v1 v2 Dynamics 1. A ball moves horizontally with an initial velocity v
advertisement

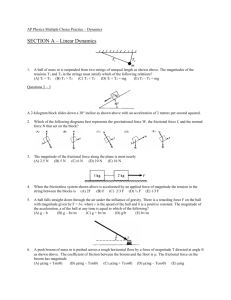
Dynamics v2 1. 2. v1 A ball moves horizontally with an initial velocity v1, as shown above. It is then struck by a tennis racket. After leaving the racket, the ball moves vertically with a velocity v2, which is smaller in magnitude than v1. Which of the following vectors best represents the direction of the average force that the stick exerts on the ball? A satellite is orbiting the Earth. If FE is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on the satellite and FS is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the Earth, then which of the following is true? (A) FE is much greater than FS. (B) FE is slightly greater than FS. (C) FE is equal to FS. (D) FE is slightly greater than FS (E) FE is much greater than FS 3. An object released from rest at time t = 0 slides down a frictionless incline 2 meters during the first 2 seconds. The distance traveled by the object during the time interval from t = 2 second to t = 3 seconds is approximately, (A) 2.5 m 4. (D) 11 m (E) 13 m (B) 3mbt1 + 2c (C) mbt1 (D) mbt1 + c (E) 2mbt1 A force F is exerted by a broom handle on the head of the broom, which has a mass m. The handle is at an angle to the horizontal, as shown above. The work done by the force on the head of the broom as it moves a distance d across a horizontal floor is (A) Fd sin 6. (C) 9 m A marble of mass m moves along a path with a speed defined by the function v = bt2 + c, where t is time and b and c are constants. What is the magnitude F of the net force on the particle at time t = t1? (A) bt1 2 + c 5. (B) 4.5 m (B) Fd cos (C) Fm cos (D) Fm tan (E) Fmd sin A body’s position as it moves on a straight path is given by the equation x = 2t3 - 3t2 + 4t, where x is in meters and t is in seconds. The net force on the body is equal to zero when t is equal to (A) zero (B) 1/2 s (C) 3 s (D) 4/5 s (E) 5 s V t 7. The parabola above is a graph of speed v as a function of time t for an object. Which of the following graphs best represents the magnitude F of the net force exerted on the object as a function of time t? (A) F 8. (B) F A descending box of mass 500 kg is uniformly decelerated to rest over a distance of 4 m by a rope in which the tension is 6000 N. The speed vi of the elevator at the beginning of the 4 m descent is most nearly (A) 4 m/s (B) 10 m/s (C) 12 m/s (D) 16 m/s (E) 22 m/s 9. When the frictionless system shown above is accelerated by an applied force of magnitude F a, the tension in the string between the blocks is (A) 2 Fa (B) Fa (C) (3/5) Fa (D) (2/5) Fa (E) 3 Fa 10. Two 0.5-kilogram blocks are connected by a string that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown above. The blocks are initially held at rest. If a third block with a mass of 0.25 kilograms is added on top of one of the 0.5-kilogram blocks as shown and the objects are released, the magnitude of the acceleration of the 0.25-kilogram object is most nearly (A) 10.0 m/s2 (B) 6.0 m/s2 (C) 4.0 m/s2 (D) 2.0 m/s2 (E) 1.0 m/s2 11. A 50-newton weight is suspended by two strings as shown above. The tension T in the slanted string is (A) 50 N (B) 100 N (C) 150 N (D) 200 N (E) 250 N 12. A rubber band ball of mass m is attached to a string of length R as shown above. The ball is released from rest from position X where the string is horizontal, swings through position Y where the string is vertical, and reaches position Z where the string is again horizontal. What are the directions of the acceleration vectors of the ball at positions Y and Z? Position Y Position Z (A) Downward Downward (B) Downward To the right (C) Upward Downward (D) Upward To the left (E) To the right To the left 13. As shown above, two blocks are pushed along a horizontal frictionless surface by a 30 newton force to the right. The force that the 4-kilogram block exerts on the 6-kilogram block is (A) 8 newtons to the left (B) 8 newtons to the right (D) 12 newtons to the left (C) 10 newtons to the left (E) 12 newtons to the right 14. A mass m moves on a curved path from point X to point Y. Which of the following diagrams indicates a possible combination of the net force F on the mass, and the velocity v and acceleration a of the mass at the location shown? (A) F X (B) X (C) m m (D) X X v Y a a m F a v Y Y X F F F (E) m m v a v v Y a Y 15. Two identical massless springs are hung from the ceiling. The springs suspend a block of mass 2.4 kg, as shown above. When the block is in equilibrium, each spring is stretched an additional 0.3 meters. The force constant of each spring is most nearly: (A) 40 N/m (B) 48 N/m (C) 60 N/m (D) 80 N/m (E) 96 N/m 16. A 10 kilogram block lies on an inclined plane, as shown above. The incline is 8 meters wide and 6 meters tall. The coefficient of friction between the plane and the block is 0.3. The magnitude of the force F necessary to move the block up the plane with constant speed is most nearly (A) 64 N (B) 76 N (C) 82 N (D) 90 N (E) 108 N W Z X Y 17. A figure of a dancer on a music box moves counterclockwise at constant speed around the path shown above. The path is such that the lengths of its segments, WX, XY, YZ, and ZW, are equal. Arcs WX and YZ are semicircles. Which of the following best represents the magnitude of the dancer's acceleration as a function of time t during one trip around the path, beginning at point W ? (C) (B) (A) a a a tW tX tY tZ t tW tW tX tY tZ tW t tW tX tY tZ tW t (E) (D) a a tW tX tY tZ tW t tW tX tY tZ tW t 18. A ball is released from rest at time t = 0 and falls in the presence of air, which exerts a resistant force. The acceleration a of the ball is given by a = g - bv, where v is the object's velocity and b is a constant. If limiting cases for large and small values of t are considered, which of the following is a possible expression for the speed of the object as an explicit function of time? (A) v = g(1 - e-bt)/b (B) V = (geht)/b (C) v = gt - bt2 (D) v = (g + a)t/b (E) v = v0+ gt, v0 0 Questions 19-20 F Θ f As shown above, a block of mass m is pulled across a rough surface by a force F exerted at an angle Θ with the horizontal. The frictional force on the block exerted by the surface has magnitude f. 19. What is the acceleration of the block? (A) F/m (B) FcosΘ /m (C) (F-f)/m (D) (FcosΘ-f)/m (E) (FsinΘ-mg)/m 20. What is the coefficient of friction between the block and the surface? (A) f/mg (B) mg/f (C) (mg-FcosΘ)/f (D) f/(mg-FcosΘ) (E) f/(mg-FsinΘ) 21. A 10 kg object moves according to the function: x=3t2-4t+7. Which of the following represents the net force that acts on the object? (A) 52 N (B) 60N (C) 67 N (D) 78 N (E) 84 N Questions 22-25 m3 m1 m2 The system above consists of three blocks, m1, m2 and m3 where m1 and m2 are attached to a virtually massless cord and m3 sits on top of m1. The system is attached to a massless pulley and accelerates downward. There is no friction between the surface and m1 however there is friction between the m1 and m3. The coefficient of kinetic friction is µ however the coefficient of static friction is not given. Block m3 does not slide off of block m1. 22. Find the acceleration of m2 (A) m1g/(m2+m3) (B) (m1+m2+m3)/m2g (C) m2g/(m1+m2+m3) (D) (m1+m3)g/m2 (E) (m1+m3)/m2g 23. What coefficient of static friction must there be in order for m3 not to slide off of block m1? (A) m2/(m1+m2+m3) (B) m1/(m2+m3) (C) (m1+m3)/m2 (D) (m1+m2+m3)/m2 (E) m3/(m1+m2+m3) Now block m3 begins to slide off block m1. 24. Find the acceleration of block m3. (A) µg(m1+m2+m3)/m3 (B) µm3g/m1 (C) µg (D) µg(m1+m3)/m2 (E) µgm3/(m1+m2+m3) 25. What is the acceleration of block m2? (A) (m2-µm3)g/(m1+m2) (B) m2g/µ(m1+m3) (C) (m1+m2+m3)µ/3m1g (D) (m1+m3) µg (E)(m1+m3)g/µ(m1+m2+m3) 26. A ball of mass m falls in the presence of air resistance. The resistive force is represented by F=bv 2 where b is a constant and v represents the ball’s velocity. The acceleration of the ball is most nearly (A) mg/v (B) b-g T1 (C) g-bv2/m (D) bv+g/m (E) bvg T2 27. A rubber band ball is suspended by two strings of unequal lengths. Which of the following is true about T 1 and T2 in the strings? (A) T1< T2 (B) T1> T2 (C) T1= T2 (D) T1- T2=mg (E) (T1+T2)sinѲ=mg Fa 53° Questions 28-30 A 60 newton force is pushing a 5 kg box is being pushed up an incline at a 53° angle (cos53°=0.6, sin53°=0.8). The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.5. 28. Which diagram best represents the block’s weight W, normal force F n and the friction force Fr on the block? (A) Fa (B) Fn W Ffr (C) Fn Fa W Ffr (D) Fn Fa W Fn Fa (E) W Fa Ffr Ffr W Ffr Fn 29. The normal force on the block is (A) 10 N (B) 20 N (C) 30 N (D) 40 N (E) 50 N 30. Calculate the block’s acceleration as it moves up the incline (A) 0.5 m/s2 (B) 1.0 m/s2 (C) 2.9 m/s2 (D) 3.5 m/s2 (E) 4.2 m/s2 31. A truck of mass 5m collides head on with a car of mass 3m. FT represents the force the truck applies to the car. FC represents the force the car applies to the truck. Which of the following is true? (A) FT> FC (B) FT<FC (C) FT=FC (D) 3FT=5FC (E) 5FT=3Fc 32. A car is traveling with velocity v and sees a kid playing with a ball in the street. The driver slams on the brakes with a force F and stops in time for the kid to move away safely. If the car was traveling twice as fast how much force would be required to stop at the same spot? (A) F/4 (B) F/2 (C) F (D) 2F (E) 4F Questions 33-34 A 30 kg block and 10 kg block are set up on an incline plane using a pulley system (Friction is not negligible). The 30 kg block accelerates downward while the 10 kg block is accelerating up the incline. The acceleration is equal to 2m/s2. 33. Determine the tension in the string. (A) 200 N (B) 210 N (C) 220 N (D) 230 N (E) 240 N 34. Determine the friction force acting on the 10 kg block. (A) 75 N Question Number (B) 100 N Answer (C) 140 N Question Number (D) 160 N Answer 1 b 18 a 2 c 19 d 3 a 20 e 4 e 21 b 5 b 22 c 6 b 23 a 7 e 24 c 8 a 25 a 9 d 26 c 10 d 27 a 11 b 28 b 12 d 29 c 13 d 30 b 14 b 31 c 15 a 32 e 16 c 33 e 17 a 34 c (E) 175 N