to mines in this way mining would result in deforestation. Mineral extraction requires large scale excavation. Problems related to mining: • Erosion • Formation of sinkholes • Loss of biodiversity • Contamination of surface and ground waters • Affect public health • Habitat destruction • Deforestation • Disturbance of ecosystem • Destroy productive grazing in areas of farming • Noise pollution • Dust pollution • Visual pollution • Affect soil fertility resulting in soil pollution