File - IB Psychology Mr Poll
advertisement

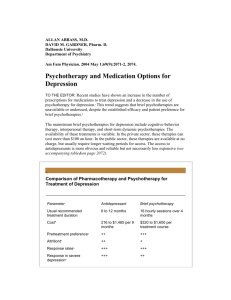
Jaenelle Murrell and Jinal Patel Learning Outcome: Discuss the use of eclectic approaches to treatment Topic Sentence: This paper will discuss the use of eclectic approaches to treatment with reference to studies by Klerman et al. and Pampallona et al.. Introduction: 1. Definition: Eclectic approach to treatment incorporates principles or techniques from various systems of theories, including biomedical, individual and group therapy. It recognizes the strengths and limitations of the various therapies, and tailors sessions to the needs of the individual client or group. Similar to other treatment plans, there are distinct advantages and disadvantages to the eclectic approach. Although there are possible disadvantages to the eclectic approach, it seems to be the most integrative approach to treatment that is most effective in reducing symptoms of psychological disorders. The most common approach to the treatment of depression is antidepressant medication. This often relieves the depressive symptoms although it may take weeks before there is an effect and dropout rates are quite high because of the adverse effect of antidepressants. Thesis: The eclectic approach is more effective in treating psychological disorders compared to using only a biomedical approach to treatment as observed through the studies conducted by Klerman et al. in 1974 and Pampallona et al in 2004 on the effectiveness of treatment with antidepressant and psychotherapy, alone or in combination. Klerman et al. (1974) Treatment of depression by drugs and/or psychotherapy Aim: The study was to investigate the effectiveness of treatment with anti-depressants and psychotherapy, alone or in combination. Procedure: Participants were 150 females diagnosed with depression. Patients were divided into groups: o Anti-depressants alone o Anti-depressants and psychotherapy o No medication but more psychotherapy o Placebo and no therapy Results: The results showed that relapse rates were highest for patients in the placebo group (36%). The group with antidepressants alone had a relapse rate of 12% The psychotherapy (IPT) alone had a relapse rate of 16.7% The combination of drug and IPT had a relapse rate of 12.5% Conclusion: Jaenelle Murrell and Jinal Patel There was no significant difference between drug therapy alone or drug therapy in combination with psychotherapy. Pampallona et al. (2004) - Meta-analysis of efficacy of drug treatment alone versus drug treatment and psychotherapy in depression. Aim: To investigate whether combining anti-depressants and psychotherapy was more effective in the treatment of depression. Procedure: 16 randomized controlled studies were conducted including: o 932 patients taking anti-depressants only o 910 receiving combined treatment. The patients had already been randomly allocated to the treatments Results: The results showed that the participants in combined treatment improved significantly more compared to those receiving drug treatment alone. This was particularly true in studies that ran over more than 12 weeks and there was also a significant reduction in dropouts. Conclusion: This could be a very good reason for the clinician to combine anti-depressants with psychotherapy. Their review of randomized controlled trials shows that the combination of drugs and psychotherapy generally leads to greater improvement. The study also showed that psychotherapy helps to keep patients in treatment.