Unit 6 Equations formuale and identities
advertisement

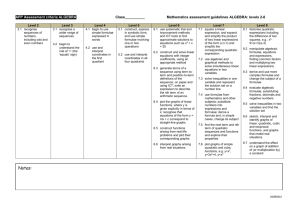
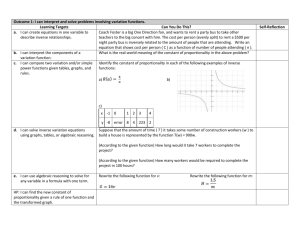
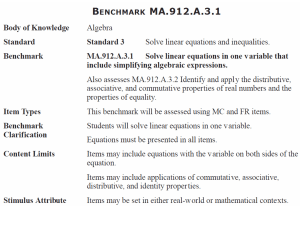
Unit 6: Equations, formulae, functions and identities Level 1 & Level 2 Know subtraction is the inverse of addition and use this to solve addition and subtraction problems. Level 3 (≈ Grade G/F) Level 4 (Grade E) Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Check solutions by applying inverse operations. Apply this to help solve one and two step equations. Understand halving is the inverse of doubling. Use basic function machines and apply inverse operations to find missing values. Begin to use the BODMAS order of operations. Know and use the BODMAS order of operations and understand that algebraic operations follow the same conventions. Solve one step equations. Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Begin to use simple formulae expressed in words. Construct, express in symbolic form, and use simple formulae involving one or two operations. Use simple functions expressed in words. Use simple functions expressed in symbols and develop to explore inverse operations. Use the knowledge that addition can be done in any order. Unit 6: Equations, formulae, functions and identities Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Level 6 (≈ Grade C) Level 7 (≈ Grade B) Level 8 and E.P. (≈ Grade A/A*) Solve simple inequalities Solve inequalities in two variables. Check solutions by applying inverse operations. Apply this to help solve one and two step equations. Know and use the BODMAS order of operations and understand that algebraic operations follow the same conventions. Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Begin to distinguish the different roles of letter symbols and algebraic conventions. Distinguish between expressions, equations, formulae, functions and identities. Construct, express in symbolic form, and use simple formulae involving one or two operations. Substitute integers into simple formulae. Change the subject of a formula. Change the subject of a formulae and use to calculate one variable, given the others, in formulae such as V = r2h. Simplify linear expressions. Evaluate algebraic formulae by substituting fractions, decimals and negative numbers. Manipulate and factorise algebraic formulae, equations and expressions. Use the basic laws of indices. Use simple functions expressed in symbols and develop to explore inverse operations. Use rules of indices for positive and negative, integer and fractional values in simplifying algebraic expressions. Multiply a single term over a bracket and simplify the result. Multiply two expressions of the form (x + n) and simplify the resulting quadratic expressions. Multiply two linear expressions. Factorise expressions by taking out a common factor. Start to use algebraic expressions for simple proofs. Know and use the identity for the difference of two squares: a2 – b2= (a + b)(a – b) Use functions expressed symbolically and find their inverses using inverse operations. Use algebraic methods to solve simultaneous linear equations in two variables. Use algebraic methods to solve simultaneous equations in two variables where one equation is linear and the other is quadratic. Formulate and solve linear equations with integer coefficients and involving brackets and unknowns on both sides. Solve simple non-linear equations by algebraic and trial-and-improvement methods. Solve quadratic equations.