Particle Motion Review Stations
advertisement

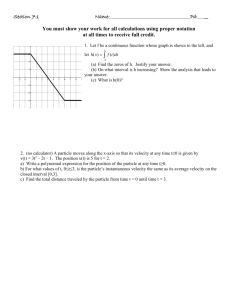
Station #1 – Integrals 1. Find y = f(x) if f ”(x) = 20x3, f ’(0) =-3 and f(0) = 8. B) x5 – 3x + 8 A) 120x + 8 2. ∫ (8𝑥 5 + 2 − 4 ) 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑥 3 3√𝑥 2 6 a. 40𝑥 4 − 𝑥 4 + b. c. d. 3. ∫ 4 6 𝑥 3 4 6 𝑥 3 4 6 𝑥 3 − 1 4 𝑥 2 2 + −𝑥 + − 1 𝑥2 8 3 3 √𝑥 5 12 3 3 D) x5 + 5 +𝑐 5 √𝑥 5 8 3 √𝑥 C) 5x4 – 3 +𝑐 +𝑐 3 − 12 √𝑥 + 𝑐 3𝑥 4 − 8𝑥 2 + 2 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑥2 2 a. 3𝑥 2 − 8 + 𝑥 2 + 𝑐 2 b. 𝑥 3 − 8𝑥 − 𝑥 + 𝑐 2 c. 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 𝑐 d. 𝑥 3 − 8𝑥 − 2 3𝑥 3 +𝑐 4. Given 𝑓(𝑥) = 4𝑐𝑠𝑐𝑥𝑐𝑜𝑡𝑥𝑑𝑥, a) Find the anti-derivative ∫ 𝑓(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 𝜋 b) Evaluate the definite integral ∫𝜋2 𝑓(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 6 Station #2 – Calculator Inactive 1. A particle moves along the x-axis so that its position at time t is given by 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑡 2 − 6𝑡 + 5. For what value of t is the velocity of the particle zero? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 2. A particle moves along the x-axis so that at time 𝑡 ≥ 0 its position is given by 𝑥(𝑡) = 2𝑡 3 − 21𝑡 2 + 72𝑡 − 53. At what time t is the particle at rest? a) t = 1 only b) t = 3 only c) t = 3.5 only d) t = 3 and t = 3.5 e) t = 3 and t = 4 3. The velocity v(t) of a particle is graphed below, minute. a) At what value of t does the particle change direction? b) What is the velocity of the particle at t = 12? t = 25? c) What is the particle’s acceleration at t = 12? t = 25? d) Is the speed of the particle increasing or decreasing at t = 25? How do you know? where v(t) is measured in meters per 4. A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at time t, for 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 6, is given by a differentiable function v whose graph is shown below. The graph has horizontal tangents at t = 1 and t = 4. At time t = 0, the particle is at x = -2. a) Where is the particle at rest? b) When does the particle change directions? c) On the interval 2 < t < 3, is the speed of the particle increasing or decreasing? Give a reason for your answer. d) During what time intervals, if any, is the acceleration of the particle negative? Justify your answer. 5. Rocket A has a positive velocity v(t) after being launched upward from an initial height of 0 feet at time t = 0 seconds. The velocity of the rocket is recorded for selected values of t over the interval 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 80 seconds, as shown in the table below. Find the average acceleration of Rocket A over the time interval 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 80 seconds. Indicate units of measure. Station #3 – Calculator Active 1. A particle moves along the x-axis so that at any time 𝑡 ≥ 0, its velocity is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = 3 + 4.1cos(0.9𝑡). What is the acceleration of the particle at time t = 4? a) -2.016 b) -0.677 c) 1.633 d) 1.814 e) 2.978 2. An object moves along the x-axis with initial position x(0) = 2. The velocity of the object at time 𝜋 𝑡 ≥ 0 is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = sin( 3 𝑡). a) What is the acceleration of the object at time t = 4? b) Consider the following two statements. Evaluate their accuracy and explain your reasoning. Statement I: For 3 < t < 4.5, the velocity of the object is decreasing. Statement II: For 3 < t < 4.5, the speed of the object is increasing. c) What is the displacement of the object from t = 0 to t = 4? d) What is the position of the object at time t = 4? 3. A particle moves along the y-axis so that its velocity v, in cm/min at time 𝑡 ≥ 0 is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = 1 − tan−1 (𝑒 𝑡 ). a) Find the acceleration of the particle at time t = 2. b) Is the speed of the particle increasing or decreasing at time t = 2? Give a reason for your answer. 6 6 c) Find ∫0 𝑣(𝑡) 𝑑𝑡. Using correct units, explain the meaning of ∫0 𝑣(𝑡) 𝑑𝑡. 4. A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity v at time t, for 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 5, is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = ln(𝑡 2 − 3𝑡 + 3). The particle is at position x = 8 at time t = 0. a) Find the acceleration of the particle at time t = 4. b) Find all times t in the open interval 0 < t < 5 at which the particle changes direction. During which time intervals, for 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 5, does the particle travel to the left? c) Find the position of the particle at time t = 2. d) Find the average acceleration of the particle over the interval 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 2. 5. A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at time t is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = −(𝑡 + 1)𝑠𝑖𝑛 (𝑡 ). 2 a) Find the velocity of the particle at t = 3. 2 b) Find the speed of the particle at t = 3. c) Find the acceleration of the particle at time t = 2. Is the speed of the particle increasing at t = 2? Why or why not? d) Find all times t on the open interval 0 < t < 3 when the particle changes direction. Justify your answer. 6. A particle moves along the x-axis so that at any time 𝑡 ≥ 0, its velocity is given by 𝑣(𝑡) = cos(2 − 𝑡 2 ). The position of the particle is 3 at time t = 0. What is the position of the particle when its velocity is first equal to 0? a) 0.411 b) 1.310 c) 2.816 d) 3,091 e) 3.411