Geol483_Lab5
advertisement

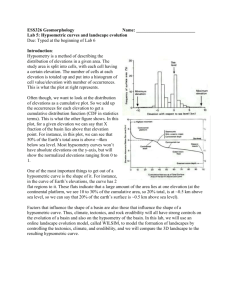
Nicole Meyer DEMS, RIVER NETWORKS AND WATERSHEDS WITH RIVERTOOLS Hypsometric analysis is the study of ground surface area distribution of a landmass with respect to elevation (Strahler) A hypsometric curve plots the elevation distribution in a watershed. Additionally, a hypsometric curve plots normalized elevation vs. cumulative basin area. Lastly these curves can be used to infer the stage of development of the drainage network (see figure below) The hypsometric integral is the proportionate area below the hypsometric curve. The integral varies from 0 to 1, with values close to 0 indicating highly eroded regions and values close to 1 indicating slightly eroded regions (Antonia Pedrera, er al. 2009). Therefore, the lower the value the more eroded the stream. (Sarp and Toprak) G. Sarpa, V. Toprakb , S. Duzgun http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/2011/ISRSE-34/211104015Final00591.pdf Keller E A and Pinter N 1996 “Active tectonics: Earthquakes Uplift and Landscapes”; Prentice Hall, New Jersey. Antonio Pedrera, José Vicente Pérez-Peña, Jesús Galindo-Zaldívar, José Miguel Azañón, Antonio Azor , 2009. “Testing the sensitivity of geomorphic indices in areas of low-rate active folding (eastern Betic Cordillera, Spain) Geomorphology 105 (2009) 218–231