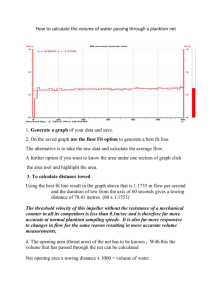
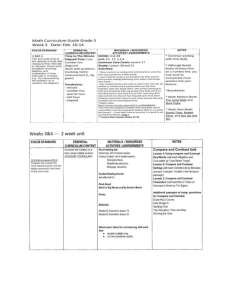
Test Review: Zones, Challenges to Life at Sea, Plankton
advertisement

Test Review: Zones, Challenges to Life at Sea, Plankton 1. Know the following ocean zones and their general characteristics a. Epipelagic (photic) b. Mesopelagic (dysphotic) c. Bathypelagic (aphotic) d. Abyssalpelagic (aphotic) e. Hadalpelagic (aphotic) 2. In which ocean zone are most organisms found? 3. In which ocean zone are most of the oxygen and nutrients? Why? 4. Which organisms are found only in the photic zone? Why? 5. What is dredging? What group of marine organisms would be most affected by it? 6. Where are most plankton found and why? 7. What adaptations do plankton have to avoid sinking? 8. Define the following types of plankton a. Phytoplankton c. Holoplankton b. Zooplankton d. Meroplankton 9. List the following types of plankton from largest to smallest: microplankton, mesoplankton, megaplankton, nanoplankton, macroplankton 10. Why are plankton important organisms in aquatic ecosystems? 11. Define the following: a. Marine snow g. Exotherm (poikilotherm) b. Bioluminescence h. Benthic c. Hyperthermophiles i. Nektonic d. Psychrophiles j. Planktonic e. Endotherm k. Osmosis l. Diffusion f. Homeotherm 12. What is the difference between osmoconformers and osmoregulators? 13. Describe the internal concentration of saltwater fish compared to their environment. How do the osmoregulators stay this way? Why can’t saltwater fish live in a freshwater environment? 14. Describe the internal concentration of freshwater fish compared to their environment. How do the osmoregulators stay this way? Why can’t freshwater fish live in a saltwater environment? 15. Which environment is the only one with osmoconformers (marine or fresh)? 16. Describe the difference between anadromous and catadromous. Give an example of each. 17. What adaptations do organisms have to help them cope with the extreme pressure deep in the ocean? 18. What is the bends and how does it occur? 19. How large is a fully grown giant kelp? 20. What time of year does plankton become scarce? 21. What do copepods eat? 22. What are the walls of the deep sea vessel Alvin are made of? 23. The “lake” ½ a mile deep in the Gulf of Mexico is composed of what type of water? What is the energy source? 24. What percentage of the earth’s surface is covered by abyssal plains? 25. What organism is the primary producer in hydrothermal vent communities? Test Review: Zones, Challenges to Life at Sea, Plankton 1. Know the following ocean zones and their general characteristics a. Epipelagic (photic) b. Mesopelagic (dysphotic) c. Bathypelagic (aphotic) d. Abyssalpelagic (aphotic) e. Hadalpelagic (aphotic) 2. In which ocean zone are most organisms found? 3. In which ocean zone are most of the oxygen and nutrients? Why? 4. Which organisms are found only in the photic zone? Why? 5. What is dredging? What group of marine organisms would be most affected by it? 6. Where are most plankton found and why? 7. What adaptations do plankton have to avoid sinking? 8. Define the following types of plankton a. Phytoplankton c. Holoplankton b. Zooplankton d. Meroplankton 9. List the following types of plankton from largest to smallest: microplankton, mesoplankton, megaplankton, nanoplankton, macroplankton 10. Why are plankton important organisms in aquatic ecosystems? 11. Define the following: a. Marine snow g. Exotherm (poikilotherm) b. Bioluminescence h. Benthic c. Hyperthermophiles i. Nektonic d. Psychrophiles j. Planktonic e. Endotherm k. Osmosis l. Diffusion f. Homeotherm 12. What is the difference between osmoconformers and osmoregulators? 13. Describe the internal concentration of saltwater fish compared to their environment. How do the osmoregulators stay this way? Why can’t saltwater fish live in a freshwater environment? 14. Describe the internal concentration of freshwater fish compared to their environment. How do the osmoregulators stay this way? Why can’t freshwater fish live in a saltwater environment? 15. Which environment is the only one with osmoconformers (marine or fresh)? 16. Describe the difference between anadromous and catadromous. Give an example of each. 17. What adaptations do organisms have to help them cope with the extreme pressure deep in the ocean? 18. What is the bends and how does it occur? 19. How large is a fully grown giant kelp? 20. What time of year does plankton become scarce? 21. What do copepods eat? 22. What are the walls of the deep sea vessel Alvin are made of? 23. The “lake” ½ a mile deep in the Gulf of Mexico is composed of what type of water? What is the energy source? 24. What percentage of the earth’s surface is covered by abyssal plains? 25. What organism is the primary producer in hydrothermal vent communities?