Chapter 1: Notes Handout
advertisement

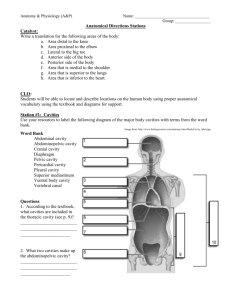
Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ Chapter 1: Notes Handout The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology • Anatomy: _________________________________________ • Subdivisions: • Gross or macroscopic (e.g., regional, surface, and systemic anatomy) • Microscopic (e.g., cytology and histology) • Developmental (e.g., embryology) • Essential tools for the study of anatomy: • Mastery of anatomical terminology • Observation • Manipulation • Palpation • Auscultation • Physiology: __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ • Subdivisions are based on organ systems (e.g., renal or cardiovascular physiology) • Essential tools for the study of physiology: • Ability to focus at many levels (from systemic to cellular and molecular) • Basic physical principles (e.g., electrical currents, pressure, and movement) • Basic chemical principles Principle of Complementarity • Anatomy and physiology are inseparable. • ___________________ always reflects ___________________ Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ • What a structure can do depends on its specific form Levels of Structural Organization • __________________: atoms and molecules • ______________________: cells and their organelles • ______________________: groups of similar cells • ______________________: contains two or more types of tissues • _______________________: organs that work closely together • _______________________: all organ systems Overview of Organ Systems • Page 6-7 Organ Systems Interrelationships • All cells depend on ________________________________ to meet their survival needs • Organ systems work _____________________to perform necessary life functions Necessary Life Functions 1.Maintaining boundaries between internal and external environments • _______________________________ • _____________________________________________ 2._______________________________________ (contractility) • Of body parts (skeletal muscle) • Of substances (cardiac and smooth muscle) Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ 3._______________________________________: The ability to sense and respond to stimuli • Withdrawal reflex • Control of breathing rate 4. _______________________________________ • Breakdown of ingested foodstuffs • Absorption of simple molecules into blood 5. _______________________________________: All chemical reactions that occur in body cells • Catabolism and anabolism 6. _______________________________________: The removal of wastes from metabolism and digestion • Urea, carbon dioxide, feces 7. _______________________________________ • Cellular division for growth or repair • Production of offspring 8. _______________________________________: Increase in size of a body part or of organism Survival Needs 1. _______________________________________ • Chemicals for energy and cell building • Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, minerals, vitamins 2. _______________________________________ • Essential for energy release (ATP production) 3. _______________________________________ • Most abundant chemical in the body • Site of chemical reactions 4. _______________________________________ • Affects rate of chemical reactions Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ 5. _______________________________________ • For adequate breathing and gas exchange in the lungs Homeostasis • Maintenance of a relatively stable _______________ environment despite continuous _______________ changes • A _______________ state of equilibrium Homeostatic Control Mechanisms • Involve continuous __________________________________ _______________of many factors (variables) • Nervous and endocrine systems accomplish the communication via nerve impulses and hormones Components of a Control Mechanism 1.Receptor (sensor) • _______________ the environment • _______________ to stimuli (changes in controlled variables) 2. ______________________________ • • • Determines the set point at which the variable is maintained Receives input from receptor Determines appropriate response 3.Effector • Receives output from _______________ • Provides the means to _______________ • Response acts to reduce or enhance the _______________ (feedback) Negative Feedback • The response reduces or _______________the original stimulus • Examples: Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ • Regulation of ______________________________ (a nervous mechanism) • Regulation of ______________________________ by ADH (an endocrine mechanism) Negative Feedback: Regulation of Blood Volume by ADH • Receptors sense _______________ blood volume • Control center in _______________ stimulates pituitary gland to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) • ADH causes the kidneys (effectors) to return more _______________to the blood Positive Feedback • The response _______________ or exaggerates the original stimulus • May exhibit a cascade or _______________ effect • Usually controls infrequent events e.g.: • Enhancement of _______________by oxytocin (Chapter 28) • Platelet plug formation and _____________________________ Homeostatic Imbalance • Disturbance of homeostasis • Increases ___________________________________________ • Contributes to changes associated with _______________ • May allow _______________ positive feedback mechanisms to take over (e.g., heart failure) Anatomical Position • Standard anatomical body position: • ____________________________________________ • _____________________________________________ • _____________________________________________ Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ Regional Terms • Two major divisions of body: • _______________ • Head, neck, and trunk • _______________ • Limbs • Regional terms designate specific areas Body Planes • ______________________________: Flat surface along which body or structure is cut for anatomical study • ______________________________ • Divides body vertically into right and left parts • Produces a sagittal section • ______________________________ (median) plane • Lies on midline • ______________________________ plane • Not on midline • ______________________________ (coronal) plane • Divides body vertically into anterior and posterior parts • _____________________________ (horizontal) plane • Divides body horizontally into superior and inferior parts • Produces a cross section • ______________________________ section • Cuts made diagonally Anatomical Variability • Over _______________ of all anatomical structures match textbook descriptions, but: • Nerves or blood vessels may be somewhat out of place • Small muscles may be missing Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ Body Cavities • _______________ cavity • Protects nervous system • Two subdivisions: • ______________________________ cavity • Encases brain • ______________________________ cavity • Encases spinal cord • ______________________________ cavity • Houses internal organs (viscera) • Two subdivisions (separated by diaphragm): • ______________________________ cavity • ______________________________ cavity Ventral Body Cavities • ______________________________ cavity subdivisions: • Two pleural cavities • Each houses a lung • ______________________________ • Contains pericardial cavity • Surrounds thoracic organs • ______________________________ cavity • Encloses heart • ______________________________ cavity subdivisions: • ______________________________ cavity • Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver Name: ______________________________________ Date: ___________ Class: _____ • ______________________________ cavity • Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum Serous Membrane (Serosa) • Thin, double-layered membrane separated by serous fluid • Parietal serosa lines ___________________________ walls • Visceral serosa covers the __________________________ Abdominopelvic Regions • Nine divisions used primarily by anatomists (Image on pg 20) Abdominopelvic Quadrants • Divisions used primarily by medical personnel (Image on pg17) Other Body Cavities • ______________________________ and digestive cavities • ______________________________ cavity • ______________________________ cavities • ______________________________ ear cavities • ______________________________ cavities