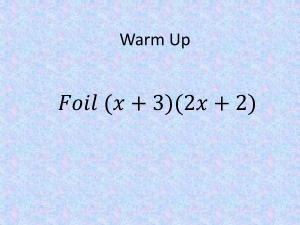Project 1
advertisement

MAC 1105 Project 1 Graphing Applications Name ______________________________ Class Time __________________________ Find a real-world application of one of the following topics. Your write-up should be one page in length, including graphs. Topics: Linear, quadratic, rational, polynomial, and radical equations, complex numbers, and linear and absolute value inequalities. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Find an example of how a mathematical concept is being used in the real-world. List the mathematical concept. Include a graph showing a relationship between variables (or other appropriate diagram). Summarize how the concept is being used. List all sources for the information. The following is an example of project 1. 2) Quadratic Equations 3) 4) This Demonstration extends the basic pattern recognition concepts introduced in Pattern Recognition Primer. Quadratic classifiers are to linear classifiers what quadratic equations are to linear equations: a step up in complexity and the range of phenomena they can model. This Demonstration illustrates a simple supervised pattern recognition situation requiring the separation of two classes represented by the red and blue dots, the positives and negatives, respectively. The process of training involves using the given data to find the quadratic curve (i.e., the parabola, ellipse, or hyperbola) that best separates the data. The easy-to-read source code implements formulas to derive the classifiers and evaluate the results. Use the buttons to choose different datasets and observe the performance of the quadratic classifier in separating the two classes. The graph on the left shows the quadratic classifier (thick quadratic curve) and the linear classifier (dashed line) overlaid on the positive (red) and negative (blue) data points. The graph on the right displays the ROC curves and areas under the curve (AUC) for both the linear and quadratic classifiers. The red dots shown on the ROC curves mark the values of 1-specificity and sensitivity associated with the particular classifiers shown. The better the classifiers are, the closer the red dots get to the top-left corner, and the AUC values get close to 1. While the quadratic classifier is shown to outperform the linear classifier on several datasets, it is always good practice to employ the simpler one, in this case the linear classifier, if it does a satisfactory job in separating the classes. The use of quadratic classifiers has been investigated in several interesting applications, including harnessing will power to press buttons—that is, recognizing intent using "brain waves" (EEG) and translating them to commands to be given to a computer [1], and to detect singing voice in recorded music for applications such as karaoke [2]. This Demonstration has introduced supervised pattern recognition. For further information, see 5) Wolfram Demonstrations search (quadratic applications)